AC circuits ch 23 S2017
... When you stand barefoot on the scale, electrodes beneath your feet send a small ac current through your lower body that allows the body's electrical impedance to be measured. This impedance is correlated with the percentage of fat in the body. The bioelectrical impedance is largely determined by res ...
... When you stand barefoot on the scale, electrodes beneath your feet send a small ac current through your lower body that allows the body's electrical impedance to be measured. This impedance is correlated with the percentage of fat in the body. The bioelectrical impedance is largely determined by res ...
Science Lesson Plan
... current passes through the galvanometer and the rest goes through the shunt resistor (very low resistance) so it doesn’t break and there is minimal impact on the circuit. ...
... current passes through the galvanometer and the rest goes through the shunt resistor (very low resistance) so it doesn’t break and there is minimal impact on the circuit. ...
Symbols for Circuits
... • Transform a combination circuit into a strictly series circuit by replacing (in your mind, but I always draw it again) the parallel section with a single resistor having a resistance value equal to the equivalent resistance of the parallel section. • Use the Ohm's law equation (V = I • R) often an ...
... • Transform a combination circuit into a strictly series circuit by replacing (in your mind, but I always draw it again) the parallel section with a single resistor having a resistance value equal to the equivalent resistance of the parallel section. • Use the Ohm's law equation (V = I • R) often an ...
Basic Circuits PPT
... the lamp lights up. This is because there is a continuous path for the electric current to flow around. ...
... the lamp lights up. This is because there is a continuous path for the electric current to flow around. ...
Chapter 21: Resonance
... and capacitor are I2X • Reactive powers are equal and opposite at resonance ...
... and capacitor are I2X • Reactive powers are equal and opposite at resonance ...
PHYS4330 Theoretical Mechanics HW #3 Due 20 Sept 2011
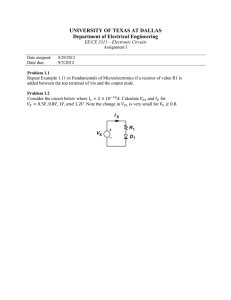
... in class. A resistor R, capacitor C, and inductor L are connected in series. An AC voltage source V (t) = V0 eiωt is put across these elements. Find the amplitude of the voltage drop VR0 (ω) across the resistor, after transients have died away, and find the resonant frequency. (Assume the system is ...
... in class. A resistor R, capacitor C, and inductor L are connected in series. An AC voltage source V (t) = V0 eiωt is put across these elements. Find the amplitude of the voltage drop VR0 (ω) across the resistor, after transients have died away, and find the resonant frequency. (Assume the system is ...
Physics 422 - Spring 2016 - Midterm Exam, March 10
... (a) When in equilibrium, the beam is horizontal. Write the differential equation that describes the small angle θ measured with respect to the equilibrium position with +θ in the direction shown on the figure. The moment of inertia ...
... (a) When in equilibrium, the beam is horizontal. Write the differential equation that describes the small angle θ measured with respect to the equilibrium position with +θ in the direction shown on the figure. The moment of inertia ...
parallel circuits
... Voltage in a parallel circuit • What apparatus would be required to measure the voltage at different points in a parallel circuit? ...
... Voltage in a parallel circuit • What apparatus would be required to measure the voltage at different points in a parallel circuit? ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.