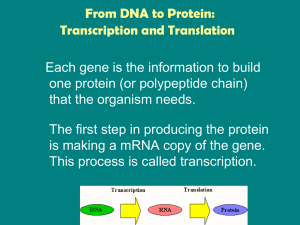
From DNA to Protein: Transcription and Translation
... In RNA, the nucleotide uracil is used in place of thymine. ...
... In RNA, the nucleotide uracil is used in place of thymine. ...
lesson x - MisterSyracuse.com
... 1. What we need to find out is how genes are controlled. We don’t want them on all the time, but we don’t want them off all the time, either. 2. In prokaryotes, things called operons control the process. 3. There is an operator gene that must be active in order for anything to happen. 4. There is pr ...
... 1. What we need to find out is how genes are controlled. We don’t want them on all the time, but we don’t want them off all the time, either. 2. In prokaryotes, things called operons control the process. 3. There is an operator gene that must be active in order for anything to happen. 4. There is pr ...
Gene Regulation
... If tryptophan is in adequate supply - pairing will occur between regions 1 & 2 and 3 & 4. This will cause the RNA polymerase to come off the DNA and stop transcription. An alternative is the ribosome makes the 2 region unavailable for pairing allowing regions 3 & 4 to pair, again causing the RNA pol ...
... If tryptophan is in adequate supply - pairing will occur between regions 1 & 2 and 3 & 4. This will cause the RNA polymerase to come off the DNA and stop transcription. An alternative is the ribosome makes the 2 region unavailable for pairing allowing regions 3 & 4 to pair, again causing the RNA pol ...
Gene Regulation Practice Questions - mr
... 12) Which of the following mechanisms is (are) used to coordinate the expression of multiple, related genes in eukaryotic cells? A) The genes share a single common enhancer, which allows appropriate activators to turn on their transcription at the same time. B) The genes are organized into a large o ...
... 12) Which of the following mechanisms is (are) used to coordinate the expression of multiple, related genes in eukaryotic cells? A) The genes share a single common enhancer, which allows appropriate activators to turn on their transcription at the same time. B) The genes are organized into a large o ...
Molecular mechanisms of the epigenetic regulation Tatiana G
... Department of Pharmacology, University of Colorado School of Medicine, Aurora, CO 80045 USA Plant homeodomain (PHD) fingers, YEATS, Tudor and bromodomains are found in proteins involved in a wide array of fundamental biological processes, including transcription, replication, DNA damage repair, cell ...
... Department of Pharmacology, University of Colorado School of Medicine, Aurora, CO 80045 USA Plant homeodomain (PHD) fingers, YEATS, Tudor and bromodomains are found in proteins involved in a wide array of fundamental biological processes, including transcription, replication, DNA damage repair, cell ...
Protein Synthesis - Helena High School
... Use notes from the PowerPoint and complete the following questions. This will be the study guide for questions about transcription/translation. 1. DNA codes for what macromolecule? Provide three examples of proteins necessary in our bodies a. b. c. 2. Where is the code within the DNA molecule that p ...
... Use notes from the PowerPoint and complete the following questions. This will be the study guide for questions about transcription/translation. 1. DNA codes for what macromolecule? Provide three examples of proteins necessary in our bodies a. b. c. 2. Where is the code within the DNA molecule that p ...
18. Gene Expression
... Three main phases: Initiation Elongation Termination Initiation: • Promoter = nucleotide sequence 5’ to the transcription start site o binding site of RNA polymerase initiation factor (sigma subunit, σ) o Promoter recognition by RNA polymerase is a prerequisite for transcription initiation o Many pr ...
... Three main phases: Initiation Elongation Termination Initiation: • Promoter = nucleotide sequence 5’ to the transcription start site o binding site of RNA polymerase initiation factor (sigma subunit, σ) o Promoter recognition by RNA polymerase is a prerequisite for transcription initiation o Many pr ...
DNA, etc Good facts to know
... 43. An animal that is genetically identical to another: 44. Describe how insulin can be made through Genetic Engineering: 45. Where does mitochondrial DNA come from? 46. Explain y-inheritance. ...
... 43. An animal that is genetically identical to another: 44. Describe how insulin can be made through Genetic Engineering: 45. Where does mitochondrial DNA come from? 46. Explain y-inheritance. ...
Analysis of 3 dimensional interactions in DNA and chromatin
... cells in the human body contain exactly the same genes, so why do we have various different cell types and tissues? The answer lies on strictly regulated gene expression. During the differentiation some genes are activated while other genes are silenced. Correct expression of the genes is crucial fo ...
... cells in the human body contain exactly the same genes, so why do we have various different cell types and tissues? The answer lies on strictly regulated gene expression. During the differentiation some genes are activated while other genes are silenced. Correct expression of the genes is crucial fo ...
