Biology 340 Molecular Biology
... --Gene expression is regulated so genes are turned on when they are needed during development and in the correct cell types. --Most genes in higher eukaryotes are regulated by controlling their transcription. General principles: 1. Transcription begins at a specific site or a cluster of neighboring ...
... --Gene expression is regulated so genes are turned on when they are needed during development and in the correct cell types. --Most genes in higher eukaryotes are regulated by controlling their transcription. General principles: 1. Transcription begins at a specific site or a cluster of neighboring ...
Control of Gene Expression - Downtown Magnets High School
... • Each tissue in our body is very different despite having the same DNA • Even identical twins have many differences due to gene expression ...
... • Each tissue in our body is very different despite having the same DNA • Even identical twins have many differences due to gene expression ...
Chapter 15 / Lecture Outline 36
... 1. The presence of lactose induces expression of the genes required for lactose utilization 2. Analysis of the lactose induction system was a wise choice for the study of gene regulation B. Experiments analyzing the behavior of lactose-utilization mutants reveal the coordinate repression and inducti ...
... 1. The presence of lactose induces expression of the genes required for lactose utilization 2. Analysis of the lactose induction system was a wise choice for the study of gene regulation B. Experiments analyzing the behavior of lactose-utilization mutants reveal the coordinate repression and inducti ...
Chapter 15
... Controls in Eukaryotic Cells Control of transcription Transcript processing controls Controls over translation ...
... Controls in Eukaryotic Cells Control of transcription Transcript processing controls Controls over translation ...
Unit 7 Study Guide ANSWERS 2014
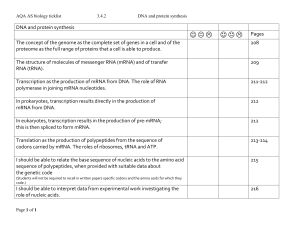
... 10. What determines the specificity of a protein? The order of the nitrogenous bases in the DNA 11. In a eukaryotic cell, where does mRNA processing take place? During Transcription 12. What are the two processes that link the gene to the protein? Transcription and Translation 13. Proteins are made ...
... 10. What determines the specificity of a protein? The order of the nitrogenous bases in the DNA 11. In a eukaryotic cell, where does mRNA processing take place? During Transcription 12. What are the two processes that link the gene to the protein? Transcription and Translation 13. Proteins are made ...
From Gene to Protein Protein Synthesis
... RNA polymerase: pries DNA apart and hooks RNA nucleotides together from the DNA code Promoter region on DNA: where RNA polymerase attaches and where initiation of RNA begins Terminator region: sequence that signals the end of transcription Transcription unit: stretch of DNA transcribed into an RNA m ...
... RNA polymerase: pries DNA apart and hooks RNA nucleotides together from the DNA code Promoter region on DNA: where RNA polymerase attaches and where initiation of RNA begins Terminator region: sequence that signals the end of transcription Transcription unit: stretch of DNA transcribed into an RNA m ...
Transcription: Synthesizing RNA from DNA
... 3 important classes (to us) of RNA: mRNA: varies in length-depends on the gene that has been transcribed tRNA: transfer appropriate amino acid to the ribosome to build proteins. Short ~70-90 nucleotides. rRNA: structural component of ribosome, along with a protein it forms the ribosome which provide ...
... 3 important classes (to us) of RNA: mRNA: varies in length-depends on the gene that has been transcribed tRNA: transfer appropriate amino acid to the ribosome to build proteins. Short ~70-90 nucleotides. rRNA: structural component of ribosome, along with a protein it forms the ribosome which provide ...
Document
... information. In this work we analyse an important class of molecules namely transcription factors which regulate gene expression. We study their domain architecture to understand their evolution, their regulatory function as transcriptional activators or repressors and the evolution of the regulator ...
... information. In this work we analyse an important class of molecules namely transcription factors which regulate gene expression. We study their domain architecture to understand their evolution, their regulatory function as transcriptional activators or repressors and the evolution of the regulator ...
Chapt16_lecture
... – trp repressor binds to the operator to block transcription – binding of repressor to the operator requires a corepressor which is tryptophan – low levels of tryptophan prevent the repressor from binding to the operator ...
... – trp repressor binds to the operator to block transcription – binding of repressor to the operator requires a corepressor which is tryptophan – low levels of tryptophan prevent the repressor from binding to the operator ...
Gene Expression Vocabulary
... 3. Gene expression: the process of information from DNA to proteins 4. Transcription: the information in DNA is transferred to mRNA 5. Translation: the information in mRNA is used to make a protein 6. RNA polymerase: an enzyme that begins transcription 7. Promoter: a specific sequence of DNA that ac ...
... 3. Gene expression: the process of information from DNA to proteins 4. Transcription: the information in DNA is transferred to mRNA 5. Translation: the information in mRNA is used to make a protein 6. RNA polymerase: an enzyme that begins transcription 7. Promoter: a specific sequence of DNA that ac ...
