* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Measurement CKT
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
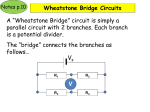
Simple Meter circuits 1. How to extend the range of a current meter? Answer: A shunt resistor can be added to the circuit to bypass the excess current. The value of the shunt resistor is computed from the current divider approach: Rshunt Rm IT 1 Im Im Ishunt IT Example: Find the shunt resistance if Im = 50 A, Rm = 2 K, and IT = 2 mA. Rshunt 2. Rm IT 1 Im 2 K 2 K 2 K 51.3 2mA 39 1 40 1 50A How to extend the range of a voltage meter? Answer: A series resistor can be added to the circuit to handle the excess voltage. The value of the series resistor is computed from the voltage divider approach: V Rseries T Rm Im V Example: Find the series resistance if Im = 50 A, Rm = 2 K, and VT = 2 V. V 2V Rseries T Rm 2 K 40 K 2 K 38 K Im 50 A 3. Capacitance measurements: Capacitance can be measured accurately with an AC bridge (p. 130-135). However, if an AC bridge is not available, the following simple circuit can be used to estimate the capacitance. Connect the above circuit and measure the AC voltages across the resistor and the capacitor. You may need to switch the positions between the two components if the AC voltmeter does not have a floating ground. C 4. VR 2 f R VC Inductance measurements: The inductance is more complicated because an inductor usually has internal resistance. Connect the above circuit and vary the variable resistance until the two voltages are equal. R2 r 2 L 2 f DC Bridge circuits 5. What is a Wheatstone bridge? Answer: Wheatstone bridge is often used in high precision measurements because it is a balance type instrument. In the following circuit the unknown resistance can be calculated from the three known resistors if the bridge circuit is under the balanced condition—zero current through the meter. R2 R1 G R3 Rx R x R3 R1 R 2 Example: Find Rx if the following resistances will balance the Wheatstone bridge: R1 = 4 K, R2 = 6 K , and R3 = 9 K. R x R3 R 9 K Rx R1 3 4 K 6 K R1 R 2 R2 6 K Note: The unbalanced Wheatstone bridge cannot be solved using the basic series/parallel circuit techniques.