Electric Circuits Prentice Hall
... 1. Changing the voltage in a circuit changes the current, but will not change the resistance C. Calculating Ohm’s Law 1. puts the relationship between current, voltage, and resistance into numbers 2. resistance is equal to the voltage divided by the current resistance = voltage current 3. another wa ...
... 1. Changing the voltage in a circuit changes the current, but will not change the resistance C. Calculating Ohm’s Law 1. puts the relationship between current, voltage, and resistance into numbers 2. resistance is equal to the voltage divided by the current resistance = voltage current 3. another wa ...
University of North Carolina-Charlotte Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
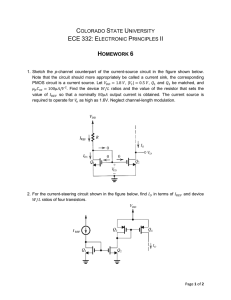
... Due: Thursday September 26, 2013 Please show all work throughout. You will lose credit if you do not. Problem 1: Basic op-amp circuit analysis You are given the following circuit: ...
... Due: Thursday September 26, 2013 Please show all work throughout. You will lose credit if you do not. Problem 1: Basic op-amp circuit analysis You are given the following circuit: ...
Science Journals 4-18 to 5-5
... What remains constant and what changes in a series circuit? In a parallel circuit? ...
... What remains constant and what changes in a series circuit? In a parallel circuit? ...
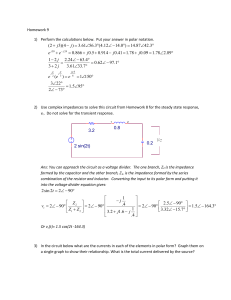
1. For the following circuit, assume the values of the resistor R is 1
... 1. For the following circuit, assume the values of the resistor R is 1 kQ, the value of the inductor L is 1 rnH, and the value of the capacitor C is 0.5 nF. The current source i,N(t)= 2xsin(lo6xt) mA and the initial voltage of the capacitor is -4 V, i.e., v,(O) = 4 v. (a). Please find the steady-sta ...
... 1. For the following circuit, assume the values of the resistor R is 1 kQ, the value of the inductor L is 1 rnH, and the value of the capacitor C is 0.5 nF. The current source i,N(t)= 2xsin(lo6xt) mA and the initial voltage of the capacitor is -4 V, i.e., v,(O) = 4 v. (a). Please find the steady-sta ...
Lab 7
... – First, a series resistor is inserted before the negative input terminal of op amp. The effect of this resistor is to act as an attenuator for the high frequency components. – Second, a capacitor is placed in the feedback network. This capacitor provides more feed-back for the high frequency compon ...
... – First, a series resistor is inserted before the negative input terminal of op amp. The effect of this resistor is to act as an attenuator for the high frequency components. – Second, a capacitor is placed in the feedback network. This capacitor provides more feed-back for the high frequency compon ...
Differentiator
... – First, a series resistor is inserted before the negative input terminal of op amp. The effect of this resistor is to act as an attenuator for the high frequency components. – Second, a capacitor is placed in the feedback network. This capacitor provides more feed-back for the high frequency compon ...
... – First, a series resistor is inserted before the negative input terminal of op amp. The effect of this resistor is to act as an attenuator for the high frequency components. – Second, a capacitor is placed in the feedback network. This capacitor provides more feed-back for the high frequency compon ...
Datasheet - CREATIVE CHIPS GmbH
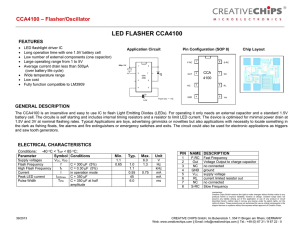
... The CCA4100 is an insensitive and easy to use IC to flash Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs). For operating it only needs an external capacitor and a standard 1.5V battery cell. The circuite is self starting and includes internal timing resistors and a resistor to limit LED current. The device is optimise ...
... The CCA4100 is an insensitive and easy to use IC to flash Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs). For operating it only needs an external capacitor and a standard 1.5V battery cell. The circuite is self starting and includes internal timing resistors and a resistor to limit LED current. The device is optimise ...
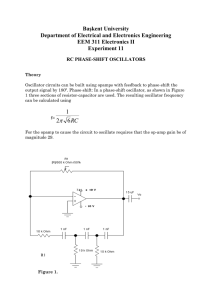
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.