* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PP-Series and Parrellel circuts
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor device wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
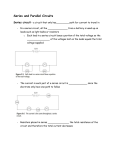
9.1 Series and Parallel Circuits Series Circuits • There is only a single pathway for current to flow • All the voltage from a battery is used up on loads such as light bulbs or resistors • • The sum of the voltages lost on the loads equals the total voltage supplied by the battery Current measured anywhere is equal since the electrons only have one path to follow -Resistance placed in series increase the total resistance of the circuit therefore the total current decreases See pages 306 - 313 Parallel Circuits Parallel Circuits • Multiple pathways for current to flow, adding more pathways lowers resistance • Voltage remains the same through each pathway of the parallel circuit • Current splits up between the different current pathways that eventually converge so a portion of electrons travel each path • • The pathway with less resistance will be able to have more electrons travel on it so the current will be greater The location where the circuit divides into multiple paths or where multiple paths combine is called a junction Parallel cont. • When resistors are in parallel, another path is available so the total resistance decreases and therefore the total current increases