Sponges, Cnidarians, Ctenophores
... 1. Bell-shaped: called a medusa is able to swim (jellyfish) 2. Vase-shaped: called a polyp is specialized for a sessile existence. 3. Two cell layers: epidermis and gastrodermis with a mesoglea layer in between them. 4. Gastrovascular cavity is a hollow gut in the center of the body. Has a single op ...
... 1. Bell-shaped: called a medusa is able to swim (jellyfish) 2. Vase-shaped: called a polyp is specialized for a sessile existence. 3. Two cell layers: epidermis and gastrodermis with a mesoglea layer in between them. 4. Gastrovascular cavity is a hollow gut in the center of the body. Has a single op ...
3) ALL LIVING THINGS RESPOND TO A STIMULUS
... To grow means to get bigger and to get bigger; more cells must be added. To increase numbers of cells, cell division must occur. Develop means to change into an adult form (mature). ...
... To grow means to get bigger and to get bigger; more cells must be added. To increase numbers of cells, cell division must occur. Develop means to change into an adult form (mature). ...
Types of cellls sem 2 2011
... • Roots and shoots have meristematic tissue at apical meristems (the tips) that are responsible for the elongation of roots and shoots • During embryonic development the shoot apical meristem is formed, but leaves and flowers after germination gives rise to the stem • The root apical meristem is als ...
... • Roots and shoots have meristematic tissue at apical meristems (the tips) that are responsible for the elongation of roots and shoots • During embryonic development the shoot apical meristem is formed, but leaves and flowers after germination gives rise to the stem • The root apical meristem is als ...
viii. milk production and secretion
... At this point, the ectoderm and endoderm are considered the embryonic disc (i.e. will become the embryonic body). ...
... At this point, the ectoderm and endoderm are considered the embryonic disc (i.e. will become the embryonic body). ...
ch1 FA11 - Cal State LA
... double membrane enclosure yields the modern nucleus and endoplasmic reticulum • Symbiotic capture of a photosynthetic bacteria and elaboration of a cell wall yields plant cells ...
... double membrane enclosure yields the modern nucleus and endoplasmic reticulum • Symbiotic capture of a photosynthetic bacteria and elaboration of a cell wall yields plant cells ...
Cells of the Body
... Cells come in a variety of shapes and sizes. Typical cells range from 5 to 50 micrometers. Despite the difference in sizes, all cells have two characteristics in common. They are all surrounded by a cell membrane and all cells contain genetic material. Cells in multicellular organisms are specialize ...
... Cells come in a variety of shapes and sizes. Typical cells range from 5 to 50 micrometers. Despite the difference in sizes, all cells have two characteristics in common. They are all surrounded by a cell membrane and all cells contain genetic material. Cells in multicellular organisms are specialize ...
Science Cumulative Review 1 Unicellular and Multicellular
... What is one example of a unicellular organism? a. Flower b. Bird c. Bacteria d. Cow What type of organism would be able to survive as a single cell? a. Algae b. Rabbit c. Human d. Grass How are the cells of a multicellular organism most different from the cells of a unicellular organism? a. Cells in ...
... What is one example of a unicellular organism? a. Flower b. Bird c. Bacteria d. Cow What type of organism would be able to survive as a single cell? a. Algae b. Rabbit c. Human d. Grass How are the cells of a multicellular organism most different from the cells of a unicellular organism? a. Cells in ...
Name - Humble ISD
... a. Nervous System 6. ____ Produces movement b. Endocrine System 7. ____ Is the system that includes the skin c. Skeletal System 8. ____ Physical barrier against pathogens, injury, dehydration d. Muscular System 9. ____ Breaks down food molecules e. Integumentary System 10. ____ Largest organ in your ...
... a. Nervous System 6. ____ Produces movement b. Endocrine System 7. ____ Is the system that includes the skin c. Skeletal System 8. ____ Physical barrier against pathogens, injury, dehydration d. Muscular System 9. ____ Breaks down food molecules e. Integumentary System 10. ____ Largest organ in your ...
