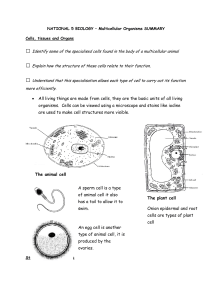
• All living things are made from cells, they are the basic units of all
... body. They have a biconcave shape that ensures that the cell has a large surface area for the absorption of oxygen. Red blood cells contain the pigment haemoglobin which combines with oxygen at high concentrations (at the alveoli) to form oxy-haemoglobin. At low concentrations (in the cells) the hae ...
... body. They have a biconcave shape that ensures that the cell has a large surface area for the absorption of oxygen. Red blood cells contain the pigment haemoglobin which combines with oxygen at high concentrations (at the alveoli) to form oxy-haemoglobin. At low concentrations (in the cells) the hae ...
The Human Body - bakerbiologykingdoms
... • Platelets: cell fragments used for clotting • Plasma: liquid transports all of the cells. ...
... • Platelets: cell fragments used for clotting • Plasma: liquid transports all of the cells. ...
Human Senses
... Choroid Vascularized to supply nutrients Melanocytes to absorb light Ciliary body Smooth muscle ring ciliary muscles control lens shape Ciliary processes secrete aqueous humor Suspensory ligaments hold lens in place Iris Colored portion of ciliary body ...
... Choroid Vascularized to supply nutrients Melanocytes to absorb light Ciliary body Smooth muscle ring ciliary muscles control lens shape Ciliary processes secrete aqueous humor Suspensory ligaments hold lens in place Iris Colored portion of ciliary body ...
Science - edl.io
... Platelets produce enzymes to form a net. This net traps other blood cells to form a __________ __________. ...
... Platelets produce enzymes to form a net. This net traps other blood cells to form a __________ __________. ...
LT #4 I can describe that cells differentiate to form
... • Just as cells join together to form tissues, different tissues join together to form organs. • An organ is a structure made up of two or more tissues that work together to carry out a specific job. • Ex: Your heart, is an organ made up of muscle tissue, blood tissue, and nerve tissue. • Others org ...
... • Just as cells join together to form tissues, different tissues join together to form organs. • An organ is a structure made up of two or more tissues that work together to carry out a specific job. • Ex: Your heart, is an organ made up of muscle tissue, blood tissue, and nerve tissue. • Others org ...
Document
... a. do not have a body cavity ... have a body cavity b. exhibit radial symmetry ... exhibit bilateral symmetry c. are protostomes ... are deuterostomes d. have a body cavity partially lined with tissue derived from mesoderm ... have a body cavity completely lined with tissue derived from mesoderm 12. ...
... a. do not have a body cavity ... have a body cavity b. exhibit radial symmetry ... exhibit bilateral symmetry c. are protostomes ... are deuterostomes d. have a body cavity partially lined with tissue derived from mesoderm ... have a body cavity completely lined with tissue derived from mesoderm 12. ...
Cell theory - Unidad Educativa Monte Tabor
... orchid plants - the nucleus. In 1833 he wrote a 'paper' about it. A paper is an article describing a scientific discovery and how it was made. Papers are collected together and published in 'journals'. Scientists buy journals to find out what other scientists have done. One famous journal today is c ...
... orchid plants - the nucleus. In 1833 he wrote a 'paper' about it. A paper is an article describing a scientific discovery and how it was made. Papers are collected together and published in 'journals'. Scientists buy journals to find out what other scientists have done. One famous journal today is c ...
EXCRETION
... Water, salts, and some urea diffuse from the blood into the sweat glands and are subsequently excreted as perspiration. ...
... Water, salts, and some urea diffuse from the blood into the sweat glands and are subsequently excreted as perspiration. ...
Basic Structure of the Human Body
... Pituitary gland, Thyroid gland, Parathyroid glands, Adrenal glands, Pancreas Testes, Ovary, Liver ...
... Pituitary gland, Thyroid gland, Parathyroid glands, Adrenal glands, Pancreas Testes, Ovary, Liver ...
Exam 7 Study Guide
... Atrium (Receive Blood) Ventricle (Pump blood out) Heart Contracts to push blood out (Systole), when muscle relaxes it fills up with blood (Diasystole) SA node controls heartbeat. 16. Blood Vessels Artery- Carries blood from heart to body Veins- Return blood to heart Capillaries- In charg ...
... Atrium (Receive Blood) Ventricle (Pump blood out) Heart Contracts to push blood out (Systole), when muscle relaxes it fills up with blood (Diasystole) SA node controls heartbeat. 16. Blood Vessels Artery- Carries blood from heart to body Veins- Return blood to heart Capillaries- In charg ...
