* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Question 1 - cloudfront.net
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Peak programme meter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Circuit breaker wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
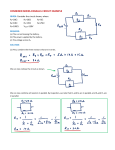
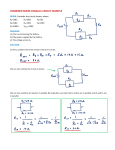
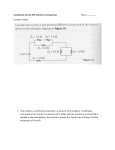
Question 1: Series Circuit In the figure above is shown a circuit with two resistors in series with a battery. What will happen to the voltage across R1 (call this V1) and the voltage across R2 (call this V2) if the resistance R1 increases? A) B) C) D) E) V1 and V2 stay the same. V1 increases and V2 stays the same V1 stays the same and V2 decreases V1 increases and V2 decreases V1 and V2 decrease Answer and discussion: D is correct. As R1 increases, the total current decreases thus reducing V2. V1 plus V2 must add up to the EMF of the battery (ignoring losses) so that V1 must increase. Other Answers: B would be true if the current in the circuit is constant. It is a common belief that batteries are ideal current sources and not voltage sources. E is the correct answer to the question: What happens to the current through the resistors? This answer is missing the fact that the resistance R1 increases causing the current to decrease, but the product still increases. A sometimes is given as an answer by students who have memorized “The current in a series circuit is constant” out of context. Notes on Demonstration: Virtual Simulation: Adding a volt meter is done by checking the box on the right under “Tools”. The ends of the meter leads can be placed on junctions in the circuit. Only one meter can be used. The resistance can be changed by right-clicking on the resistor, selecting “Change Resistance” and varying the resistance using the sliding bar. Changes will be shown immediately in the meter. The change will need to be made first with the meter connected to R1, then to R2. Circuits can be constructed before the class and loaded into the simulation. Real Experiment: Changing the resistance can be done either with a variable resistor or by changing resistors. If two meters are used to measure the voltages simultaneously, the connection between resistor and meter should be very clear.