* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Folding Of Embryo
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
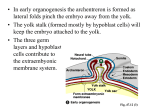
Folding of the Embryo Formation of Gut Endodermal Derivatives By: Dr. Mujahid Khan Folding Of Embryo Flat trilaminar disc folds into a somewhat cylindrical embryo Folding occurs in both median & horizontal planes Results from rapid growth of the embryo Long axis increases rapidly than the sides Occurs simultaneously on both axis Constriction at the junction of embryo & yolk sac Folding in Median Plane Occurs in the cranial and caudal ends Causing Moving head and tail folds ventrally as the embryo elongates cranially and caudally Head Fold At the beginning of the 4th week Neural folds in the cranial region thickened to form primordium of the brain Initially the developing brain projects dorsally into the amniotic cavity Later grows cranially beyond the oropharyngeal membrane Overhangs the developing heart Head Fold Septum transversum, primordial heart, pericardial coelom & oropharyngeal membrane move onto the ventral surface Endoderm of the yolk sac is incorporated into the embryo as a foregut The foregut lies between the brain & heart Oropharyngeal membrane separates the foregut from the stomodeum Head Fold Septum transversum lies caudal to heart after the folding and develops into central tendon of diaphragm Head fold also affects the arrangement of the primordium of body cavity which consists of a flattened horseshoe shaped cavity before folding Tail Fold Results primarily from growth of the distal part of the neural tube This is primordium of the spinal cord As embryo grows, the caudal eminence projects over the cloacal membrane During folding, part of endoderm is incorporated into the embryo as a hindgut Tail Fold Terminal part of the hindgut soon dilates to form the cloaca Cloaca is the primordium of urinary bladder and rectum Before folding primitive streak lies cranial to the cloacal membrane After folding it lies caudal to it After Tail Fold The connecting stalk (primordium of umbilical cord) is attached to the ventral surface of the embryo Allantois (a diverticulum of yolk sac) is partially incorporated into the embryo Folding in Horizontal Plane Folding on sides of the embryo produces right and left lateral folds Is produced by rapidly growing spinal cord and somites Ventrolateral rolling of the edges of embryonic disc form roughly cylindrical embryo Folding in Horizontal Plane As the abdominal walls form, part of endoderm is incorporated into the embryo as the midgut Initially there is a wide connection between midgut & yolk sac After folding the connection is reduced to yolk stalk Folding in Horizontal Plane Umbilical cord forms from the connecting stalk As it forms, ventral fusion of the lateral folds reduces the region of communication between intraembryonic and extraembryonic coelomic cavities to a narrow communication Amniotic cavity expands and obliterates extraembryonic coelom Derivatives of Endoderm Endoderm gives rise to the epithelial lining of: Trachea Bronchi lungs Derivatives of Endoderm Endoderm gives rise to the epithelial lining of: Gastrointestinal tract Liver Pancreas Urinary bladder urachus Derivatives of Endoderm Endoderm gives rise to the epithelial lining of: Pharynx Thyroid Tympanic cavity Pharyngotympanic tube Tonsils Parathyroid glands Formation of Gut gut at the beginning of the 4th week is closed at its: Primordial Cranial end by oropharyngeal membrane Caudal end by the cloacal membrane Formation of Gut gut forms during the 4th week as the head, tail and lateral fold incorporate the dorsal part of the yolk sac into the embryo Primordial The endoderm of the primordial gut gives rise to most of the epithelium and glands of the digestive tract Formation of Gut The epithelium at the cranial and caudal ends of the tract is derived from ectoderm of the stomodeum (mouth) proctodeum (anal pit) The muscular, connective tissue, and other layers of the wall of the digestive tract are derived from the splanchnic mesenchyme surrounding the primordial gut Formation of Gut For descriptive purposes the primordial gut is divided into 3 parts: Foregut Midgut Hindgut