* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Part 8 - glenbrook s hs
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
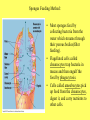
Body Cavities a fluid-filled space separating the digestive tract from the outer body wall. (body cavity = coelom or gut) • • • • • • • Functions: Its fluid cushions the suspended organs to prevent internal injury It enables internal organs to grow and move independently of the outer body wall; makes exercise not harmful to internal organs In soft-bodied animals (earthworms) it functions as a hydrostatic skeleton against which muscles can work. (ex: for burrowing) Ex: Flatworms lack a body cavity = Acoelomate Ex: Roundworms have a body cavity partially lined by mesoderm (middle layer of tissue) = Pseudocoelomate Ex: Earthworms have a body cavity completely lined by mesoderm = Coelomate Details of embryonic development: • Of the animals with a true coelom, there are 2 branches : • Branch 1: mollusks, annelids, arthropods: mouth develops first in embryo = Protostomes. • Branch 2: echinoderms and chordates: anus develops first in embryo = Deuterostomes. Animalia Kingdom 8 Major Invertebrate Phyla: • • • • • • • • Porifera Cnidaria Platyhelminthes Nematoda Mollusca Annelida Arthropoda Echinodermata Invertebrates, animals without backbones, represent more than 95% of the animal kingdom! Sea Anemone: Which Phylum? __________________________ 1. Phylum Porifera - Sponges • Sponges are sessile. • Sponges are the simplest animals, probably evolved very early from colonial protists • Range in height from about 1 cm to 2 meters. • Have no nerves or muscles, and consist of about 9,000 species. • About 100 species lives in fresh water and the rest are marine. • The body of a sponge resembles a sac perforated with holes. Sponges Feeding Method: • Most sponges feed by collecting bacteria from the water which streams through their porous bodies(filter feeding). • Flagellated cells called choanocytes trap bacteria in mucus and then engulf the food by phagocytosis. • Cells called amoebocytes pick up food from the choanocytes, digest it, and carry nutrients to other cells.