* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CHAPTER 3
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic resistance to malaria wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
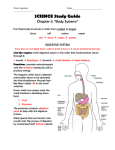
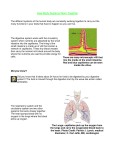
CHAPTER 3 8TH GRADE I Human Body A. The perfect machine—all parts work together for the whole- life. B. Atoms—basic particles of all matter—smallest part of matter. C. Body needs a. Elements—made of only one kind of atom i. Ex: periodic table b. Compounds—made up of more than one element—chemically combined i. Ex: CO c. Inorganic substances—come from non-living sources air, soil, water i. Minerals—inorganic and help with many body chemical reactions—need only small amounts (pg 65 Table 1) ii. Needed by body—water 1. 70% of all body tissues 2. Helps with body functions 3. Not enough water—headache, fatigue, dry skin. d. Organic substances—compounds containing carbon. Except- carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide i. 4 groups 1. Carbohydrates-provide energy, made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen 2. Lipids-fats and oils stored for energy 3. nucleic acids-large complex organic compounds. They store information in codes---DNA. 4. Proteins-forms structures for body carry out important processes. II Cell A. Basic unit of life. B. Microscopic C. All shapes and sizes—pg 69 D. Take in food, O, HO, and minerals make proteins and release energy. E. All cells or groups of cells have specific functions. III Levels of Organization A. Cells- basic unit of life. B. Tissues-groups of similar cells that do same sort of work—nerve tissue C. Organ-structure made up of different types of tissues –heart, lungs D. Organ system-group of organs that work together to do a job SECTION 2 I Body systems A. Feeding cells a. Chemicals are in blood to feed cells. b. Blood carries chemicals from respitory system (O) and digestive system (minerals). B. Digestive system a. Like an assembly line-disassembly line b. Breaks down food so body can use them. c. Basically a tube runs through the body. d. Food is made smaller and simple as it passes through. e. Other body parts help too. i. Brain-saliva released to soften food. Enzymes are released to help with chemical reactions. ii. Stomach-has bile, HCL, and enzymes C. Digestive and Circulatory System a. Small intestine contains villi. b. Villi-fingerlike projections that have capillaries in them. c. Absorption occurs in villi-nutrients move into blood. d. Cells in blood carry nutrients to body cells. e. Wastes are not absorbed and expelled from the body. II Body energy A. Mitochondria- cellular respiration occurs. B. Cellular respiration- series of chemical processes in which O combines with foodenergy is released. C. Carbon dioxide (CO) and water are given off as waste by cells. D. Food and O must be constant supply. E. Low O lactic acid produced and causes muscles to fatigue and rapid breathing. III Respitory system A. Brings in O and releases CO. B. Capillaries surround alveoli in lungs. C. Alveoli-thin lined sacs at end of bronchial tubes. D. O comes in and goes into capillaries CO is released back into lungs exhaled. E. Diaphragm causes the lungs to expand. IV Excretory system A. Removal of waste from body-toxic levels if not removed. B. Respitory—CO C. Urinary—urine D. Kidneys remove cell wastes and excess water a. Nephrons-filter the blood b. Water, sugar, and salt V Homeostasis A. Process by which body maintains a stable internal environment. B. Body temperature regulation a. Breathing heavy- lets heat out b. Flushing-brings blood to skin surface cooling c. Sweating-water on skin cools body C. Achieved 2 ways a. Negative feedback-changes internal condition to go back to normal i. Ex: pancreas-insulin to reduce glucose— glucogen released when sugar is lowdone by the liver. b. Positive feedback-changes normal state to abnormal state-body does not try to be in a normal state---rare i. Ex: contraction of uterus more intense as head goes into birth canal. ii. Ex: blood clotting-platelets and fibrinogen make clots-White blood cells eat any bacteria around the wound.