* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AC Circuits - WordPress.com
Superheterodyne receiver wikipedia , lookup
Phase-locked loop wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Mechanical filter wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Distributed element filter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Crystal radio wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Standing wave ratio wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Antenna tuner wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Impedance matching wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
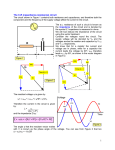
USE OF ICT IN EDUCATION FOR ONLINE AND BLENDED LEARNING-IIT BOMBAY BIRLA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MESRA, RANCHI ASSIGNMENT( MODULE AC SERIES CIRCUIT) Submitted by: Dr. Deepak Kumar(Group Leader) Dr. Vikash Kumar Gupta 1 AC Circuits • Rules and laws developed for dc circuits apply equally well for ac circuits. • Analysis of ac circuits requires vector algebra and use of complex numbers. •Voltages and currents in phasor form. •Expressed as RMS (or effective) values. Fig 3.1 Example of AC circuit Phasor Diagram of Resistor • Voltage and current of a resistor will be in phase • Impedance of a resistor is: ZR = R0° I V I R0 Figure 3.2 Phasor diagram of resistance 3 Phasor Diagram of Inductor • Current through an inductor lags the voltage by 90° XL j L Z L X L 90 I V X L 90 I I 90 Fig 3.3 Phasor Diagram of Inductor 4 Phasor Diagram of Capcitor • Current through a capacitor leads the voltage by 90° 1 XC jC Z C X C 90 V I X C 90 I I 90 Fig 3.4 Phasor Diagram of Capacitor Frequency Effects on Capacitive Reactance • Impedance of a capacitor decreases as the frequency increases. • For dc (f = 0 Hz), impedance of the capacitor is infinite Fig 3.5 Variation of capacitive reactance with frequency • For a series RC circuit, total impedance approaches R as the frequency increases 6 Frequency Effects on Inductive Reactance • Impedance of an inductor increases as frequency increases. • At dc (f = 0 Hz), inductor looks like a short. At high frequencies, it looks like an open. Fig 3.6 Variation of inductive reactance with the variation of frequency AC Series Circuit • Impedance vectors will appear in either the first or the fourth quadrants because the resistance vector is always positive. • When impedance vector appears in first quadrant, the circuit is inductive. • If impedance vector appears in fourth quadrant, the circuit is capacitive AC Series Circuit • Current everywhere in a series circuit is the same. • Impedance used to collectively determine how resistance, capacitance, and inductance impede current in a circuit. Z R jX X XL XC XL j L XC 1 jC Where L and C are inductance and capacitance of the circuit elements AC Series Circuit • Total impedance in a circuit is found by adding all individual impedances vectorially. • Zeq Z1 Z 2 Z 3 ........Zn Voltage Divider Rule • Voltage divider rule works the same as with dc circuits. • From Ohm’s law: I x IT Vx VT Zx ZT Vx Zx VT ZT Kirchhoff’s Law • KVL is same as in dc circuits. • Kirchoff’s Voltage Law: Phasor sum of voltage drops and rises around a closed loop is equal to zero. • Voltages may be added in phasor form or in rectangular form. VA VB VC 0 Fig 3.7 Kirchhoff’s Voltage law in AC circuit Kirchhoff’s Law • KCL is same as in dc circuits. • Kirchhoff’s Current Law : Summation of current phasors entering and leaving a node is equal to zero. • Currents must be added vectorially-currents entering are positive, and currents leaving are negative Fig 3.8 Kirchhoff’s Current Law in Ac Ccircuit Remarks • In a series RL circuit, impedance increases from R to a larger value • In a parallel RL circuit, impedance increases from a small value to R Corner Frequency • Corner frequency is a break point on the frequency response graph. • For a capacitive circuit C = 1/RC = 1/ • For an inductive circuit C = R/L = 1/ Series Resonance • In a circuit with R, L, and C components combined in seriesparallel combinations, impedance may rise or fall across a range of frequencies. • In a series branch – Impedance of inductor may equal the capacitor. – Impedances would cancel leaving impedance of resistor as the only impedance. – Such condition is referred to as resonance Series resonance Fig 3.9 Resonating frequency in AC series circuit. • Expression for Resonating Frequency Thank You 18