ECE 103: DC Circuit Analysis Concepts: IN
... - Can use node and mesh analysis, source transformation and linearity to determine node voltage and loop currents - Can find Thevenin and Norton Equivalent ...
... - Can use node and mesh analysis, source transformation and linearity to determine node voltage and loop currents - Can find Thevenin and Norton Equivalent ...
Homework 5
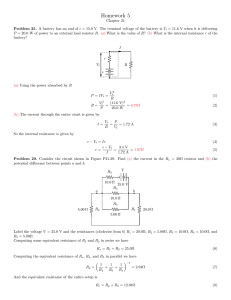
... Problem 25. A battery has an emf of ε = 15.0 V. THe terminal voltage of the battery is Vt = 11.6 V when it is delivering P = 20.0 W of power to an external load resistor R. (a) What is the value of R? (b) What is the internal resistance r of the battery? (a) Using the power absorbed by R ...
... Problem 25. A battery has an emf of ε = 15.0 V. THe terminal voltage of the battery is Vt = 11.6 V when it is delivering P = 20.0 W of power to an external load resistor R. (a) What is the value of R? (b) What is the internal resistance r of the battery? (a) Using the power absorbed by R ...
603 A DIGITAL PROGRAMMABLE ROBOT
... MOTORS RUN WELL ONLY WHEN GEARS ARE TURINING AT A CERTAIN SPEED. A PROPER COMBINATION OF THE RIGHT KINDS OF GEARS IS A MUST TO CONTROL THE SPEED AND PRODUCE THE REQUIRED TORQUE. ...
... MOTORS RUN WELL ONLY WHEN GEARS ARE TURINING AT A CERTAIN SPEED. A PROPER COMBINATION OF THE RIGHT KINDS OF GEARS IS A MUST TO CONTROL THE SPEED AND PRODUCE THE REQUIRED TORQUE. ...
Homework 5
... Label the voltage V = 25.0 V and the resistances (clockwise from b) R1 = 20.0Ω, R2 = 5.00Ω, R3 = 10.0Ω, R4 = 10.0Ω, and R5 = 5.00Ω. Computing some equivalent resistance of R1 and R2 in series we have Rs = R1 + R2 = 25.0Ω Computing the equivalent resistance of Rs , R4 , and R5 in parallel we have ...
... Label the voltage V = 25.0 V and the resistances (clockwise from b) R1 = 20.0Ω, R2 = 5.00Ω, R3 = 10.0Ω, R4 = 10.0Ω, and R5 = 5.00Ω. Computing some equivalent resistance of R1 and R2 in series we have Rs = R1 + R2 = 25.0Ω Computing the equivalent resistance of Rs , R4 , and R5 in parallel we have ...
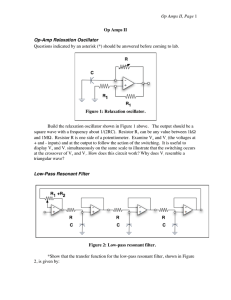
... The concepts investigated in this experiment are reactance, impedance, and resonance circuits. Many features of the scope will be used: including dual traces; differential inputs; and external triggering. Since this is the first experiment in which you have used the oscilloscope so a little extra ca ...
precision microfluidic oscillators for on
... 1.A precision pneumatic oscillator which provides timing signals for integrated microfluidic digital logic circuits 2.The design is based on the classical ring oscillator circuit and requires only a vacuum supply for power 3.Integrate pneumatic and fluidic circuits to create an autonomously driven p ...
... 1.A precision pneumatic oscillator which provides timing signals for integrated microfluidic digital logic circuits 2.The design is based on the classical ring oscillator circuit and requires only a vacuum supply for power 3.Integrate pneumatic and fluidic circuits to create an autonomously driven p ...
Word - IPFW.edu
... current, impedance, frequency and waveform measurements. Frequency and transient response. Elements of circuit modeling and design. ...
... current, impedance, frequency and waveform measurements. Frequency and transient response. Elements of circuit modeling and design. ...
... since I VR R . Since I is maximized, the magnitude of both VC and VL are individually at maximum, although 180o out of phase with each other. When the frequency is not near the resonant frequency, the phasors representing VC, and VL do not cancel, so VR is less for a given Vs. It is convenient to ...
Freshman Science Study Guide
... 7. The voltage difference in a circuit is a measure of the ________________ per _____________ of electricity flowing in a circuit. The symbol for voltage difference is: ...
... 7. The voltage difference in a circuit is a measure of the ________________ per _____________ of electricity flowing in a circuit. The symbol for voltage difference is: ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.