Controls - Warren`s Science Page
... of different tissues are differentiated (specialized) because of selective gene expression Every body cell arose by mitotic division from the same fertilized eggs Nearly all of your body cells become specialized in composition, structure, and function (Cell ...
... of different tissues are differentiated (specialized) because of selective gene expression Every body cell arose by mitotic division from the same fertilized eggs Nearly all of your body cells become specialized in composition, structure, and function (Cell ...
Bio 313 worksheet 14 - Iowa State University
... For the following state whether it is a characteristic of Prokaryotes, Eukaryotes, or both 1. Transcription occurs in the nucleus and translation in the cytoplasm 2. Able to utilize post-transcriptional control 3. Transcription unit contains promoter, RNA coding region, and terminator 4. Transcripti ...
... For the following state whether it is a characteristic of Prokaryotes, Eukaryotes, or both 1. Transcription occurs in the nucleus and translation in the cytoplasm 2. Able to utilize post-transcriptional control 3. Transcription unit contains promoter, RNA coding region, and terminator 4. Transcripti ...
CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION - Doral Academy Preparatory
... contributes to the development of form in an organism. causes the uncontrolled proliferation of cells. is caused by the transfer of cells from one organism to another. results from mutations that destroy normal gene functioning. ...
... contributes to the development of form in an organism. causes the uncontrolled proliferation of cells. is caused by the transfer of cells from one organism to another. results from mutations that destroy normal gene functioning. ...
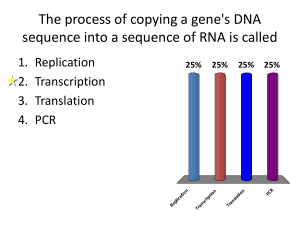
The process of copying a gene`s DNA sequence into a sequence of
... true regarding introns? 1. Introns are the parts of mRNA that are translated 2. Introns have no function. 3. In general, human genes have fewer introns than genes of other organisms. 4. Introns may be involved in exon shuffling ...
... true regarding introns? 1. Introns are the parts of mRNA that are translated 2. Introns have no function. 3. In general, human genes have fewer introns than genes of other organisms. 4. Introns may be involved in exon shuffling ...
Slide 1
... Start site. A start site for transcription. A promoter. A region a few hundred nucleotides 'upstream' of the gene (toward the 5' end). It is not transcribed into mRNA, but plays a role in controlling the transcription of the gene. Transcription factors bind to specific nucleotide sequences in the pr ...
... Start site. A start site for transcription. A promoter. A region a few hundred nucleotides 'upstream' of the gene (toward the 5' end). It is not transcribed into mRNA, but plays a role in controlling the transcription of the gene. Transcription factors bind to specific nucleotide sequences in the pr ...
Timing and Development of Growth
... • Ex: as eye forms, one cell causes others to express genes necessary to make eye cells • Allows each cell to develop at correct time ...
... • Ex: as eye forms, one cell causes others to express genes necessary to make eye cells • Allows each cell to develop at correct time ...
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Objectives: The objective of this course is to
... different modes of gene regulation in bacteria and eukaryotes at both pre- and posttranscriptional levels; to compare and contrast various ways in which gene expression is regulated by small RNAs; to interpret and critique data from primary research articles; to write a review about a primary resear ...
... different modes of gene regulation in bacteria and eukaryotes at both pre- and posttranscriptional levels; to compare and contrast various ways in which gene expression is regulated by small RNAs; to interpret and critique data from primary research articles; to write a review about a primary resear ...
Biology 303 EXAM II 3/14/00 NAME
... B. typically a single mutation is involved in carcinogenesis. C. most cancers are inherited. D. sometimes cancers seem to reverse course and “vanish” although ...
... B. typically a single mutation is involved in carcinogenesis. C. most cancers are inherited. D. sometimes cancers seem to reverse course and “vanish” although ...
regulatory gene
... ◦ Transposition (DNA segments move with and between molecules) “jumping genes”—move from chromosome to plasmid ...
... ◦ Transposition (DNA segments move with and between molecules) “jumping genes”—move from chromosome to plasmid ...
Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes
... Adjacent genes (RNA-coding as well as protein-coding) are often separated by an insulator which helps them avoid cross-talk between each other's promoters and enhancers (and/or silencers). Transcription start site This is where a molecule of RNA polymerase II (pol II, also known as RNAP II) binds. P ...
... Adjacent genes (RNA-coding as well as protein-coding) are often separated by an insulator which helps them avoid cross-talk between each other's promoters and enhancers (and/or silencers). Transcription start site This is where a molecule of RNA polymerase II (pol II, also known as RNAP II) binds. P ...