Unit 5 Day 11: RL Circuits
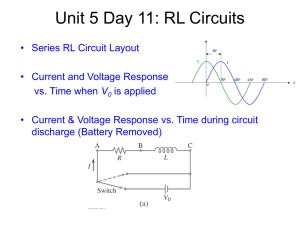
... Unit 5 Day 11: RL Circuits • Series RL Circuit Layout • Current and Voltage Response vs. Time when V0 is applied ...
... Unit 5 Day 11: RL Circuits • Series RL Circuit Layout • Current and Voltage Response vs. Time when V0 is applied ...
Ch14
... • The quality factor is the ratio of its resonant frequency to its bandwidth. • If the bandwidth is narrow, the quality factor of the resonant circuit must be high. • If the band of frequencies is wide, the quality factor must be low. ...
... • The quality factor is the ratio of its resonant frequency to its bandwidth. • If the bandwidth is narrow, the quality factor of the resonant circuit must be high. • If the band of frequencies is wide, the quality factor must be low. ...
ch4_L1_i
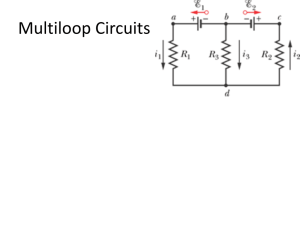
... without passing through any intermediate node more than once Kirchhoff’s first (or current) law: at a circuit node, the current flowing into the node equals the current flowing out (charge is conserved) Kirchhoff’s second (or voltage) law: around a circuit loop, the sum of the voltages equal zero (e ...
... without passing through any intermediate node more than once Kirchhoff’s first (or current) law: at a circuit node, the current flowing into the node equals the current flowing out (charge is conserved) Kirchhoff’s second (or voltage) law: around a circuit loop, the sum of the voltages equal zero (e ...
AlexanderCh14finalR1
... • The quality factor is the ratio of its resonant frequency to its bandwidth. • If the bandwidth is narrow, the quality factor of the resonant circuit must be high. • If the band of frequencies is wide, the quality factor must be low. ...
... • The quality factor is the ratio of its resonant frequency to its bandwidth. • If the bandwidth is narrow, the quality factor of the resonant circuit must be high. • If the band of frequencies is wide, the quality factor must be low. ...
Department of Computer Science & Engineering
... circuit, but in many other high voltage applications too. Also, it was found out that using the boost converter design, it doesn’t matter how high of current you draw, it is the physical amount of current you draw. So you can use a small amount of current, but pulse the circuit really fast and achie ...
... circuit, but in many other high voltage applications too. Also, it was found out that using the boost converter design, it doesn’t matter how high of current you draw, it is the physical amount of current you draw. So you can use a small amount of current, but pulse the circuit really fast and achie ...
ECE 3041 - ECE Users Pages
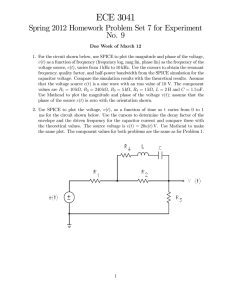
... that the voltage source () is a sine wave with an rms value of 10 V. The component values are 1 = 10 kΩ, 2 = 240 kΩ, 3 = 5 kΩ, 4 = 1 kΩ, = 2 H and = 15 nF. Use Mathcad to plot the magnitude and phase of the voltage (); assume that the phase of the source () is zero with the orientatio ...
... that the voltage source () is a sine wave with an rms value of 10 V. The component values are 1 = 10 kΩ, 2 = 240 kΩ, 3 = 5 kΩ, 4 = 1 kΩ, = 2 H and = 15 nF. Use Mathcad to plot the magnitude and phase of the voltage (); assume that the phase of the source () is zero with the orientatio ...
LAB 3 Tank circuit procedure and other information 1. Verify that the
... 3. Build the tank circuit in the lab using the variable capacitor. Use a large resistor in series with the function generator to mimic a current source. Observe the resonant frequency and the Q of the circuit. There is more detail on testing the LC tank in the appendix to this lab. Note that it is t ...
... 3. Build the tank circuit in the lab using the variable capacitor. Use a large resistor in series with the function generator to mimic a current source. Observe the resonant frequency and the Q of the circuit. There is more detail on testing the LC tank in the appendix to this lab. Note that it is t ...
Line Test - Microelettrica Scientifica
... High Speed DC circuit breakers are valuable components which must be protected against wear and tear and excessive current flow. Before closing High Speed Circuit Breaker on a power line, it is therefore advisable to test whether a short circuit is occurring by means of line test resistors. The resi ...
... High Speed DC circuit breakers are valuable components which must be protected against wear and tear and excessive current flow. Before closing High Speed Circuit Breaker on a power line, it is therefore advisable to test whether a short circuit is occurring by means of line test resistors. The resi ...
Robobug Components Resistor Resistors determine the flow of
... small, where the resistance is low the flow of current is large. Resistance, voltage and current are connected in an electrical circuit. ...
... small, where the resistance is low the flow of current is large. Resistance, voltage and current are connected in an electrical circuit. ...
RLC Circuits (7/22)
... An L-R-C series circuit as shown is operating at its resonant frequency. At this frequency, how are the values of the capacitive reactance XC, the inductive reactance XL, and the resistance R related to each other? A. XL = R; XC can have any value. B. XC = R; XL can have any value. C. XC = XL; R can ...
... An L-R-C series circuit as shown is operating at its resonant frequency. At this frequency, how are the values of the capacitive reactance XC, the inductive reactance XL, and the resistance R related to each other? A. XL = R; XC can have any value. B. XC = R; XL can have any value. C. XC = XL; R can ...
Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating current
... Show that in a series LCR circuit connected to an a.c. source exhibits resonance at its natural frequency equal to ...
... Show that in a series LCR circuit connected to an a.c. source exhibits resonance at its natural frequency equal to ...
Signal Attenuation - Department of Information Technologies
... Ch. 3: Simple Resistive Circuits. Ch. 4: Techniques of Circuit Analysis. Ch. 4: Techniques of Circuit Analysis. Ch. 5: The Operational Amplifier. Ch. 5: The Operational Amplifier. ...
... Ch. 3: Simple Resistive Circuits. Ch. 4: Techniques of Circuit Analysis. Ch. 4: Techniques of Circuit Analysis. Ch. 5: The Operational Amplifier. Ch. 5: The Operational Amplifier. ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.