* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Schematic Symbols - CTE-Auto
Crystal radio wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
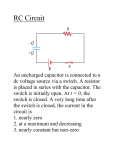
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
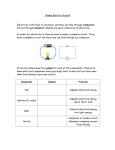
Schematic Symbols The Key to Understanding Wiring Diagrams Battery Supplies a Direct Current (DC) source Resistor Resistors impede the flow of electricity SPST Switch Opens (off) or closes (on) an electrical circuit Light Bulb Converts electricity into light Fuse Only allows a predetermined amount of current (AMPS) to pass through and if that amount is exceeded it will melt in half (open) Capacitor Blocks Direct Current (DC) flow, but allows Alternating Current (AC) to pass through Diode/Rectifier Allows current to flow through only one direction Transistor A solid-state electronic device that is used to control the flow of electricity in electronic equipment and usually consists of a small block of a semiconductor (as germanium) with at least three electrodes Motor Converts electrical energy into motion Electric Fuel Pump FP A motor driven pump, which supplies fuel to the engine Chassis Ground Connects the circuit to the metal body or frame of the vehicle using the body as a conductor in the circuit Ground Connects the circuit to the metal body or frame of the vehicle using the body as a conductor in the circuit (More commonly used than chassis ground) Relay An electromagnetically controlled switch Electromagnet Becomes magnetic when Direct Current (DC) is passed through it Light Emitting Diode A one-way check valve for electricity that lights up when current is passing through Variable Resistor The resistance to the flow of electricity can be adjusted Variable Capacitor A variable capacitor is a capacitor whose capacitance may be intentionally and repeatedly changed mechanically or electronically. Variable capacitors are often used in L/C circuits (tuners) to set the resonance frequency, e.g. to tune a radio (therefore they are sometimes called tuning capacitors) Transformer/Coil The secondary induced voltage VS is scaled from the primary VP by a factor ideally equal to the ratio of the number of turns of wire in their respective windings: By appropriate selection of the numbers of turns (N), a transformer thus allows an alternating voltage to be stepped up — by making NS more than NP — or stepped down, by making it less. Rotary Switch Multi-position switch like the one used in the DVOM! Horn/Speaker Converts electrical energy into sound