Cells
... Nerve cells have long, branched fibers running from the main part of the cell, shaped to carry nerve signals from one part of the body to another. ...
... Nerve cells have long, branched fibers running from the main part of the cell, shaped to carry nerve signals from one part of the body to another. ...
phylum porifera and cnidaria
... B. no true tissues or organs C. 3 layers: 1. endoderm: inner layer of cells (choanocytes) a. choanocytes (collar cells) whip flagella to create a current inside the sponge (make own current) and food is also trapped in their stickiness and nutrients are passed on to the mesenchyme 2. mesenchyme: mid ...
... B. no true tissues or organs C. 3 layers: 1. endoderm: inner layer of cells (choanocytes) a. choanocytes (collar cells) whip flagella to create a current inside the sponge (make own current) and food is also trapped in their stickiness and nutrients are passed on to the mesenchyme 2. mesenchyme: mid ...
Immunity - 1st and 2nd lines of defense
... attack pathogens, but don’t “remember” for next time leukocytes phagocytic white blood cells macrophages, neutrophils, natural killer cells ...
... attack pathogens, but don’t “remember” for next time leukocytes phagocytic white blood cells macrophages, neutrophils, natural killer cells ...
Cell Function CC
... Compound Light Microscope: lets light pass through an object then through 2 or more lenses Electron microscope: for objects way too small to be seen with a light microscope; uses magnetic field to bend beams of electrons and can magnify 1,000,000 times ...
... Compound Light Microscope: lets light pass through an object then through 2 or more lenses Electron microscope: for objects way too small to be seen with a light microscope; uses magnetic field to bend beams of electrons and can magnify 1,000,000 times ...
VDB Learning Objectives - V14-Study
... The inner ear is very complex and is innervated by CN VIII. Because the inner ear is derived from ectoderm, the type of fibers within CN VIII are considered special somatic afferent (SSA). ...
... The inner ear is very complex and is innervated by CN VIII. Because the inner ear is derived from ectoderm, the type of fibers within CN VIII are considered special somatic afferent (SSA). ...
Cells Study Guide
... barrier by protecting the cell from the outside world. o All cells need to take in energy and raw materials and give off wastes. o Materials move through the cell membrane both into and outward by the use of active transport and passive transport. o Passive Transport is when the cell does not use en ...
... barrier by protecting the cell from the outside world. o All cells need to take in energy and raw materials and give off wastes. o Materials move through the cell membrane both into and outward by the use of active transport and passive transport. o Passive Transport is when the cell does not use en ...
Flatworms - YVHS Science
... B) Free-living flatworms have organ systems for digestion, excretion, response, and reproduction. ...
... B) Free-living flatworms have organ systems for digestion, excretion, response, and reproduction. ...
Mitosis Worksheet
... The diagram below shows six cells in various phases of the cell cycle. Note the cells are not arranged in the order in which mitosis occurs and one of the phases of mitosis occurs twice. Use the diagram to answer questions 1-7. ...
... The diagram below shows six cells in various phases of the cell cycle. Note the cells are not arranged in the order in which mitosis occurs and one of the phases of mitosis occurs twice. Use the diagram to answer questions 1-7. ...
Chapter 32: Intro to Animal Diversity Kingdom Animalia • Multi
... Human lineage diverged 6-7 mya (species ~195,000 yrs old) ...
... Human lineage diverged 6-7 mya (species ~195,000 yrs old) ...
Chapter 8 Principles of Development
... Determines larval development direct development: enough yolk support growth to juvenile stages (reptiles & birds) telolecithal egg indirect development: larval stages between egg & adult isolecithal/mesolecithal eggs Development single cell—differentiate into different body parts commonality among ...
... Determines larval development direct development: enough yolk support growth to juvenile stages (reptiles & birds) telolecithal egg indirect development: larval stages between egg & adult isolecithal/mesolecithal eggs Development single cell—differentiate into different body parts commonality among ...
Cells to Body Systems
... • Just as cells that work together form a tissue, tissues that work together form an organ. • Organs that work together to perform a function ...
... • Just as cells that work together form a tissue, tissues that work together form an organ. • Organs that work together to perform a function ...
Cells - Livingstone High School
... • Just as cells that work together form a tissue, tissues that work together form an organ. • Organs that work together to perform a function ...
... • Just as cells that work together form a tissue, tissues that work together form an organ. • Organs that work together to perform a function ...
Respiratory Levels of Organization
... hemoglobin is concentrated) at the interface of the circulatory system and respiratory system, called the respiratory membrane. Oxygen diffuses from the inhaled air in the lungs across the aveolar and capillary membranes and into the blood plasma. It then enters the red blood cells where it will be ...
