* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Red Blood Cells Red blood cells main job, or function, is to take in
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Somatic cell nuclear transfer wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic resistance to malaria wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
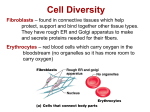
Red Blood Cells Red blood cells main job, or function, is to take in oxygen as blood passes by the lungs, and then travel along in the bloodstream to deliver that oxygen throughout the body to all the body tissues. How does the structure of a red blood cell help it do it’s job? Structure Function Disk Shaped, Flattened and Smooth Can easily pass through small blood vessels Flexible Can squeeze through narrow blood vessels Don’t have a nucleus Leaves more space to carry oxygen Fat Cell (Lipocyte) Fat cells main job, or function is to store extra fat in the body until it is needed by the body as a source of energy. How does the structure of a fat cell help it do it’s job? Structure Large, round, empty looking Function Has plenty of room to store fat when there is an excess. Nerve Cells (Neurons) A nerve cell’s main job is to quickly relay information to and from the brain. They sense stimuli in the environment and send the information to the brain. Then they send a signal from the brain back to the body so that the body can respond to the stimuli. How does the structure of a nerve cell help it do it’s job? Structure Function Long, thin branching arms Lets messages move rapidly over longer distances Many branches connecting to other nerve cells Allows cells to pass messages in a chain form one to the next. Skin Cells Skin cells cover your entire body and also line body cavities. The skin plays a key role in protecting the body against invaders and excessive water loss. Its other functions are insulation, temperature regulation, sensation. How does the structure of a skin cell help it do it’s job? Structure Function Very thin, flat, and overlapping So gases can pass through, and overlapping for protection Contain a lot of keratin( a protien that provides strength and support) Makes it strong for protection Sperm Cells Sperm cells main job is to carry genetic material from the father, and deliver it to the egg during fertilization. This way the offspring gains genes from both of its parents. It swims through the female reproductive tract until it finds the egg. How does the structure of a sperm cell help it do it’s job? Structure Function Have a long flagellum (tail) To help it swim up the female reproductive tract to meet the egg Have a pointed tip (head) To help it push into the egg through the eggs cell membrane Muscle Cells The main job of muscle cells is to contract, or shorten in order to produce movement. They may contract to move your body, or pump your heart, or move food along your digestive tract. How does the structure of a muscle cell help it do its job? Structure Function Long and narrow So that they can pack closely together, and then shorten and relax to produce movement. Guard Cells When you get hot, you sweat, and when you sweat, water comes out of your skin through pores called sweat glands. Plants also 'sweat' through a process called transpiration, and the plant's pores, which are found on the leaves, are called stomata. How do plants keep from losing all their water through stomata? Surrounding each stomata are two guard cells, which regulate the opening and closing of stomata to facilitate gas exchange and control transpiration in plants.. Structure Flexible Curved Shape Function Regulates movement water and gases into and out of the plant cell Has Vacuoles Aids in photosynthesis