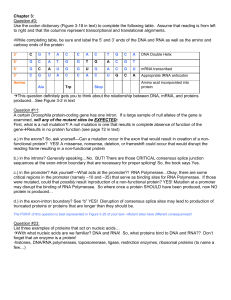
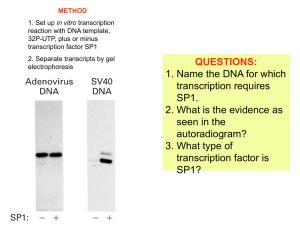
1. Explain how a gene directs the synthesis of an mRNA molecule
... _____ polymerase is the enzyme which carries out transcription. ...
... _____ polymerase is the enzyme which carries out transcription. ...
DNA Replication, RNA Molecules and Transcription
... A transcription reaction requires a DNA molecule to serve as template for transcription with a promoter (and, in vivo, transcription factors) to indicate where to begin transcribing and which strand to transcribe. Transcription reactions also require an RNA polymerase that recognizes the promoter on ...
... A transcription reaction requires a DNA molecule to serve as template for transcription with a promoter (and, in vivo, transcription factors) to indicate where to begin transcribing and which strand to transcribe. Transcription reactions also require an RNA polymerase that recognizes the promoter on ...
Recent progress in understanding transcription factor binding
... Recent progress in understanding transcription factor binding specificity Gene expression levels can vary greatly from gene to gene and between individuals. To understand how these differences arise, and be able to predict and manipulate them, we need to dissect the molecular mechanisms by which the ...
... Recent progress in understanding transcription factor binding specificity Gene expression levels can vary greatly from gene to gene and between individuals. To understand how these differences arise, and be able to predict and manipulate them, we need to dissect the molecular mechanisms by which the ...
No Slide Title
... • Hairpin formation in RNA destabilizes the DNA/RNA hybrid and releases RNA transcript • In some cases, termination depends on the rho () termination factor ...
... • Hairpin formation in RNA destabilizes the DNA/RNA hybrid and releases RNA transcript • In some cases, termination depends on the rho () termination factor ...
Molecular Genetics
... • Promoter is where the RNA polymerase will bond • Contains TATA box, which is located 25 nucleotides away from the site where transcription is initiated. • Transcription Factors attach first • RNA Polymerase then bonds to complete assembly ...
... • Promoter is where the RNA polymerase will bond • Contains TATA box, which is located 25 nucleotides away from the site where transcription is initiated. • Transcription Factors attach first • RNA Polymerase then bonds to complete assembly ...
Virtual Labs: Class Set Building DNA, transcription, translation
... Answer the following questions in complete sentences: 1. Define a gene. 2. What is the function of hemoglobin? 3. What is the name of a mutation that happens to hemoglobin? 4. What is the name of the protein found in hair and nails? 5. List the different types of proteins and give an example of each ...
... Answer the following questions in complete sentences: 1. Define a gene. 2. What is the function of hemoglobin? 3. What is the name of a mutation that happens to hemoglobin? 4. What is the name of the protein found in hair and nails? 5. List the different types of proteins and give an example of each ...
ExPlain: Causal Analysis of Gene Expression Data from Promoter
... in providing fast and appropriate response to any extracellular signal. This is achieved through combinatorial usage of a rather limited set of signaling molecules and pathways. These combinatorics must be mirrored by the structure of gene promoters as combinations of transcription factor binding si ...
... in providing fast and appropriate response to any extracellular signal. This is achieved through combinatorial usage of a rather limited set of signaling molecules and pathways. These combinatorics must be mirrored by the structure of gene promoters as combinations of transcription factor binding si ...
Controlling the genes
... • TFIID binds to the ‘TATA’ box - a short region of DNA located about 25 bases upstream of the gene start site • TFIIA and TFIIB bind to TFIID causing local unraveling of the DNA • TFIIE, TFIIH, TFIIF, and RNA Pol II bind next • Addition of phosphate groups to the RNA Pol II allows transcription to ...
... • TFIID binds to the ‘TATA’ box - a short region of DNA located about 25 bases upstream of the gene start site • TFIIA and TFIIB bind to TFIID causing local unraveling of the DNA • TFIIE, TFIIH, TFIIF, and RNA Pol II bind next • Addition of phosphate groups to the RNA Pol II allows transcription to ...
Document
... were mutated, could that possibly result inproduction of a non-functional protein? YES! Mutation at a promoter may disrupt the binding of RNA Polymerase. So where once a protein SHOULD have been produced, now NO protein is produced… d.) in the exon-intron boundary? See “b” YES! Disruption of consens ...
... were mutated, could that possibly result inproduction of a non-functional protein? YES! Mutation at a promoter may disrupt the binding of RNA Polymerase. So where once a protein SHOULD have been produced, now NO protein is produced… d.) in the exon-intron boundary? See “b” YES! Disruption of consens ...
