* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Inverse Transmission Parameter
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Power dividers and directional couplers wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Topology (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Valve audio amplifier technical specification wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Negative-feedback amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
Wilson current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
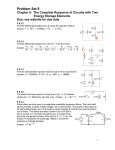
Hybrid (H) Parameter • The third possible set of parameters is known as hybrid parameters or hparameters. • The input and output terminal current and voltage can be presented as follow: (V 1, I 2) f (I1,V 2) 1 V1 h 11 I h 2 21 h12 I1 h22 V2 V1 = h11I1 + h12V2 I2 = h21I1 + h22V2 Where h= h 11 h 21 h12 h22 These parameters are very useful in analyzing the transistor compare to the z-parameters and y-parameters. 2 Case –I Assuming the output of the two port to be short circuit, V2 =0 short circuit input impedance short circuit forward current gain 3 Case –II Assuming the input of the same two port to be open circuit, II =0 open circuit reverse voltage gain open circuit output admittance 4 Circuit based on π network 5 Circuit based on T network 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 INTERCONNECTION OF TWO-PORT NETWORKS Three ways that two ports are interconnected: Y parameters ya * Parallel y ya yb Z parameters z za za * Series yb zb zb ABCD parameters * Cascade Ta Tb T Ta Tb 15 Interconnections permit the description of complex systems in terms of simpler components or subsystems The basic interconnections to be considered are: parallel, series and cascade PARALLEL: Voltages are the same. Current of interconnection is the sum of currents SERIES: Currents are the same. Voltage of interconnection is the sum of voltages CASCADE: Output of first subsystem acts as input for the second 16 Find the equivalent y-parameters for the bridge T-network 17 the z-parameters of network N2 are 18 We can convert the z-parameters to y-parameters 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31