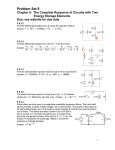
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Series And Parallel Circuits Vocabulary Teacher Guide
Electromagnetic compatibility wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electronic musical instrument wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
Fault tolerance wikipedia , lookup
Printed circuit board wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Circuit breaker wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Electrical wiring in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
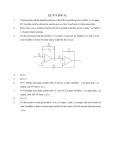
Unit FE 10 Vocabulary Review Key Schematic – A drawing used to represent electronic components in an electronic circuit or wiring diagram. Block Diagram – A picture using boxes to represent sections of a complicated device or process. The block diagram will show the connections and relationships of the sections. Series Circuit – An electrical circuit in which all the electrons must flow through every part of the circuit. There is only one path for the electrons to follow. Parallel Circuit – An electrical circuit in which the electrons follow more than one path in going from the negative supply terminal to the positive terminal. Simulation - Simulation is used to show the eventual real effect of alternative conditions anticipated in a circuit before actual assembly. It is helpful in performance optimization, testing, safety training, education and other times when actual construction is not desired or possible. Transient – A transient is a short-lived burst of energy caused by a sudden change in state of a device or power source. Without adequate protection through proper design, a transient can be destructive to sensitive circuit components. Bias - A direct-current voltage applied to a transistor control electrode to establish the desired operating point. Combination Circuit – A combination circuit consists of multiple series and parallel circuits for proper operation. Equivalent Series Resistance – Sometimes referred to as ESR. Practical capacitors and inductors as used in electronic circuits are not ideal components with only capacitance and inductance. They can be treated as capacitors and inductors in series with a series resistance. This value is known as ESR. Equivalent Resistance – Through the use of Kirchoff’s Law and Ohm’s Law, the equivalent resistance of a circuit is found through simplifying and combining the resistance in each of its individual series and parallel sections into one combined circuit. In other words, even a complex circuit can be represented by a single equivalent resistance. Soldering – Soldering is a process of ensuring good electrical contact between joined conductors by melting and flowing solder into the joint. Soldering is not the same as welding because the conductors are not melted together.