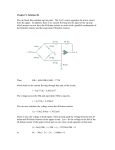
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Series and Parallel Circuits
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Wilson current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
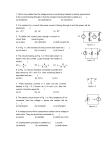
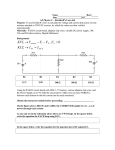
Series and Parallel Circuits 1. Connect the two current probes to the labquest device. 2. Connect the series circuit shown in Figure 4 using the 10 resistor and the 51 resistor. The Current Probes will measure the current flowing into and out of the two resistors. The red terminal of each Current Probe should be toward the + terminal of the power supply. Figure 4 3. Connect the parallel circuit as shown in Figure 5 using the 51 resistor and the 68 resistor. The two Current Probes will measure the current through each resistor individually. The red terminal of each Current Probe should be toward the + terminal of the power supply. Figure 5 ANALYSIS 1. For each circuit, determine current and voltage data (total voltage, and voltage across each resistor) for the circuit at steady state. 2. Determine the theoretical equivalent resistance of each circuit. 3. Determine if the actual data is comparable to the theoretical analysis.