Lab-in-a-Box
... 1. Derive the transfer function for the circuit in Figure 1(b) of the text. 2. Calculate the values of R1 and C1 so that the gyrator matches the RL filter in Figure 1(a) of the text. Use only components in the parts list given in Appendix A of the text. Modeling: 3. Simulate the RL circuit in Figure ...
... 1. Derive the transfer function for the circuit in Figure 1(b) of the text. 2. Calculate the values of R1 and C1 so that the gyrator matches the RL filter in Figure 1(a) of the text. Use only components in the parts list given in Appendix A of the text. Modeling: 3. Simulate the RL circuit in Figure ...
Series Circuits
... A LED only works in one direction. Make sure the longer wire or lead is towards the positive (red) side. Also, never directly connect and LED to a voltage source (battery) because it will burn out. ...
... A LED only works in one direction. Make sure the longer wire or lead is towards the positive (red) side. Also, never directly connect and LED to a voltage source (battery) because it will burn out. ...
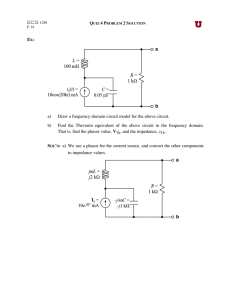
EX: a) Draw a frequency-domain circuit model for the above circuit. b
... Find the Thevenin equivalent of the above circuit in the frequency domain. That is, find the phasor value, VTh, and the impedance, zTh. ...
... Find the Thevenin equivalent of the above circuit in the frequency domain. That is, find the phasor value, VTh, and the impedance, zTh. ...
Variable Frequency Response I
... • The quality factor is the ratio of its resonant frequency to its bandwidth. • If the bandwidth is narrow, the quality factor of the resonant circuit must be high. • If the band of frequencies is wide, the quality factor must be low. ...
... • The quality factor is the ratio of its resonant frequency to its bandwidth. • If the bandwidth is narrow, the quality factor of the resonant circuit must be high. • If the band of frequencies is wide, the quality factor must be low. ...
Chapter 25 Powerpoint
... What is the voltage across the resistor? VR = 50A x 2Ω = 100V What is the voltage across the capacitor? VC = 50A x –j5Ω = 250-90˚V What is the voltage across the inductor? VL = 50A x j5Ω = 25090˚V Kirchoff’s Voltage Law still holds Although it seems like there is no VT = VR + VC + VL voltage left ...
... What is the voltage across the resistor? VR = 50A x 2Ω = 100V What is the voltage across the capacitor? VC = 50A x –j5Ω = 250-90˚V What is the voltage across the inductor? VL = 50A x j5Ω = 25090˚V Kirchoff’s Voltage Law still holds Although it seems like there is no VT = VR + VC + VL voltage left ...
sheet3
... minimum value of the feedback resistor and frequency of oscillation with Ri=15 kΩ, L1 = 10 μH, L2 = 270 μH, and C = 0.001μf? 6. A Hartley oscillator has Ri= 10 kΩ, C = 0.015 μf, L1 = 15 μH. Determine the value of L2 if the frequency of oscillation is to be 100 kHz. 7. Determine the operating frequen ...
... minimum value of the feedback resistor and frequency of oscillation with Ri=15 kΩ, L1 = 10 μH, L2 = 270 μH, and C = 0.001μf? 6. A Hartley oscillator has Ri= 10 kΩ, C = 0.015 μf, L1 = 15 μH. Determine the value of L2 if the frequency of oscillation is to be 100 kHz. 7. Determine the operating frequen ...
PowerPoint Sunusu
... circuit consisting of a resistor, an inductor, and a capacitor, connected in series or in parallel. • The RLC part of the name is due to those letters being the usual electrical symbols for resistance, inductance and capacitance respectively. • The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current and ...
... circuit consisting of a resistor, an inductor, and a capacitor, connected in series or in parallel. • The RLC part of the name is due to those letters being the usual electrical symbols for resistance, inductance and capacitance respectively. • The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current and ...
Parent Signature
... Circuit is what you call the path for electricity. If a circuit is broken and does not let current flow, it is called an open circuit. A series circuit only has one path. A parallel circuit has more than one path. A switch is a device that controls whether a circuit is open or closed. If the switch ...
... Circuit is what you call the path for electricity. If a circuit is broken and does not let current flow, it is called an open circuit. A series circuit only has one path. A parallel circuit has more than one path. A switch is a device that controls whether a circuit is open or closed. If the switch ...
Risistor
... A capacitor (originally known as a condenser) is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store electrical energy temporarily in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors (plates) separated by a dielectric (i.e. an ...
... A capacitor (originally known as a condenser) is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store electrical energy temporarily in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors (plates) separated by a dielectric (i.e. an ...
Powerpoint Slides
... When using AC circuits, inductors and capacitors have a delayed response to the changing voltage and current ...
... When using AC circuits, inductors and capacitors have a delayed response to the changing voltage and current ...
Series Circuits
... From our Breadboarding Experiment, we found that the total resistance of this circuit is 11.3 kΩ, which happens to be equal to the sum of all of the resistances in the series loop. ...
... From our Breadboarding Experiment, we found that the total resistance of this circuit is 11.3 kΩ, which happens to be equal to the sum of all of the resistances in the series loop. ...
energy discharge capacitors uctance sangamo electric - sonar-info
... and the dissipation factor of standord units ore measured on a Generai Radio 161 IA bridge or equivalent at a frequency of 60 cycles per second and referred to a temperature of 25°C. The voltage rating of each unit is the peak d-c voltage to which the capacitors ore to be chorged. The chorging ti me ...
... and the dissipation factor of standord units ore measured on a Generai Radio 161 IA bridge or equivalent at a frequency of 60 cycles per second and referred to a temperature of 25°C. The voltage rating of each unit is the peak d-c voltage to which the capacitors ore to be chorged. The chorging ti me ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.