Embryological Development of Skeletal Structures of Head and
... Toward the end of the fourth week, nasal placodes develop bilaterally at the inferolateral corners of the frontonasal process. As the region surrounding the nasal placodes develops into medial and lateral nasal processes, the deepening nasal placodes are transformed into nasal pits, in time forming ...
... Toward the end of the fourth week, nasal placodes develop bilaterally at the inferolateral corners of the frontonasal process. As the region surrounding the nasal placodes develops into medial and lateral nasal processes, the deepening nasal placodes are transformed into nasal pits, in time forming ...
2017 Year 8 Term3 Programme
... examining a variety of cells using a light microscope, by digital technology or by viewing a simulation distinguishing plant cells from animal or fungal cells identifying structures within cells and describing their function recognising that some organisms consist of a single cell recognising that c ...
... examining a variety of cells using a light microscope, by digital technology or by viewing a simulation distinguishing plant cells from animal or fungal cells identifying structures within cells and describing their function recognising that some organisms consist of a single cell recognising that c ...
The Role of Differential Gene Expression in Cell Differentiation
... • Unlike other animals, gene expression plays a role during mammalian cleavage. • At the 8-cell stage of a mammal embryo, the cells form tight junctions and a compact mass. • At the transition from the 16-cell to 32-cell stage, the cells separate into two masses. • The inner cell mass develops into ...
... • Unlike other animals, gene expression plays a role during mammalian cleavage. • At the 8-cell stage of a mammal embryo, the cells form tight junctions and a compact mass. • At the transition from the 16-cell to 32-cell stage, the cells separate into two masses. • The inner cell mass develops into ...
Human Body Systems
... The egg is surrounded by a protective layer that has binding sites where sperm can attach. Fertilization of the egg restores the chromosome number to 46 (23 egg plus 23 sperm= 46) Once the single sperm enters the egg, the egg releases a barrier to the outside of the cell that prevents any other sper ...
... The egg is surrounded by a protective layer that has binding sites where sperm can attach. Fertilization of the egg restores the chromosome number to 46 (23 egg plus 23 sperm= 46) Once the single sperm enters the egg, the egg releases a barrier to the outside of the cell that prevents any other sper ...
Animal Organ Systems
... Tissues that are alike work together to form organs which complete jobs. Organs work together in organ systems to carry out processes. Organ systems work together to support the life of an organism. ...
... Tissues that are alike work together to form organs which complete jobs. Organs work together in organ systems to carry out processes. Organ systems work together to support the life of an organism. ...
100 Biology
... 28. Excretion is the removal of waste material from the body via the kidneys and bladder. 29. Chlorophyll is the green substance found in plant cell chloroplasts where photosynthesis takes place. 30. Pollination, the transfer of pollen between stamens and stigma, should not be confused with seed dis ...
... 28. Excretion is the removal of waste material from the body via the kidneys and bladder. 29. Chlorophyll is the green substance found in plant cell chloroplasts where photosynthesis takes place. 30. Pollination, the transfer of pollen between stamens and stigma, should not be confused with seed dis ...
PPT
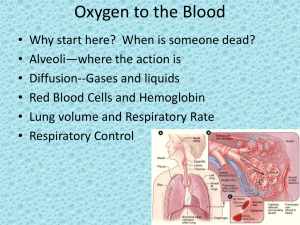
... • Open a can of soda…what happens? • Diffusion of O2 at from inside alveolus into capillary is also movement from air (gas) into plasma (liquid) • Mass movement of oxygen into blood works because: – Differences in partial pressures are great – Distance is short – Oxygen is lipid soluble so it passes ...
... • Open a can of soda…what happens? • Diffusion of O2 at from inside alveolus into capillary is also movement from air (gas) into plasma (liquid) • Mass movement of oxygen into blood works because: – Differences in partial pressures are great – Distance is short – Oxygen is lipid soluble so it passes ...
What is an animal?
... Endoskeletons can be made of calcium carbonate, like in sea stars; cartilage, like in sharks; and bone, like in vertebrate animals ...
