* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Symbols for Circuits
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Surface-mount technology wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
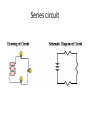
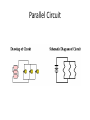
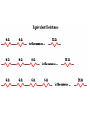
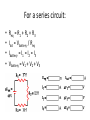
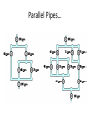
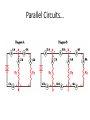
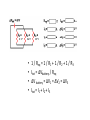
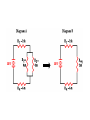
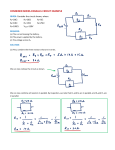
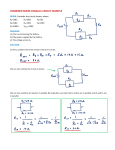
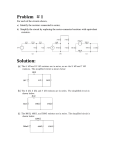
Symbols for Circuits Series circuit Parallel Circuit For a series circuit: • • • • Req = R1 + R2 + R3 Itot = Vbattery / Req Ibattery = I1 = I2 = I3 Vbattery = V1 + V2 + V3 Parallel Pipes… Parallel Circuits… Parallel Resistors… 1 / Req = 1 / R1 + 1 / R2 + 1 / R3 + ... Series Circuits •The current is the same in every resistor; this current is equal to that in the battery. •The sum of the voltage drops across the individual resistors is equal to the voltage rating of the battery. •The overall resistance of the collection of resistors is equal to the sum of the individual resistance values, Rtot = R1 + R2 + R3 + ... Parallel Circuits •The voltage drop is the same across each parallel branch. •The sum of the current in each individual branch is equal to the current outside the branches. •The equivalent or overall resistance of the collection of resistors is given by the equation 1/Req = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3 ... • • • • 1 / Req = 1 / R1 + 1 / R2 + 1 / R3 Itot = ΔVbattery / Req ΔV battery = ΔV1 = ΔV2 = ΔV3 Itot = I1 + I2 + I3 • If a schematic diagram is not provided, take the time to construct one. • When approaching a problem involving a combination circuit, take the time to organize yourself, writing down known values and equating them with a symbol such as Itot, I1, R3, V2, etc. • Know and use the appropriate formula for the equivalent resistance of series-connected and parallel-connected resistors. Use of the wrong formula will guarantee failure! • Transform a combination circuit into a strictly series circuit by replacing (in your mind, but I always draw it again) the parallel section with a single resistor having a resistance value equal to the equivalent resistance of the parallel section. • Use the Ohm's law equation (V = I • R) often and appropriately. Most answers will be determined using this equation. When using it, it is important to substitute the appropriate values into the equation. For instance, if calculating I2, it is important to substitute the V2 and the R2 values into the equation.