* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Phylum Porifera
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
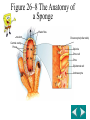
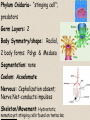
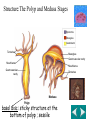
Kingdom Animalia Invertebrates Phylum Porifera Phylum Cnideria SPONGES Sponges Phylum Porifera (pore-bearers)/ simplest animal Body Symmetry/Shape: Asymmetrical Segmentation: None Coelom/body cavity: Acoelomates Nervous system: No Cephalization Skeleton/Movement: Sessile, EndoskeletonSpicules SPONGES Digestion: filter feeders / many pores .Choanocytes are flagellated cells that pull food in thru ostia (pores) and the amoebocyte cells circulate food around the organism Excretion: diffusion; wastes exit thru osculum Circulation: None Respiration: diffusion-obtain oxygen from water Reproduction: sexual-Hermaphrodites(have sperm & egg)-Both sexes in same organism called monoecious: asexual- bud; Regenerate body parts Sponge examples &Uses Examples: natural & kitchen sponges Uses: cleaning, bathing, & makeup application Body structure: A. Osculum: water exits-part of feeding B. Pore cells (ostia): water enters-part of feeding C. Collar cells:(choanocytes)- line interior, have flagella to filter out food from water D. Amoebocytes: carry nutrients from collar cells to body of the sponge E. Spicules- support/skeleton F. Epithelial cells-”skin”support/protection Figure 26–8 The Anatomy of a Sponge Section 26-2 Water flow Osculum Central cavity Pores Choanocyte(collar cells) Spicule Pore cell Pore Epidermal cell Archaeocyte Cnidarians Aurelia Portugueseman-of-war Sea Aneome Hydras Phylum Cnidaria- “stinging cell”; predators Germ Layers: 2 Body Symmetry/shape: Radial, 2 body forms: Polyp & Medusa Segmentation: none Coelom: Acoelomate Nervous: Cephalization absent; Nerve Net-conducts impulses Skeleton/Movement: Hydrostatic; nematocyst: stinging cells found on tentacles; Digestion: one body opening for food & wastes Excretion: Circulation: none Respiration: oxygen diffuses into body from water Reproduction: asexual-budding-Polyp form- ex. Hydra sexual-Medusa form- ex. Jellyfish regenerates body parts Groups & Uses of Cnidarians • 3 Groups of Cnidarians: 1. Hydrozoans: colonies which appear to be one organism Ex: Portuguese-man-of-war 2. Scyphozoans: independent medusa forms Ex: jellyfish, box jelly 3. Anthozoans: colonies of polyps Ex: corals, sea anemone Riches of the sea Structure:The Polyp and Medusa Stages Epidermis Mesoglea Gastroderm Tentacles Mesoglea Gastrovascular cavity Mouth/anus Mouth/anus Gastrovascular cavity Tentacles Medusa Polyp basal disc: sticky structure at the bottom of polyp ; sessile