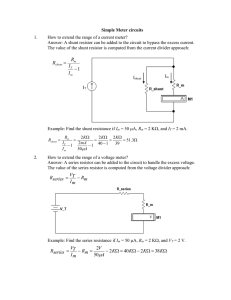
Experiment 3 - Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering
... bandwidth). When XL is low and R is high, the opposite is true. It can be seen that additional R causes the bandwidth to increase. Mathematically, bandwidth is defined as being BW= fr/Q where fr, is the resonant frequency and Q is the quality figure for the circuit. The Parallel Tuned Circuits The p ...
... bandwidth). When XL is low and R is high, the opposite is true. It can be seen that additional R causes the bandwidth to increase. Mathematically, bandwidth is defined as being BW= fr/Q where fr, is the resonant frequency and Q is the quality figure for the circuit. The Parallel Tuned Circuits The p ...
FIGURE 4.2-1 Circuit with an independent voltage source and an
... FIGURE 4.5-4 Mesh currents, i1 and i2, and element current, i1 – i2, of a (a) generic circuit element, (b) current source, and (c) resistor. ...
... FIGURE 4.5-4 Mesh currents, i1 and i2, and element current, i1 – i2, of a (a) generic circuit element, (b) current source, and (c) resistor. ...
Transient currents and voltages
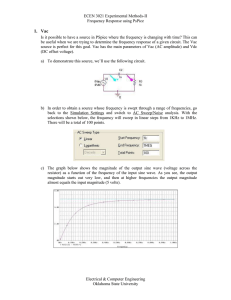
... The dataset has Time(s) in the first column and Amplitude (Volt) in the second. Data was acquired as with an oscilloscope: zero amplitude is at the middle of the graph. You have to adjust (lift) all the amplitude values so that all are positive: find the largest negative amplitude and add its ab ...
... The dataset has Time(s) in the first column and Amplitude (Volt) in the second. Data was acquired as with an oscilloscope: zero amplitude is at the middle of the graph. You have to adjust (lift) all the amplitude values so that all are positive: find the largest negative amplitude and add its ab ...
Slide 1
... The circuit/system designed, through generation of equal but opposite currents forced to pass through the parasitic branches (ICo and IGo), will cancel out their effect on the output so that the true resonance frequency characteristics can be displayed. The resonance frequency generated by an oscill ...
... The circuit/system designed, through generation of equal but opposite currents forced to pass through the parasitic branches (ICo and IGo), will cancel out their effect on the output so that the true resonance frequency characteristics can be displayed. The resonance frequency generated by an oscill ...
fateme km proposed ece1250 2240 project
... We propose having a plastic crate of demos to be given to the instructor of ECE1250 and another for ECE2240 that particular semester. Each demo will be numbered/correlated to the textbook chapters it is associated with. Proposed graduate TA: Fateme Km. Fateme is working on her MS degree with Dr. Nei ...
... We propose having a plastic crate of demos to be given to the instructor of ECE1250 and another for ECE2240 that particular semester. Each demo will be numbered/correlated to the textbook chapters it is associated with. Proposed graduate TA: Fateme Km. Fateme is working on her MS degree with Dr. Nei ...
AC Series Circuit: Power and Resonance
... should use frequency values which are grouped near resonance as well as some which are more widely spaced when away from the resonance frequency. Apparatus: The same RLC circuit board used last week, audio frequency sine wave generator, 2 DMMs, wires Discussion: The impedance of an RLC series circu ...
... should use frequency values which are grouped near resonance as well as some which are more widely spaced when away from the resonance frequency. Apparatus: The same RLC circuit board used last week, audio frequency sine wave generator, 2 DMMs, wires Discussion: The impedance of an RLC series circu ...
Measurement CKT
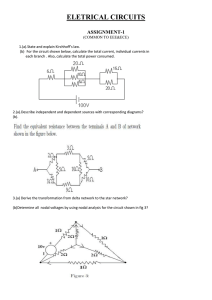
... it is a balance type instrument. In the following circuit the unknown resistance can be calculated from the three known resistors if the bridge circuit is under the balanced condition—zero current through the meter. ...
... it is a balance type instrument. In the following circuit the unknown resistance can be calculated from the three known resistors if the bridge circuit is under the balanced condition—zero current through the meter. ...
Here we have some circuits with voltage sources.
... Here we have some circuits with voltage sources. We will determine whether these are valid circuits. The first circuit is 1 V applied across a resistor, which is valid. The second circuit is two series voltage sources, and the voltage simply add together to produce a net voltage of -1 V across the r ...
... Here we have some circuits with voltage sources. We will determine whether these are valid circuits. The first circuit is 1 V applied across a resistor, which is valid. The second circuit is two series voltage sources, and the voltage simply add together to produce a net voltage of -1 V across the r ...
20091119084719!Filter_Instructions
... Now, we will do some circuit analysis. First, input a square wave to your circuit. Observe the output waveform for low frequencies, say under 100 Hz. Notice how the signal rises and falls exponentially? Determine the rising and falling time constant of the system. The time constant is defined as the ...
... Now, we will do some circuit analysis. First, input a square wave to your circuit. Observe the output waveform for low frequencies, say under 100 Hz. Notice how the signal rises and falls exponentially? Determine the rising and falling time constant of the system. The time constant is defined as the ...
Electrical Circuits Lab. 0903219 Series RLC Resonance Circuit
... * Figure (2) shows important plot of how capacitor impedance XC and inductor impedance XL change with frequency and the place of fr on the plot (in this case when XC equal XL). ...
... * Figure (2) shows important plot of how capacitor impedance XC and inductor impedance XL change with frequency and the place of fr on the plot (in this case when XC equal XL). ...
Parallel circuits - Journal of Pyrotechnics
... elements are added to the circuit. As a result, the total amount of current flowing always decreases. • To maintain the same current as more elements are added, greater and greater voltage will be needed from the power source. • If the wire size is sufficient (or can be ignored) for a single element ...
... elements are added to the circuit. As a result, the total amount of current flowing always decreases. • To maintain the same current as more elements are added, greater and greater voltage will be needed from the power source. • If the wire size is sufficient (or can be ignored) for a single element ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.