Word of the Day
... From DNA to You Proteins are made from chains of amino acids, the order of these AA’s determines the structure of a protein. The genetic code is a way of reading the sequence of amino acids. A codon is a combination of three nitrogen containing bases in a row. Each codon codes for a different amino- ...
... From DNA to You Proteins are made from chains of amino acids, the order of these AA’s determines the structure of a protein. The genetic code is a way of reading the sequence of amino acids. A codon is a combination of three nitrogen containing bases in a row. Each codon codes for a different amino- ...
wanted - Copenhagen Plant Science Centre
... DNA that does not code for proteins (non-coding DNA) makes up the vast majority of bases in many genomes yet we understand little about its role. Non-coding regions are actively transcribed by the same complex transcribing genes (RNA polymerase II, Pol II). Transcription of non-coding sequences resu ...
... DNA that does not code for proteins (non-coding DNA) makes up the vast majority of bases in many genomes yet we understand little about its role. Non-coding regions are actively transcribed by the same complex transcribing genes (RNA polymerase II, Pol II). Transcription of non-coding sequences resu ...
Protein Synthesis Digital Guide
... • Identify the nitrogen bases that form RNA nucleotides • List three differences between RNA and DNA • Differentiate between the three main types of RNA and their functions • Explain what comprises the central dogma • Identify the location in an eukaryotic cell where the processes of replicatio ...
... • Identify the nitrogen bases that form RNA nucleotides • List three differences between RNA and DNA • Differentiate between the three main types of RNA and their functions • Explain what comprises the central dogma • Identify the location in an eukaryotic cell where the processes of replicatio ...
Eukaryotic Gene Regulation
... Turning On and Off Genes (Gene Regulation) in Eukaryotes Conserves energy that the cell needs for other ...
... Turning On and Off Genes (Gene Regulation) in Eukaryotes Conserves energy that the cell needs for other ...
Chapter 10 - Power Point Presentation
... before making the protein. The portions that remain and ARE used are called exons So, eukaryotes undergo RNA splicing This is one way a gene can have some variability in its outcome ...
... before making the protein. The portions that remain and ARE used are called exons So, eukaryotes undergo RNA splicing This is one way a gene can have some variability in its outcome ...
How many nucleotides are in 12 mRNA codons?
... The first amino acid will be wrong, but the last three will be correct. ...
... The first amino acid will be wrong, but the last three will be correct. ...
LKCMedicine Lecture Series by Asst Prof Chng Toh Hean
... transcription of new genes and synthesis of new proteins. The transport of synaptically-localised transcriptional regulators during neuronal activity provides a method of coupling synaptic activation with changes in the transcription. Asst Prof Chng’s lab is interested in studying the molecular basi ...
... transcription of new genes and synthesis of new proteins. The transport of synaptically-localised transcriptional regulators during neuronal activity provides a method of coupling synaptic activation with changes in the transcription. Asst Prof Chng’s lab is interested in studying the molecular basi ...
Postdoc Opening
... genome-scale regulation in bacteria. Current goals include understanding how transcriptional regulators alter RNA polymerase conformation to control RNA synthesis (Nayak et al., 2013; Hein et al., 2014; Project 1) and how nucleoprotein filaments formed on bacterial chromosomes and transcriptional pa ...
... genome-scale regulation in bacteria. Current goals include understanding how transcriptional regulators alter RNA polymerase conformation to control RNA synthesis (Nayak et al., 2013; Hein et al., 2014; Project 1) and how nucleoprotein filaments formed on bacterial chromosomes and transcriptional pa ...
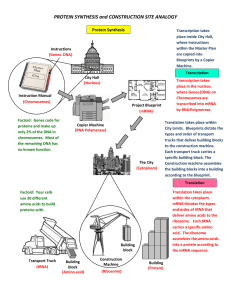
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS and CONSTRUCTION SITE ANALOGY
... Transcription takes place in the nucleus, where Genes (DNA) on Chromosomes are transcribed into mRNA by RNA Polymerase. Translation takes place within City Limits. Blueprints dictate the types and order of transport trucks that deliver building blocks to the construction machine. Each transport truc ...
... Transcription takes place in the nucleus, where Genes (DNA) on Chromosomes are transcribed into mRNA by RNA Polymerase. Translation takes place within City Limits. Blueprints dictate the types and order of transport trucks that deliver building blocks to the construction machine. Each transport truc ...
Control of Gene Express in Prokaryotes
... • Different cell types make different proteins • role of transcription regulation • two sources of cellular instructions for determination: cytoplasmic determinants and neighboring cells ...
... • Different cell types make different proteins • role of transcription regulation • two sources of cellular instructions for determination: cytoplasmic determinants and neighboring cells ...
DNA to RNA
... information you need—shorter/simpler Think of it like this: DNA = master copy RNA = blueprints…you don’t need the blueprints for the whole house to build the foundation ...
... information you need—shorter/simpler Think of it like this: DNA = master copy RNA = blueprints…you don’t need the blueprints for the whole house to build the foundation ...