... hemoglobin is concentrated) at the interface of the circulatory system and respiratory system, called the respiratory membrane. Oxygen diffuses from the inhaled air in the lungs across the aveolar and capillary membranes and into the blood plasma. It then enters the red blood cells where it will be ...
Chapter 37- The Circulatory System
... 1. Carry nutrients from small intestine and oxygen from lungs to the cells of the body 2. Transport waste from cells to kidney, lungs and skin 3. Transport hormones from endocrine glands to cells 4. Control water level in cells 5. Provide antibodies and WBC (white blood cells) to prevent infection 6 ...
... 1. Carry nutrients from small intestine and oxygen from lungs to the cells of the body 2. Transport waste from cells to kidney, lungs and skin 3. Transport hormones from endocrine glands to cells 4. Control water level in cells 5. Provide antibodies and WBC (white blood cells) to prevent infection 6 ...
08 - folding
... After folding, the septum transversum lies caudal to the heart where it develops into the central tendon of the diaphragm. ...
... After folding, the septum transversum lies caudal to the heart where it develops into the central tendon of the diaphragm. ...
Lecture 5 Sponges and hydra
... remarkable variation on this theme, and in so doing appears to have achieved immortality. The solitary medusa of this species can revert to its polyp stage after becoming sexually mature. In the laboratory, 100% of these medusae regularly undergo this change. Thus, it is possible that organismic dea ...
... remarkable variation on this theme, and in so doing appears to have achieved immortality. The solitary medusa of this species can revert to its polyp stage after becoming sexually mature. In the laboratory, 100% of these medusae regularly undergo this change. Thus, it is possible that organismic dea ...
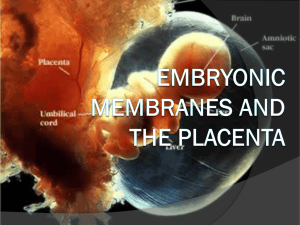
Amnion - Epiblast / Extraembryonic Mesoderm
... activity of fetal adrenal gland and liver Chorionic Somatomammotropin – Human Placental Lactogen – similar to GH (growth, lactation, lipid and carbohydrate metabolism) Placental Growth Hormone – similar to GH – Replaces maternal GH by 15 wks – enhances blood glucose levels ...
... activity of fetal adrenal gland and liver Chorionic Somatomammotropin – Human Placental Lactogen – similar to GH (growth, lactation, lipid and carbohydrate metabolism) Placental Growth Hormone – similar to GH – Replaces maternal GH by 15 wks – enhances blood glucose levels ...
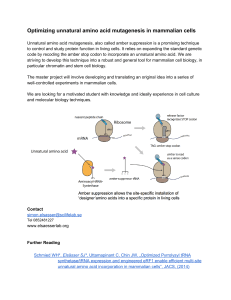
Optimizing unnatural amino acid mutagenesis in mammalian cells
... Unnatural amino acid mutagenesis, also called amber suppression is a promising technique to control and study protein function in living cells. It relies on expanding the standard genetic code by recoding the amber stop codon to incorporate an unnatural amino acid. We are striving to develop this ...
... Unnatural amino acid mutagenesis, also called amber suppression is a promising technique to control and study protein function in living cells. It relies on expanding the standard genetic code by recoding the amber stop codon to incorporate an unnatural amino acid. We are striving to develop this ...
Chapter 8: Embryonic Induction
... Many other cell types originate as a result of inductive interaction throughout development of the organism; this is secondary induction. Inductive interactions have been classified as either instructive or permissive. In an instructive interaction, the inducing tissue apparently gives precise infor ...
... Many other cell types originate as a result of inductive interaction throughout development of the organism; this is secondary induction. Inductive interactions have been classified as either instructive or permissive. In an instructive interaction, the inducing tissue apparently gives precise infor ...
Tissues and Organs
... tissues gathered together for a particular task, e.g. – The heart is made up of muscle, valves, coverings and chords. Each bit has a different function, and they work together to perform the task of pumping blood around the body ...
... tissues gathered together for a particular task, e.g. – The heart is made up of muscle, valves, coverings and chords. Each bit has a different function, and they work together to perform the task of pumping blood around the body ...
DNA Technology - Loyalsock Township School District
... – Germ layering covering the surface of the embryo – Gives rise to outer covering and central nervous system ...
... – Germ layering covering the surface of the embryo – Gives rise to outer covering and central nervous system ...
Why do we need a circulatory system?
... The same blood that run to your toes one minute, is re-circulated to your head the next ...
... The same blood that run to your toes one minute, is re-circulated to your head the next ...
Organ systems
... information throughout the body Structural, functional unit is a neuron Tissue contains neurons and other supporting cells ...
... information throughout the body Structural, functional unit is a neuron Tissue contains neurons and other supporting cells ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.