series circuits
... What have we learned today? • In a series circuit, the current is the same at all points. • Is = I1 = I2… • In a series circuit, the sum of all the voltages is the same as the supply. • V s = V1 + V2… ...
... What have we learned today? • In a series circuit, the current is the same at all points. • Is = I1 = I2… • In a series circuit, the sum of all the voltages is the same as the supply. • V s = V1 + V2… ...
OHM’S LAW
... R = V/I = 120V / 0.75Amp R= 160Ω b) What is the power of the bulb? P=VI = 120V(0.75Amp) P = 90 Watts ...
... R = V/I = 120V / 0.75Amp R= 160Ω b) What is the power of the bulb? P=VI = 120V(0.75Amp) P = 90 Watts ...
Ch14_PPT_Fund_Elec_Circ_5e (1)
... Resonance • The most prominent feature of the frequency response of a circuit may be the sharp peak in the amplitude characteristics. • Resonance occurs in any system that has a complex conjugate pair of poles. • It enables energy storage in the firm of ...
... Resonance • The most prominent feature of the frequency response of a circuit may be the sharp peak in the amplitude characteristics. • Resonance occurs in any system that has a complex conjugate pair of poles. • It enables energy storage in the firm of ...
Questions on Electricity
... 20kJ of energy. The charges that passed were 250C. What is the voltage of the motor? ...
... 20kJ of energy. The charges that passed were 250C. What is the voltage of the motor? ...
Lab 3
... Lab 3 – An LC tank circuit Consider an underdamped RLC circuit if R 0. The natural response will be an oscillation at 0 = 1 with no damping - an undamped natural response. The circuit in Figure 1 (a) consisting of LC an inductor and a capacitor only is called an LC tank. It has a very strong resp ...
... Lab 3 – An LC tank circuit Consider an underdamped RLC circuit if R 0. The natural response will be an oscillation at 0 = 1 with no damping - an undamped natural response. The circuit in Figure 1 (a) consisting of LC an inductor and a capacitor only is called an LC tank. It has a very strong resp ...
Chapter 4 : Resonance Circuit
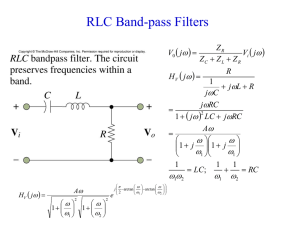
... Half-power Frequency Half-power frequencies is the frequency when the magnitude of the output voltage or current is decrease by the factor of 1 / 2 from its maximum value. Also known as cutoff frequencies. ...
... Half-power Frequency Half-power frequencies is the frequency when the magnitude of the output voltage or current is decrease by the factor of 1 / 2 from its maximum value. Also known as cutoff frequencies. ...
Circuits - Physics-project-12-06
... To start off, Simple circuits:- is a closed loop of conducter through which charges can flow. I.E: ...
... To start off, Simple circuits:- is a closed loop of conducter through which charges can flow. I.E: ...
Dual Supply From Single Battery SourCe
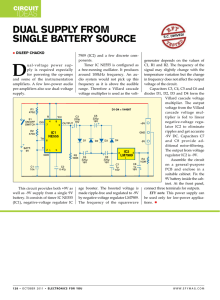
... voltage of the circuit. Capacitors C3, C4, C5 and C6 and diodes D1, D2, D3 and D4 form the Villard cascade voltage multiplier. The output voltage from the Villard cascade voltage multiplier is fed to linear negative-voltage regulator IC2 to eliminate ripples and get accurate -9V DC. Capacitors C7 an ...
... voltage of the circuit. Capacitors C3, C4, C5 and C6 and diodes D1, D2, D3 and D4 form the Villard cascade voltage multiplier. The output voltage from the Villard cascade voltage multiplier is fed to linear negative-voltage regulator IC2 to eliminate ripples and get accurate -9V DC. Capacitors C7 an ...
EC6401-EC II -model exam
... 3. What are the advantages and disadvantages of RC phase shift oscillators? 4. Crystal oscillators possess high degree of frequency stability – justify 5. Define ‘Q’ of tank circuit. 6. A tuned amplifier has its maximum gain at a frequency of 2 MHz and has a bandwidth of 50 kHz. Calculate the Q-fact ...
... 3. What are the advantages and disadvantages of RC phase shift oscillators? 4. Crystal oscillators possess high degree of frequency stability – justify 5. Define ‘Q’ of tank circuit. 6. A tuned amplifier has its maximum gain at a frequency of 2 MHz and has a bandwidth of 50 kHz. Calculate the Q-fact ...
Circuit Circuit means closed path
... • 1. source of potential difference (battery or power source) • 2. resistor (appliance) • 3. connecting wires ...
... • 1. source of potential difference (battery or power source) • 2. resistor (appliance) • 3. connecting wires ...
Document
... circuit with 100 ohms of resistance. – How much current flows through this circuit? ...
... circuit with 100 ohms of resistance. – How much current flows through this circuit? ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.