Lecture#5 - Introduction to gene regulation and operons in
... First understanding of gene regulation comes from the work of Jacob and Monod in the 1950's and ‘60's -> Nobel prize in 1965. Inducers - specific substrates that induced the appearance of specific enzymes (new synthesis of the enzymes). beta-galactosidase could be induced with several types of beta- ...
... First understanding of gene regulation comes from the work of Jacob and Monod in the 1950's and ‘60's -> Nobel prize in 1965. Inducers - specific substrates that induced the appearance of specific enzymes (new synthesis of the enzymes). beta-galactosidase could be induced with several types of beta- ...
Computer science
... • Analysis of protein-DNA interactions: breaking the cis-regulatory code. “ Regulatory interactions mandated by circuitry encoded in the genome determine whether each gene is expressed in each cell, throughout developmental space and time, and, if so, at what amplitude.” Eric Davidson • Analysis of ...
... • Analysis of protein-DNA interactions: breaking the cis-regulatory code. “ Regulatory interactions mandated by circuitry encoded in the genome determine whether each gene is expressed in each cell, throughout developmental space and time, and, if so, at what amplitude.” Eric Davidson • Analysis of ...
Gene Expression - Biology Department | Western Washington
... UTRs are transcribed, but not translated. UTR sequences diverge more rapidly during evolution ...
... UTRs are transcribed, but not translated. UTR sequences diverge more rapidly during evolution ...
October 3, 2016 Worksheet
... Do we use introns or exons? Draw a strand of DNA that contains silencer, repressor, basal transcription factors, TATA box, (transcription factors): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ysxtZJUeTCE Why does these processes need to happen? ...
... Do we use introns or exons? Draw a strand of DNA that contains silencer, repressor, basal transcription factors, TATA box, (transcription factors): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ysxtZJUeTCE Why does these processes need to happen? ...
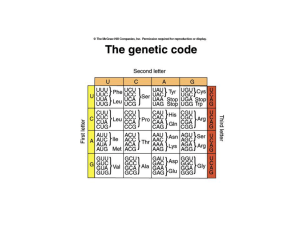
Features of the genetic code
... • Mutations that modify the genetic code are of 3 types: frameshift (include deletions and insertions), missense (lead to an amino acid replacement) and nonsense (mutation that generates any of the three stop codons leading a a premature truncation of the polypeptide. ...
... • Mutations that modify the genetic code are of 3 types: frameshift (include deletions and insertions), missense (lead to an amino acid replacement) and nonsense (mutation that generates any of the three stop codons leading a a premature truncation of the polypeptide. ...
RNA Transcription
... once 'information' has passed into protein it cannot get out again. The transfer of information from nucleic acid to nucleic acid, or from nucleic acid to protein, may be possible, but transfer from protein to protein, or from protein to nucleic acid, is ...
... once 'information' has passed into protein it cannot get out again. The transfer of information from nucleic acid to nucleic acid, or from nucleic acid to protein, may be possible, but transfer from protein to protein, or from protein to nucleic acid, is ...
How do we get proteins? - Sebastian Charter Junior High
... DNA is used to make a single strand of RNA that is ...
... DNA is used to make a single strand of RNA that is ...
CHAPTER 12
... • HLH-containing transcription factors play a key role in the differentiation of certain tissues. • HLH-containing transcription factors also participate in the control of cell proliferation and cancer. ...
... • HLH-containing transcription factors play a key role in the differentiation of certain tissues. • HLH-containing transcription factors also participate in the control of cell proliferation and cancer. ...
Chapter 16 Gene Regulation Levels of Gene Regulation Bacterial
... • Multicellular specialization – Genes for one cell type are not expressed in other cell types ...
... • Multicellular specialization – Genes for one cell type are not expressed in other cell types ...
Regulation
... Adaptive – Ability to initiate Transcription –Control by signal Proteins Environmental Signals facilitate Transcription Positive Regulation Environmental Signals interfere with Transcription Negative Regulation ...
... Adaptive – Ability to initiate Transcription –Control by signal Proteins Environmental Signals facilitate Transcription Positive Regulation Environmental Signals interfere with Transcription Negative Regulation ...
Document
... having evolved one from another through gene duplication. Paralogs are separated by a gene duplication event. • Each specific gene family member (e.g. a specific gene in human) is an ortholog of the same family member in another species (e.g. mouse). Both evolved from an ancestral globin gene. Ortho ...
... having evolved one from another through gene duplication. Paralogs are separated by a gene duplication event. • Each specific gene family member (e.g. a specific gene in human) is an ortholog of the same family member in another species (e.g. mouse). Both evolved from an ancestral globin gene. Ortho ...
Cellular Control miniQUIZ
... Using the diagram above answer the following questions: a) Which segment of the fruit fly develops wings? b) Are plant homeobox genes homologous to the homeobox genes in the fruit fly? 17. Apoptosis is important during development. Define the meaning of apoptosis and give an example. ...
... Using the diagram above answer the following questions: a) Which segment of the fruit fly develops wings? b) Are plant homeobox genes homologous to the homeobox genes in the fruit fly? 17. Apoptosis is important during development. Define the meaning of apoptosis and give an example. ...