... Endoskeletons can be made of calcium carbonate, like in sea stars; cartilage, like in sharks; and bone, like in vertebrate animals ...
New B1 B2 B3 Revision
... The concentration of blood plasma varies with external temperature, exercise level, intake of fluids and salt. The concentration of urine is controlled by a hormone called ADH, which is released into the bloodstream by the ...
... The concentration of blood plasma varies with external temperature, exercise level, intake of fluids and salt. The concentration of urine is controlled by a hormone called ADH, which is released into the bloodstream by the ...
Chap 20 – Organization of Multicellular Organisms
... exchange materials across the plasma membrane Cell size must – be large enough to house DNA, proteins, and structures needed to survive and reproduce, but – remain small enough for a SA:volume ratio that will allow for adequate exchange with the environment. ...
... exchange materials across the plasma membrane Cell size must – be large enough to house DNA, proteins, and structures needed to survive and reproduce, but – remain small enough for a SA:volume ratio that will allow for adequate exchange with the environment. ...
Immune System
... been destroyed, memory T and B cells are left over. It is their job to make sure the next time that this virus enters the body they remember how to defeat it. ...
... been destroyed, memory T and B cells are left over. It is their job to make sure the next time that this virus enters the body they remember how to defeat it. ...
Ancient Art of Biblical Healing 50-Hour ModuleAroma Hut Institute
... up, in meiosis the cells pair off together. Defects which appear in the pairing in meiosis can lead to chromasomal birth defects. As the cells multiply they group and in turn start to form tissues. There are four main types of tissue. There are Muscle tissue, connective tissues, nervous tissues and ...
... up, in meiosis the cells pair off together. Defects which appear in the pairing in meiosis can lead to chromasomal birth defects. As the cells multiply they group and in turn start to form tissues. There are four main types of tissue. There are Muscle tissue, connective tissues, nervous tissues and ...
Cells
... respiratory system: consisting of nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, lungs circulatory system: consisting of heart, blood vessels nervous system: consisting of sense organs, brain, spinal cord, nerves skeletal system: consisting of vertebral column, limb bones, ribs muscular system: muscles ...
... respiratory system: consisting of nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, lungs circulatory system: consisting of heart, blood vessels nervous system: consisting of sense organs, brain, spinal cord, nerves skeletal system: consisting of vertebral column, limb bones, ribs muscular system: muscles ...
powerpoint
... (a) Early organogenesis. The archenteron forms when lateral folds (b) pinch the embryo away from the yolk. The embryo remains open to the yolk, attached by the yolk stalk, about midway along its length, as shown in this cross section. The notochord, neural tube, and somites subsequently form much as ...
... (a) Early organogenesis. The archenteron forms when lateral folds (b) pinch the embryo away from the yolk. The embryo remains open to the yolk, attached by the yolk stalk, about midway along its length, as shown in this cross section. The notochord, neural tube, and somites subsequently form much as ...
Respiratory System
... Questions • semilunar valve cusps look like half moons • artery lining is simple squamous endothelial cells (a kind of epithelium) • antibiotics can cause a fever • immunosuppressive drugs (for organ transplants, skin grafts) often need to be taken for life • WBC response time? think of how long it ...
... Questions • semilunar valve cusps look like half moons • artery lining is simple squamous endothelial cells (a kind of epithelium) • antibiotics can cause a fever • immunosuppressive drugs (for organ transplants, skin grafts) often need to be taken for life • WBC response time? think of how long it ...
60 Vertebrate Development
... Stages of Development In vertebrates, as in all sexual animals, the first step in development is the union of male and female gametes, a process called fertilization. Fertilization is typically external in fish and amphibians, which reproduce in water, and internal in all other vertebrates. In inter ...
... Stages of Development In vertebrates, as in all sexual animals, the first step in development is the union of male and female gametes, a process called fertilization. Fertilization is typically external in fish and amphibians, which reproduce in water, and internal in all other vertebrates. In inter ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.