Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Circuits and Electronics Name:__________________________________
... (d) It is observeed that the peeak short-cirrcuit current for the inveerter is 150µA A. If the ...
... (d) It is observeed that the peeak short-cirrcuit current for the inveerter is 150µA A. If the ...
The following step-by-step procedure may be used to solve RC or
... vii) For t→∞, assume the circuit has been stable for a long time, as in (iii), and replace C's with open circuits and L's with wires. Find vC (t → ∞) or iL (t → ∞) . ...
... vii) For t→∞, assume the circuit has been stable for a long time, as in (iii), and replace C's with open circuits and L's with wires. Find vC (t → ∞) or iL (t → ∞) . ...
Analyzing Circuits
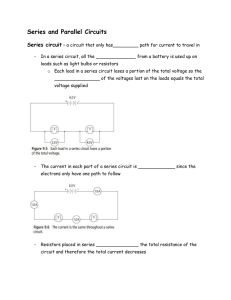
... The sum of the potential drops across each component in a series circuit will be equal to the total potential supplied by the source ...
... The sum of the potential drops across each component in a series circuit will be equal to the total potential supplied by the source ...
Chapter 20, Section 3 - Sts. Peter And Paul Elementary School
... If one bulb burns out in a parallel circuit, the current can still move through the other branches. Switches can be replaced along the branch without affecting the others. Additional branches will decrease resistance. Electric current has more paths to follow so the total resistance is decrease ...
... If one bulb burns out in a parallel circuit, the current can still move through the other branches. Switches can be replaced along the branch without affecting the others. Additional branches will decrease resistance. Electric current has more paths to follow so the total resistance is decrease ...
RF Measurement and Control - Colorado State University
... considerations and external field interruptions cause us to operate elsewhere on the curves. This causes loss and unnecessary heat. Reduce the size of the circuit to achieve benefits of a portable device. ...
... considerations and external field interruptions cause us to operate elsewhere on the curves. This causes loss and unnecessary heat. Reduce the size of the circuit to achieve benefits of a portable device. ...
Analysis Methods for Transient Circuits
... Analysis Methods for Transient Circuits Dr. Holbert March 17, 2008 ...
... Analysis Methods for Transient Circuits Dr. Holbert March 17, 2008 ...
RLC circuits
... At time t = 0–, assume the circuit has been stable for a long time, causing derivative values to become zero: dvC (t) di (t) = 0 and L = 0 dt dt This means that iC (t = 0- ) = 0 A and v L (t = 0- ) = 0 V , which in turn means that a C looks like an open circuit and an L looks like a wire. Thus, the ...
... At time t = 0–, assume the circuit has been stable for a long time, causing derivative values to become zero: dvC (t) di (t) = 0 and L = 0 dt dt This means that iC (t = 0- ) = 0 A and v L (t = 0- ) = 0 V , which in turn means that a C looks like an open circuit and an L looks like a wire. Thus, the ...
SERIES AND PARALLEL RESISTANCE CIRCUIT
... complex circuits. In this post I will explain the most important ideas in DC circuits. ...
... complex circuits. In this post I will explain the most important ideas in DC circuits. ...
PHY124 Course Spring 2016
... Safety issue – transient duration (protect user, protect component) I-2-Two new dipoles : C and L I-3- RLC series I-4- Energy conservation (stored vs lost electrical energy) II Transient regime II-1 RL circuit + characteristic time II-2 RLC circuit aperiodic, quasiperiodic, critical solutions (remin ...
... Safety issue – transient duration (protect user, protect component) I-2-Two new dipoles : C and L I-3- RLC series I-4- Energy conservation (stored vs lost electrical energy) II Transient regime II-1 RL circuit + characteristic time II-2 RLC circuit aperiodic, quasiperiodic, critical solutions (remin ...
ac-circuits-test-16
... 9. When an alternating voltage of 200 V - 50 Hz is applied across a device X, a current of 2 A flows through the circuit and is in phase with the applied voltage. When the same voltage is applied across another device Y, the same current flows through the circuit but it leads the applied voltage by ...
... 9. When an alternating voltage of 200 V - 50 Hz is applied across a device X, a current of 2 A flows through the circuit and is in phase with the applied voltage. When the same voltage is applied across another device Y, the same current flows through the circuit but it leads the applied voltage by ...
Here we have five circuit connections, and we want to... for some reason.
... Here we have five circuit connections, and we want to determine which might be invalid, for some reason. For the first circuit, 1 A is sent through a resistor. This is fine. The second circuit has two different currents joining at the top node to form a current of 3 A, which flows through the resist ...
... Here we have five circuit connections, and we want to determine which might be invalid, for some reason. For the first circuit, 1 A is sent through a resistor. This is fine. The second circuit has two different currents joining at the top node to form a current of 3 A, which flows through the resist ...
Problem Set 11
... does not accelerate all things the same—it is easier to push a lightweight bicycle than a heavy car, for example. Likewise, electromagnetic waves kick lightweight electrons a lot, whereas heavy ionized atoms are hardly disturbed. If all of the negatively charged electrons in the plasma are displaced ...
... does not accelerate all things the same—it is easier to push a lightweight bicycle than a heavy car, for example. Likewise, electromagnetic waves kick lightweight electrons a lot, whereas heavy ionized atoms are hardly disturbed. If all of the negatively charged electrons in the plasma are displaced ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.