Resonance
... The frequencies corresponding to 0.707 of the maximum current are called the band frequencies, cutoff frequencies, or half-power frequencies (ƒ1, ƒ2). Half-power frequencies are those frequencies at which the power delivered is onehalf that delivered at resonant frequency. The range of frequen ...
... The frequencies corresponding to 0.707 of the maximum current are called the band frequencies, cutoff frequencies, or half-power frequencies (ƒ1, ƒ2). Half-power frequencies are those frequencies at which the power delivered is onehalf that delivered at resonant frequency. The range of frequen ...
Series and Parallel Circuits
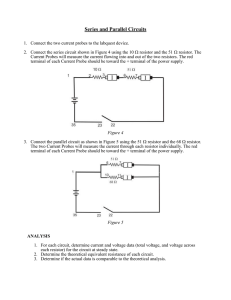
... Current Probes will measure the current flowing into and out of the two resistors. The red terminal of each Current Probe should be toward the + terminal of the power supply. ...
... Current Probes will measure the current flowing into and out of the two resistors. The red terminal of each Current Probe should be toward the + terminal of the power supply. ...
Series and Parallel - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... • Series circuits are used when there is a need for a lot of power to operate an electric device. • An example would be a portable stereo which contains a number of batteries in series. ...
... • Series circuits are used when there is a need for a lot of power to operate an electric device. • An example would be a portable stereo which contains a number of batteries in series. ...
Lecture Notes 2 File
... • The first step is to convert a time domain circuit to frequency domain by calculating the impedances of the circuit elements at the operating frequency. • Note that AC sources appear as DC sources with their values expressed as their ...
... • The first step is to convert a time domain circuit to frequency domain by calculating the impedances of the circuit elements at the operating frequency. • Note that AC sources appear as DC sources with their values expressed as their ...
PhET Circuit Construction Kit
... https://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/legacy/circuit-construction-kit-ac or google phet circuit construction kit ac and dc push play on the phet, then push play in the pop up it should open in java 1. Build a circuit using wires, a battery, and a light bulb **Draw your circuit on the front of your ...
... https://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/legacy/circuit-construction-kit-ac or google phet circuit construction kit ac and dc push play on the phet, then push play in the pop up it should open in java 1. Build a circuit using wires, a battery, and a light bulb **Draw your circuit on the front of your ...
Ch10_PPT_Fund_Elec_Circ_5e
... • The first step is to convert a time domain circuit to frequency domain by calculating the impedances of the circuit elements at the operating frequency. • Note that AC sources appear as DC sources with their values expressed as their ...
... • The first step is to convert a time domain circuit to frequency domain by calculating the impedances of the circuit elements at the operating frequency. • Note that AC sources appear as DC sources with their values expressed as their ...
ECE1250 Practice Quiz (node,series,parallel)
... “R11 is in parallel with the series combination of R14andR15 in parallel and R12andR13 in parallel.” (Ok, at about this point in the conference call, you better send a circuit diagram….the spoken description gets confusing quickly.) Circuit 3: R7-R10, R8-R9, R6|| (R7-R10) || (R8-R9) || short circuit ...
... “R11 is in parallel with the series combination of R14andR15 in parallel and R12andR13 in parallel.” (Ok, at about this point in the conference call, you better send a circuit diagram….the spoken description gets confusing quickly.) Circuit 3: R7-R10, R8-R9, R6|| (R7-R10) || (R8-R9) || short circuit ...
Op Amps II
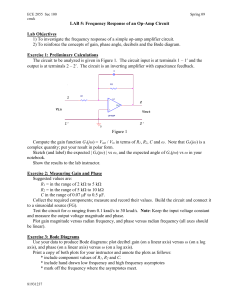
... versus ωτ for four different values of x. It can be shown (you do not have to do this) that ...
... versus ωτ for four different values of x. It can be shown (you do not have to do this) that ...
Parallel circuits
... your lab today, you took data about lights in a series and in parallel. What did your data imply about how much voltage series lights get as you add more lights? ...
... your lab today, you took data about lights in a series and in parallel. What did your data imply about how much voltage series lights get as you add more lights? ...
R07 Set No. 2
... NETWORK ANALYSIS Common to BME, E.COMP.E, ETM, E.CONT.E, EIE, ECE Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks ...
... NETWORK ANALYSIS Common to BME, E.COMP.E, ETM, E.CONT.E, EIE, ECE Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks ...
Em05: Series-Resonant LCR Circuit
... resistances. I also aimed to find the resonant frequency, which should’ve been the same at all resistances. I also compared the value of the resonant frequency to that of a calculated theoretical value in order to view the error involved in the calculation. I used the various values obtained from th ...
... resistances. I also aimed to find the resonant frequency, which should’ve been the same at all resistances. I also compared the value of the resonant frequency to that of a calculated theoretical value in order to view the error involved in the calculation. I used the various values obtained from th ...
ω 2 - UniMAP Portal
... It is to be a high-Q circuit when its quality factor is equal or greater than 10. For a high-Q circuit (Q 10), the half-power frequencies are, for all practical purposes, symmetrical around the resonant frequency and can be approximated as ...
... It is to be a high-Q circuit when its quality factor is equal or greater than 10. For a high-Q circuit (Q 10), the half-power frequencies are, for all practical purposes, symmetrical around the resonant frequency and can be approximated as ...
1422-1 Resonance and Filters - Cleveland Institute of Electronics
... Theoretically, the ratio is 45:1, but in practice; when circuit conditions are taken into account, this ratio may be as low as 5:1. The ratio can be reduced even further, the larger the internal resistance of the conductor. ...
... Theoretically, the ratio is 45:1, but in practice; when circuit conditions are taken into account, this ratio may be as low as 5:1. The ratio can be reduced even further, the larger the internal resistance of the conductor. ...
Standard Operating Procedure Title:_SOP-017 Multi
... Electrical Shock The multi meter can test circuits with high voltages. There is a risk of electrical shock when using the multi meter on these circuits. If body comes into contact with test leads while testing on circuit, shock may occur. This could cause injury. ...
... Electrical Shock The multi meter can test circuits with high voltages. There is a risk of electrical shock when using the multi meter on these circuits. If body comes into contact with test leads while testing on circuit, shock may occur. This could cause injury. ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.