* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download VDB Learning Objectives - V14-Study
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
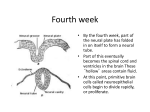
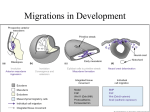
Chapter 18: Development of the Structures of Head and Neck - Part 3 1. True/ False- Ectodermal cells of the embryo form the periderm. (After neurulation, ectodermal cells proliferate to form the periderm, a new outer squamous cell layer on top of the original basal cell layer) 2. True/ False- Neural crest cells invade the skin dermis to form melanocytes. (Invade epidermis) 3. True/ False- All the cutaneous glands of the skin are derived by ectodermal invaginations into dermis. (Sebaceous, sweat, mammary, and scent-marking glands) 4. True/ False- The mammary gland is basically a cutaneous gland, similar to a sweat gland in origin. 5. True/ False- The neurocranium of the skull houses the nasal cavity. (Houses the brain, whereas the maxilla houses the nasal cavity) 6. True/ False- The rhomboncephalon forms cerebrum. (The hindbrain forms the cerebellum, pons, and medulla oblongata) 7. True/ False: The infundibulum is a part of the midbrain. (Part of the diencephalon of the forebrain) 8. True/ False-In the adult lens of the eye, only the posterior surface has an epithelium. (Anterior surface exhibits epithelium in the adult eye) 9. True/ False- The primary lens fibers are formed by the epithelium of the lens on its rostral surface. (The primary lens fibers are formed from cells of the caudal wall of the lens vesicle. Cells of the rostral wall form the secondary lens fibers) 10. True/ False- The outer layer of the optic cup gives rise to the photoreceptors. (The most caudal layer of the inner epithelium give rise to rods and cones) 11. True/ False- SSA fibers innervate the otic vesicle. 12. True/ False- The hyaloid artery supplies developing lens. 13. Describe the development of the inner ear. The first indication of formation of the inner ear is the appearance of an ectodermal thickening called the otic placode on the dorsolateral aspect of the head next to the rhombencephalon. The otic placode gradually invaginates, first forming an otic pit. This pit deepens, the lips of the pit fusing to form the otic vesicle. This vesicle detaches from the surface ectoderm and sinks deeper into the underlying mesenchyme. It then develops a dorsal appendage called the endolymphatic appendage, which forms the endolymphatic sac. The rest of the otic vesicle differentiates into a utricle (dorsal) and a saccule (ventral). The tip of the saccule extends and curls to forms the cochlear duct. The utricle differentiates into a flattened diverticulum that will form the 3 semi-circular canals. The inner ear is very complex and is innervated by CN VIII. Because the inner ear is derived from ectoderm, the type of fibers within CN VIII are considered special somatic afferent (SSA). 14. Describe the 3 primary parts of the neural tube that form the brain, and their divisions. 1 The neural groove forms the neural tube, which develops into the CNS. The cranial part of the neural tube exhibits 3 dilations: the proencephalon (forebrain), mesencephalon (midbrain), and the rhombencephalon (hindbrain), which contribute to the formation of the brain. Forebrain The development of the proencephalon takes place after the closure of the cranial neuropore. At this point, the forebrain gives rise to 2 ventrolateral diverticulae called the optic vesicles. It also forms telencephalic vesicles, which are forerunners of the cerebral hemispheres. The neural tube cavity is retained within the forebrain and eventually forms the lateral ventricles of the brain. The caudal part of the forebrain develops into a midline structure, the diencephalon, which houses numerous centers including the hypothalamus, thalamus, epithalamus, and pineal gland. Midbrain The mesencephalon undergoes little change compared to the forebrain and hindbrain, but contains numerous ascending and descending tracts. The original neural canal is retained as the cerebral aqueduct, a short canal connecting the 3rd and 4th ventricles. Neuroblasts aggregate at the roof of the midbrain to form the rostral and caudal colliculi. Hindbrain During early development, the rhombencephalon exhibits 7 segments, rhombomeres, which contribute to the formation of pharyngeal arches. Later, the hindbrain is separated from the spinal cord by the development of the cervical flexure (not apparent in domestic animals). The pontine flexure also divides the hindbrain into a rostral metencephalon, which develops into the cerebellum and pons, and a caudal myelencephalon, which forms the medulla oblongata. 15. What is palatine raphe, and how is it formed? The palate develops from 2 primordia: the primary palatine process and the secondary palatine process. The primary palatine processes is small and contributes to the formation of the incisive bone (premaxilla) and later the incisive papilla. The secondary palatine processes grow towards the midline, separate the nasal cavity from the oral cavity, and fuse. Their line of fusion in the adult is retained as the palatine raphe. 16. Describe the development of the optic cup, and its developmental fate. The optic vesicles are a pair of outgrowths from the diencephalon (caudal part of forebrain). These vesicles grow towards the surface ectoderm. The ventral aspects of the optic stalks exhibit grooves (choroidal fissure) to accommodate hyaloid arteries that supply the developing eye (but disappear in the mature eye). Eventually, the fissure will close to surround the artery. The distal ends of the optic vesicles invaginate to form optic cups. As this happens, the surface ectoderm near the cups thickens to form the lens placodes, which eventually invaginate to form a lens pits, which soon close to form lens vesicles. These vesicles detach from surface ectoderm, sink into the underlying mesenchyme, the optic cups, and are supplied by hyaloid arteries. The optic cups gave external and internal layers of epithelium that fuse. The outer layer differentiates into the pigment layer of the retina, while the inner layer forms the retina proper. The retina proper consists of several layers of cells. The most cranial layer forms the ganglion cell layer. The middle layer forms the bipolar cell layer. The most caudal cells become photoreceptors (rods and cones). 2 17. Describe where retinal detachment usually occurs. Because the retina proper develops from the inner epithelial layer of the optic cup, the retina is not firmly attached to the outer pigment layer. As the eye ages, the vitreous gel within the inner epithelium tends to shrink and detach from the outer retinal epithelium, a process known as posterior (caudal) vitreous detachment, which is normally benign but can sometimes tear the retina. 18. Most of the adult nasal mucosal epithelium is derived from: a. Nasal pit ectoderm (Neural plate cells (neuroepithelium, neuroectoderm) invade nasal pit and differentiate into olfactory cells) b. Neural crest cells c. Olfactory placode d. Encroaching gut endoderm e. Nasomedial processes 19. All of the following are part of the brain except: a. Metencephalon b. Myelencephalon c. Telencephalon d. Procencephalon e. Cranial neural crest 20. Select the wrong item: a. The Rhinencephalon is part of procencephalon developmentally b. The 2 lateral ventricles of the brain develop within the mesencephalon (From the retention of the neural tube cavity within the forebrain) c. The pia mater and arachnoid coverings of the brain are derived from neural crest d. The diencephalon is part of procencephalon e. Only telencephalic lobes of the developing brain are paired 21. For the following bones of the skull- mention their developmental origin, and type of ossification process involved: Bone Malleus Mandible Ethmoid Basioccipital Basisphenoid Parietal Incisive Basihyoid Vomer Maxilla Embryological Origin Ossification Type Mandibular (Meckel’s) cartilage of branchial arch I (neural crest cells) Endochondral Mandibular cartilage (neural crest cells) Membranous Medial wall of left and right cartilaginous nasal capsules (neural crest) Endochondral Sclerotome Endochondral Sclerotome Endochondral Sclerotome Membranous Upper jaw component of the intermaxillary segment (neural crest cells) Membranous Hyoid (Reichert’s) cartilage of branchial arch II (neural crest cells) Endochondral Nasal septum (neural crest cells) Membranous Neural crest cells Membranous 3