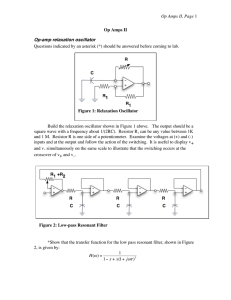
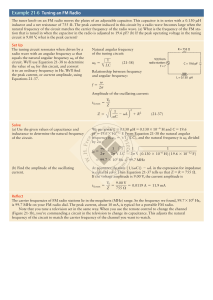
8.5.1 worksheet - Digilent Learn site
... 2. Attach, to this worksheet, plots of the input step function you applied to the circuit and the resulting circuit step response. Annotate your plot to indicate the rise time, overshoot, and oscillation frequency. Provide the rise time, overshoot, and oscillation frequency in the space below. (9 pt ...
... 2. Attach, to this worksheet, plots of the input step function you applied to the circuit and the resulting circuit step response. Annotate your plot to indicate the rise time, overshoot, and oscillation frequency. Provide the rise time, overshoot, and oscillation frequency in the space below. (9 pt ...
Chapter 33 - University of Utah Physics
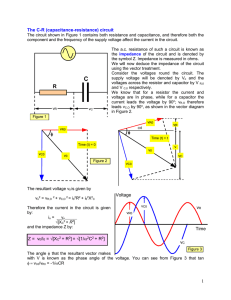
... The sign of f can be positive or negative, depending on whether X L is greater or less than X C . The phase angle is zero when X L 5 X C . ...
... The sign of f can be positive or negative, depending on whether X L is greater or less than X C . The phase angle is zero when X L 5 X C . ...
Circuits with more than one resistor, then Watt happens?
... Circuits with more than one resistor, then Watt happens? Series and Parallel are the 2 ways of connecting multiple resistors ...
... Circuits with more than one resistor, then Watt happens? Series and Parallel are the 2 ways of connecting multiple resistors ...
Electric Potential - McMaster Physics and Astronomy
... provides the fastest dissipation of energy. ...
... provides the fastest dissipation of energy. ...
Lecture 11 AC Circuits Frequency Response
... • The quality factor is the ratio of its resonant frequency to its bandwidth. • If the bandwidth is narrow, the quality factor of the resonant circuit must be high. • If the band of frequencies is wide, the quality factor must be low. ...
... • The quality factor is the ratio of its resonant frequency to its bandwidth. • If the bandwidth is narrow, the quality factor of the resonant circuit must be high. • If the band of frequencies is wide, the quality factor must be low. ...
Chapter 2. Active Filter Design
... 5. A piece of communication equipment has two stages of amplification with gains of 40 and 60 and two loss stages with attenuation factor of 0.03 and 0.075. The output voltage is 2.2 V. What are the overall gain (or attenuation) and the input voltage? 21. What circuit Q is required to give a bandwid ...
... 5. A piece of communication equipment has two stages of amplification with gains of 40 and 60 and two loss stages with attenuation factor of 0.03 and 0.075. The output voltage is 2.2 V. What are the overall gain (or attenuation) and the input voltage? 21. What circuit Q is required to give a bandwid ...
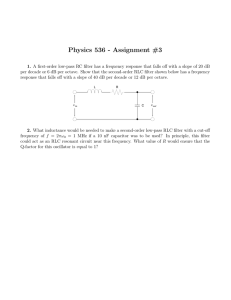
Physics 536 - Assignment #3
... per decade or 6 dB per octave. Show that the second-order RLC filter shown below has a frequency response that falls off with a slope of 40 dB per decade or 12 dB per octave. L ...
... per decade or 6 dB per octave. Show that the second-order RLC filter shown below has a frequency response that falls off with a slope of 40 dB per decade or 12 dB per octave. L ...
Document
... impedances, voltage/ current divider, KVL,KCL,Mesh, Thevenin etc.) Impedances combine like restances in a DC circuit. – Find the real part of the solution, and write it as a function of time. ...
... impedances, voltage/ current divider, KVL,KCL,Mesh, Thevenin etc.) Impedances combine like restances in a DC circuit. – Find the real part of the solution, and write it as a function of time. ...
Physics 4700 Experiment 2 R-L-C Circuits
... Measure the frequency response of the circuit built in part 2) to a sine wave. Measure VR, VC and VL as the frequency is varied from 10 Hz to 100 kHz. Measure the phase relationship between R and the voltage source. Measure the Q of the circuit using the half power points and the resonant frequency ...
... Measure the frequency response of the circuit built in part 2) to a sine wave. Measure VR, VC and VL as the frequency is varied from 10 Hz to 100 kHz. Measure the phase relationship between R and the voltage source. Measure the Q of the circuit using the half power points and the resonant frequency ...
Fluid flow analogy
... 7-2 The natural response of an RC circuit • An RC circuit is analogous to an RL circuit • The switch has been in the position for a long time such that all the elements in the circuit reach a steady-state condition . • A source voltage exists between the terminals. • Circuit after switching is show ...
... 7-2 The natural response of an RC circuit • An RC circuit is analogous to an RL circuit • The switch has been in the position for a long time such that all the elements in the circuit reach a steady-state condition . • A source voltage exists between the terminals. • Circuit after switching is show ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.