* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download TWO TYPES OF CELLS
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Induced pluripotent stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
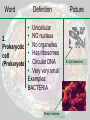
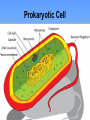
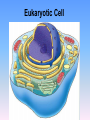
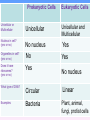
Into to cells? Objective: 1. You will be able to explain what cells are and 2. You will be able to differentiate between the 2 types of cells. Warm up 1. What are cells? 2. What do cells do? Word Definition 1. Cell Basic functional unit of all living things (building blocks) Picture Paramecium - Tiniest part of a living thing E. Coli (bacteria) Red blood cell Cells - FYI All living things are made up of cells! (including you!) Cells do all the life functions that we do: - grow - make energy - reproduce - get rid of wastes - need food (to make energy) - die Cells - FYI E. Coli (bacteria) Cells can look very different There are many types of cells Living things can be made up of ONE CELL or MANY CELLS! Paramecium There are approximately 100 trillion cells in the human body…….100,000,000,000,000 Red blood cell Examples of Cells Amoeba Proteus Plant Stem Bacteria Red Blood Cell Nerve Cell What are cells made of? Cells are mostly water. The rest of the present molecules are: •protein •nucleic acid •carbohydrate •lipid •other There are many cells but scientists classify cells into 2 types: • Procaryotic cells • Eukaryotic cells Word Definition • Unicellular • NO nucleus 2. Prokaryotic • No organelles • Has ribosomes cell (Prokaryote) • Circular DNA • Very very small Examples: BACTERIA Strept. bacteria Picture E. Coli (bacteria) Prokaryotic Cell Did you know? Prokaryotic cells were probably the first type of cells to exist on Earth and are commonly found in the oldest fossils ever found. Word Definition Picture • Unicellular and Multicellular 3. • Membrane bound Eukaryotic Nucleus cell • Contains Organelles (Eukaryote) • Has ribosomes Red blood cell • Linear DNA • Big compared to prokaryotic cells Examples: Shark skin Animals, Plants, Fungi,Human cheek cells Protists (algae) Eukaryotic Cell Did you know…. Eukaryotic cells are more complex and are larger. This type of cell has a nucleus and many organelles inside. This allows the cell to perform many different jobs in multicellular organisms! Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells Unicellular or Multicellular Unicellular Unicellular and Multicellular Nucleus in cell? (yes or no) No nucleus Yes Organelles in cell? (yes or no) No Yes Does it have ribosomes? (yes or no) Yes What type of DNA? Examples: No nucleus Circular Linear Bacteria Plant, animal, fungi, protist cells Exit Slip Prokaryotes Eukaryotes What they both have in common