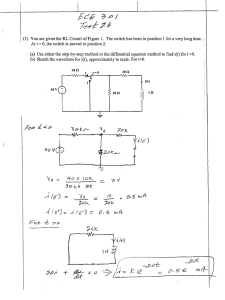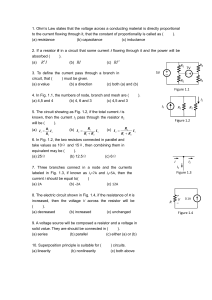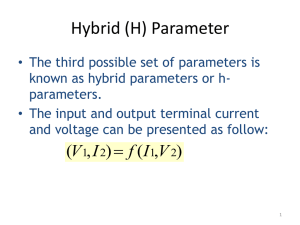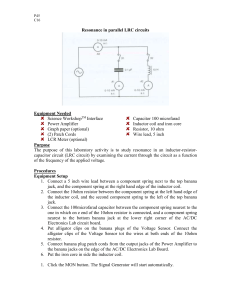
PHYSICS 100 CIRCUITS
... A circuit is a closed loop where current flows continuously from high voltage to low voltage. A battery or power supply is needed to supply the potential energy difference. For conductors, Ohm’s Law states that the voltage difference across a circuit element is proportional to the current that flows ...
... A circuit is a closed loop where current flows continuously from high voltage to low voltage. A battery or power supply is needed to supply the potential energy difference. For conductors, Ohm’s Law states that the voltage difference across a circuit element is proportional to the current that flows ...
Name - Seattle Central College
... In your write up you will show your circuits, describe your procedure and summarize how your most excellent data proves you correct. Please wordprocess all text integrating your circuit diagrams throughout. ...
... In your write up you will show your circuits, describe your procedure and summarize how your most excellent data proves you correct. Please wordprocess all text integrating your circuit diagrams throughout. ...
answer sheet
... Pick a frequency and add the magnitudes of the capacitor and resistor voltages. How does this compare to the generator voltage? This seems to contradict Kirchhoff's loop law. Why is this not the case? Questions ...
... Pick a frequency and add the magnitudes of the capacitor and resistor voltages. How does this compare to the generator voltage? This seems to contradict Kirchhoff's loop law. Why is this not the case? Questions ...
Electric Circuits
... Power Source-cells, photocell, thermocouple, generator Wire-Copper, aluminum Load-Energy consuming device;light bulb, motors, appliances ...
... Power Source-cells, photocell, thermocouple, generator Wire-Copper, aluminum Load-Energy consuming device;light bulb, motors, appliances ...
APPENDIX C: THE RLC CIRCUIT MODEL FOR A PIEZOELECTRIC
... the crystal is radiating. From these expressions, it is clear that a voltage drop across R1 would correspond to power radiated by the crystal. Before, leaving this section, it is important to point out that the circuit resonant frequency given by ω o′ = to the crystal resonant frequency given by ω e ...
... the crystal is radiating. From these expressions, it is clear that a voltage drop across R1 would correspond to power radiated by the crystal. Before, leaving this section, it is important to point out that the circuit resonant frequency given by ω o′ = to the crystal resonant frequency given by ω e ...
Chabot College Fall 2002 44 - Introduction to Circuit Analysis
... Upon completion of the course the student should be able to: ...
... Upon completion of the course the student should be able to: ...
EC6401-EC II -CAT2 SET2
... 1. What is the effect of cascading n stages of identical single tuned amplifiers (synchronously tuned) on the overall 3 dB bandwidth? 2. Define unloaded Q factor 3. A tuned amplifier has its maximum gain at a frequency of 2 MHz and has a bandwidth of 50 kHz. Calculate the Q- factor. 4. What are the ...
... 1. What is the effect of cascading n stages of identical single tuned amplifiers (synchronously tuned) on the overall 3 dB bandwidth? 2. Define unloaded Q factor 3. A tuned amplifier has its maximum gain at a frequency of 2 MHz and has a bandwidth of 50 kHz. Calculate the Q- factor. 4. What are the ...
AC Circuits - WordPress.com
... • In a series branch – Impedance of inductor may equal the capacitor. – Impedances would cancel leaving impedance of resistor as the only impedance. – Such condition is referred to as resonance ...
... • In a series branch – Impedance of inductor may equal the capacitor. – Impedances would cancel leaving impedance of resistor as the only impedance. – Such condition is referred to as resonance ...
EGM 180 Take Home Quiz 1
... discussion of an ammeter’s impact on a circuit. Note that an ideal voltmeter has infinite resistance and an ideal ammeter has zero resistance. With that in mind, explain how attempting to measure current by placing an ammeter in parallel with the circuit (as opposed to in series in the circuit) coul ...
... discussion of an ammeter’s impact on a circuit. Note that an ideal voltmeter has infinite resistance and an ideal ammeter has zero resistance. With that in mind, explain how attempting to measure current by placing an ammeter in parallel with the circuit (as opposed to in series in the circuit) coul ...
AC Circuits Tip Sheet - faculty at Chemeketa
... inductors is zero. Average power for a single power supply is the sum of the powers of all the other circuit elements. Notation AC currents and potential differences can be reported as maximum, rms, or instantaneous. Equations for AC circuits typically use rms values, though maximum values can also ...
... inductors is zero. Average power for a single power supply is the sum of the powers of all the other circuit elements. Notation AC currents and potential differences can be reported as maximum, rms, or instantaneous. Equations for AC circuits typically use rms values, though maximum values can also ...
I 1 I 2 I 3 I 4 I V 1 V 2 V 3 V 4 V 5 V 6
... PROCEDURE: In order to understand the circuit you need to reduce the complex circuit to equivalent circuits until you can analyze the voltage and current components. The first steps consist of reducing each resistor set to one equivalent resistor so you can find the total current in the circuit. Whe ...
... PROCEDURE: In order to understand the circuit you need to reduce the complex circuit to equivalent circuits until you can analyze the voltage and current components. The first steps consist of reducing each resistor set to one equivalent resistor so you can find the total current in the circuit. Whe ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.