Transcription/Translation
... • Genes contained in the heterochromatin regions of a chromosome are usually not expressed because the packaging of DNA into nucleosomes can make DNA physically inaccessible to RNA polymerase for transcription. • In a process called chromatin remodeling, specialized proteins can cause the nucleosome ...
... • Genes contained in the heterochromatin regions of a chromosome are usually not expressed because the packaging of DNA into nucleosomes can make DNA physically inaccessible to RNA polymerase for transcription. • In a process called chromatin remodeling, specialized proteins can cause the nucleosome ...
Document
... Eukaryotic vs. Prokaryotic Transcription • In eukaryotes, transcription and translation occur in separate ...
... Eukaryotic vs. Prokaryotic Transcription • In eukaryotes, transcription and translation occur in separate ...
Nature Methods article on Programming transcription
... the multimerization of weak TFs to fine-tune expression levels. These modular complexes are more like their natural counterparts, and the synthetic recapitulation of transcriptional regulation will allow insights into how a cell regulates its transcription. Khalil, A.S. et al. Cell 150, 647–658 (201 ...
... the multimerization of weak TFs to fine-tune expression levels. These modular complexes are more like their natural counterparts, and the synthetic recapitulation of transcriptional regulation will allow insights into how a cell regulates its transcription. Khalil, A.S. et al. Cell 150, 647–658 (201 ...
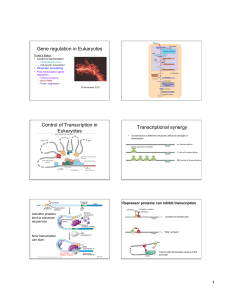
Gene regulation in Eukaryotes Control of Transcription in
... Degradation Degradation of protein of protein ...
... Degradation Degradation of protein of protein ...
Book 11.5 HB Questions
... 5. The process of joining exons together to form an mRNA molecule is called _________________________. 6. During transcription, the _________________________ between base pairs are broken. 7. A mutation will cause the cell to make an incomplete polypeptide if the mutation results in a(an) __________ ...
... 5. The process of joining exons together to form an mRNA molecule is called _________________________. 6. During transcription, the _________________________ between base pairs are broken. 7. A mutation will cause the cell to make an incomplete polypeptide if the mutation results in a(an) __________ ...
Eukaryotic Gene Regulation
... • An expressed gene is one that is transcribed into RNA • Not all genes are expressed by every cell • How does an organism know when to “turn on” or “turn off” a gene? ...
... • An expressed gene is one that is transcribed into RNA • Not all genes are expressed by every cell • How does an organism know when to “turn on” or “turn off” a gene? ...
Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Exercise - KEY
... Question 1: Eukaryotic genes can be regulated by DNA regions far away from the gene. ...
... Question 1: Eukaryotic genes can be regulated by DNA regions far away from the gene. ...
Chapter 17 - Denton ISD
... All translation begins with free ribosomes. If a growing polypeptide includes a signal peptide, a ___________________(SRP) helps attach it to the ER. ...
... All translation begins with free ribosomes. If a growing polypeptide includes a signal peptide, a ___________________(SRP) helps attach it to the ER. ...
Ch 18.2-18.5 PPT
... transcription DNA methylation: methyl groups added to DNA; tightly packed; transcription Histone acetylation: acetyl groups added to histones; loosened; transcription ...
... transcription DNA methylation: methyl groups added to DNA; tightly packed; transcription Histone acetylation: acetyl groups added to histones; loosened; transcription ...
power point presentation
... Substituting 1 base seems to be perfectly fine as the data in blue boxes lies perfectly on the prediction line. Substitution of 2 bases seems to be ok, but then about half of the data points lie distinctively far away from the line. ...
... Substituting 1 base seems to be perfectly fine as the data in blue boxes lies perfectly on the prediction line. Substitution of 2 bases seems to be ok, but then about half of the data points lie distinctively far away from the line. ...
Gene expression of eukaryotic cells
... 2. Transcription • proteins that bind to DNA and facilitate of inhibit ...
... 2. Transcription • proteins that bind to DNA and facilitate of inhibit ...
Postdoc position in Regulation of Gene Transcription by RNA
... at: http://www.ceitec.cz/en/inherited-diseases-ii-transcriptional-regulation/rg38? langselect=1 ). The project focuses on transcription cycle-related cyclin-dependent kinases (mainly Cdk9 and Cdk12) involved in the regulation of gene transcription by RNA Polymerase II and their roles in modulation o ...
... at: http://www.ceitec.cz/en/inherited-diseases-ii-transcriptional-regulation/rg38? langselect=1 ). The project focuses on transcription cycle-related cyclin-dependent kinases (mainly Cdk9 and Cdk12) involved in the regulation of gene transcription by RNA Polymerase II and their roles in modulation o ...