Lect19.RNA.part2
... complex into a core octamer. DNA wraps around the core, stabilized by electrostatic interaction between histone tails and backbone phosphates along DNA chain. Each nucleosome contains 140 bp DNA, with an internucleosomal distance usually 40 bp. Tight binding of DNA to histones in nucleosomes inhibit ...
... complex into a core octamer. DNA wraps around the core, stabilized by electrostatic interaction between histone tails and backbone phosphates along DNA chain. Each nucleosome contains 140 bp DNA, with an internucleosomal distance usually 40 bp. Tight binding of DNA to histones in nucleosomes inhibit ...
Feb 26
... 1) UBF (upstream binding factor) binds UCE and core element UBF is a transcription factor: DNA-binding proteins which recruit polymerases and tell them where to begin ...
... 1) UBF (upstream binding factor) binds UCE and core element UBF is a transcription factor: DNA-binding proteins which recruit polymerases and tell them where to begin ...
Epigenetic regulators as novel treatments
... Some definitions: Epigenetics-the study of heritable changes in gene expression without changing the DNA sequence; this occurs at 3 levels of organization: 1) methylation of cytosine nucleotides within coding sequences and at promoter sites that alter transcription rates 2) changes in chromatin pro ...
... Some definitions: Epigenetics-the study of heritable changes in gene expression without changing the DNA sequence; this occurs at 3 levels of organization: 1) methylation of cytosine nucleotides within coding sequences and at promoter sites that alter transcription rates 2) changes in chromatin pro ...
L15 Gene Regulation Part1 Fa08
... – Sequence of nucleotides near the start of an operon to which an active repressor can attach – On-off “switch” for the cluster of genes ...
... – Sequence of nucleotides near the start of an operon to which an active repressor can attach – On-off “switch” for the cluster of genes ...
REGULATING GENE EXPRESSION
... so transcription and translation occur at different times Eukaryotic gene regulation can occur at transcription or after transcription Prokaryotic gene regulation can occur only at transcription Eukaryotic gene regulation can control how much transcription occurs Prokaryotic gene regulation ...
... so transcription and translation occur at different times Eukaryotic gene regulation can occur at transcription or after transcription Prokaryotic gene regulation can occur only at transcription Eukaryotic gene regulation can control how much transcription occurs Prokaryotic gene regulation ...
Chapter 19: Eukaryotic Genomes: Organization
... 1. Fill in the table below to help you organize the major mechanisms that can regulate the expression of eukaryotic genes. Level of Control Examples Chromatin structure DNA packing into nucleosomes; histone tail acetylation increases, whereas deacetylation and methylation of tails decreases transcr ...
... 1. Fill in the table below to help you organize the major mechanisms that can regulate the expression of eukaryotic genes. Level of Control Examples Chromatin structure DNA packing into nucleosomes; histone tail acetylation increases, whereas deacetylation and methylation of tails decreases transcr ...
Lecture 10/11/06
... o The half-life of most mRNAs is short (on the order of a few minutes). o Transcription and translation are coupled in a single cellular compartment o Genes are regulated in units called operons. All of the genes necessary for a particular function are generally located on the same operon with the s ...
... o The half-life of most mRNAs is short (on the order of a few minutes). o Transcription and translation are coupled in a single cellular compartment o Genes are regulated in units called operons. All of the genes necessary for a particular function are generally located on the same operon with the s ...
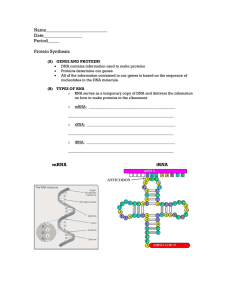
Name___________________________ Date_________________ Period_____
... Process: This process involves the use of enzymes, particularly RNA Polymerase. A)________________________________________________ ...
... Process: This process involves the use of enzymes, particularly RNA Polymerase. A)________________________________________________ ...
Gene Regulation and Expression Notes
... When lactose is not present, the lac genes are turned off by regulatory proteins that bind to DNA and block transcription. ...
... When lactose is not present, the lac genes are turned off by regulatory proteins that bind to DNA and block transcription. ...
Slide 1
... present in some -phage and E. coli genes • The Rho factor is a hexameric protein around which a 70- to 80-base segment of the growing RNA transcript wraps • Rho then moves along the RNA in the 3 direction until it eventually unwinds the RNA-DNA hybrid at the active site of RNA polymerase • Whether ...
... present in some -phage and E. coli genes • The Rho factor is a hexameric protein around which a 70- to 80-base segment of the growing RNA transcript wraps • Rho then moves along the RNA in the 3 direction until it eventually unwinds the RNA-DNA hybrid at the active site of RNA polymerase • Whether ...