Practice Questions - Elevate Education
... 1. What is the difference between the primary structure and secondary structure of a protein? 2. Describe what is meant by the tertiary structure and quaternary structure of a protein? 3. How many different polypeptides are possible from joining the amino acid residues alanine, glycine and glutamic ...
... 1. What is the difference between the primary structure and secondary structure of a protein? 2. Describe what is meant by the tertiary structure and quaternary structure of a protein? 3. How many different polypeptides are possible from joining the amino acid residues alanine, glycine and glutamic ...
Practice Questions - the Elevate Student Portal.
... 1. What is the difference between the primary structure and secondary structure of a protein? 2. Describe what is meant by the tertiary structure and quaternary structure of a protein? 3. How many different polypeptides are possible from joining the amino acid residues alanine, glycine and glutamic ...
... 1. What is the difference between the primary structure and secondary structure of a protein? 2. Describe what is meant by the tertiary structure and quaternary structure of a protein? 3. How many different polypeptides are possible from joining the amino acid residues alanine, glycine and glutamic ...
Human Body Systems Notes for Coloring
... Digestive Tract/Path of food: mouth→ esophagus→ stomach→ small intestine→ large intestine→ rectum Villi – Line the small intestine; increases surface area so more nutrients can be absorbed from food. Intestines are named based on their diameter (how big around) not their length. Other/Helper Organs ...
... Digestive Tract/Path of food: mouth→ esophagus→ stomach→ small intestine→ large intestine→ rectum Villi – Line the small intestine; increases surface area so more nutrients can be absorbed from food. Intestines are named based on their diameter (how big around) not their length. Other/Helper Organs ...
MatchCard Science© Zoology - 9
... the tree of life by scientists. Can you imagine a type of creature that would not fit into these five kingdoms? Describe it and name the kingdom. ...
... the tree of life by scientists. Can you imagine a type of creature that would not fit into these five kingdoms? Describe it and name the kingdom. ...
4- Blood
... cannot replace defective proteins. Human erythrocytes normally survive in the circulation for about 120 days. By this time defects in the membrane's cytoskeletal lattice or ion transport systems begin to produce swelling or other shape abnormalities, as well as changes in the cells' surface oligosac ...
... cannot replace defective proteins. Human erythrocytes normally survive in the circulation for about 120 days. By this time defects in the membrane's cytoskeletal lattice or ion transport systems begin to produce swelling or other shape abnormalities, as well as changes in the cells' surface oligosac ...
Structural Levels of Organization
... Covering cells are flat Structure and function change with age (Thymus disappears, bones become brittle…) ...
... Covering cells are flat Structure and function change with age (Thymus disappears, bones become brittle…) ...
cleavage
... Overview: Welcome to Your Kingdom • 1.3 million living species of animals have been identified ...
... Overview: Welcome to Your Kingdom • 1.3 million living species of animals have been identified ...
Cells and Systems UNIT Test Unit 2 1. Growth and development
... purpose of the mucus is … digest proteins into smaller particles prevent the gastric juice from digesting the stomach assist the hydrochloric acid with digestion prevent heartburn from occurring The transportation of nutrients in plants is the role of the plant's tissue. Specialized tissue connects ...
... purpose of the mucus is … digest proteins into smaller particles prevent the gastric juice from digesting the stomach assist the hydrochloric acid with digestion prevent heartburn from occurring The transportation of nutrients in plants is the role of the plant's tissue. Specialized tissue connects ...
Cells and Systems Notes
... The circulatory system transports food and oxygen through the body Made of the heart, blood and blood vessels Circulates blood around the body to deliver food particles, dissolved gas and other materials to cells Also takes away waste material from the cells Circulatory System Drawing Assignment ...
... The circulatory system transports food and oxygen through the body Made of the heart, blood and blood vessels Circulates blood around the body to deliver food particles, dissolved gas and other materials to cells Also takes away waste material from the cells Circulatory System Drawing Assignment ...
UNIT ONE - Cells and Heredity
... cells that float in it. It is a specialized bodily fluid that supplies essentials substances and nutrients, such as sugar, oxygen, and hormones to our cells, and carries waste away from those cells, this waste is eventually flushed out of the body in urine, feces, sweat, and lungs (carbon dioxide). ...
... cells that float in it. It is a specialized bodily fluid that supplies essentials substances and nutrients, such as sugar, oxygen, and hormones to our cells, and carries waste away from those cells, this waste is eventually flushed out of the body in urine, feces, sweat, and lungs (carbon dioxide). ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.























