* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electrical Current and Circuits
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
War of the currents wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor device wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
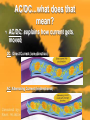
Current and Circuits Power and control all rolled into one fun filled adventure…not really What Is A Current? • Current: the rate at which charges pass a given point Made by electrons moving in a wire AC/DC...what does that mean? • AC/DC: explains how current gets moved DC: Direct Current (one-direction) AC: Alternating Current (bi-directional) Voltage • Depends on Potential Energy • Voltage: the number of electrons that are in an energy source Voltage can vary Resistance • Resistance: opposition to the flow of charge Expressed in ohms Ώ As resistance increases…current decreases!!!! Ohm’s Law • Amperes (A) = volts (V) ohms (Ώ) I = Current V = Voltage R = Resistance I=V R Electric Power • The rate at which electrical energy is used to do work Expressed in Watts (W) P=VxI Power = voltage x current Circuits • Complete, closed path through which electric charges flow Closed Open Two Types of Circuits • 1. Series: all parts are connected in one loop Types Of Circuits • 2. Parallel: different loads are located on separate branches