Carbon-Carbon Bond Forming Reactions
... - cationic intermediate rearrangements of side chain possible - overalkylation is possible - deactivated benzenes and anilines do not react - must consider regioselectivity when using substituted benzenes directing effects: o/p or m (see handout) ...
... - cationic intermediate rearrangements of side chain possible - overalkylation is possible - deactivated benzenes and anilines do not react - must consider regioselectivity when using substituted benzenes directing effects: o/p or m (see handout) ...
Synthesis/Decomposition Reactions
... In these reactions, two different molecules or atoms combine to form a single substance. ...
... In these reactions, two different molecules or atoms combine to form a single substance. ...
dr. Zdenko Časar - Fakulteta za kemijo in kemijsko tehnologijo
... and bortezomib will be presented. Then, discovery and some process optimization of asymmetric iridium-catalyzed chemoselective hydrogenation approach to chiral (α-chloroalkyl) boronic esters will be discussed. Firstly, synthesis of (1-chloro-1-alkenyl)boronic ester starting materials from commercial ...
... and bortezomib will be presented. Then, discovery and some process optimization of asymmetric iridium-catalyzed chemoselective hydrogenation approach to chiral (α-chloroalkyl) boronic esters will be discussed. Firstly, synthesis of (1-chloro-1-alkenyl)boronic ester starting materials from commercial ...
Chapter 11 Introduction to Organic Chemistry Part 2
... 5. The two isomers, configurations (a) and (b), are enantiomers because each molecule contains two stereogenic centers (asymmetric carbon atoms) and their mirror images are non-superimposable to each other. 6. A. ...
... 5. The two isomers, configurations (a) and (b), are enantiomers because each molecule contains two stereogenic centers (asymmetric carbon atoms) and their mirror images are non-superimposable to each other. 6. A. ...
Reactions of Hydrocarbons & their functional groups
... • Occurs in presence of oxidizing agents [O] such as KMnO4, K2Cr2O7, and O3 • For now, focus on organic reactant only ...
... • Occurs in presence of oxidizing agents [O] such as KMnO4, K2Cr2O7, and O3 • For now, focus on organic reactant only ...
Document
... Positive ion or molecule with + Attracted to an electron rich centre Accepts a pair of electrons to make a dative covalent bond. ...
... Positive ion or molecule with + Attracted to an electron rich centre Accepts a pair of electrons to make a dative covalent bond. ...
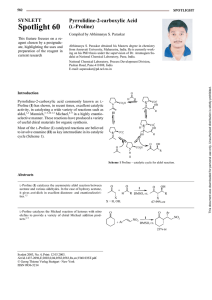
Pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic Acid (l
... from Amravati University, Maharastra, India. He is currently working on his PhD thesis under the supervision of Dr. Arumugum Sudalai at National Chemical Laboratory, Pune, India. ...
... from Amravati University, Maharastra, India. He is currently working on his PhD thesis under the supervision of Dr. Arumugum Sudalai at National Chemical Laboratory, Pune, India. ...
Exam 3 Review Sheet
... o Friedel-Crafts acylation: acid chloride, AlCl3 Can be followed by Wolff-Kishner (N2H4, KOH) or Clemmenson (Zn(Hg), HCl) reduction to eliminate oxygen. • Addition of the second and third groups o ortho/para vs. meta directors. Resonance structures, inductive effects. Activating the ring. • Sy ...
... o Friedel-Crafts acylation: acid chloride, AlCl3 Can be followed by Wolff-Kishner (N2H4, KOH) or Clemmenson (Zn(Hg), HCl) reduction to eliminate oxygen. • Addition of the second and third groups o ortho/para vs. meta directors. Resonance structures, inductive effects. Activating the ring. • Sy ...
Nucleophilic Substitution Swapping
... There is very little difference in these reactions. Both have 2 steps and the same product , the same reactants. Hard to see any difference S = substitution (both will swap) N= Nucleophile (both will use the same Nu: 1 =Rate of reaction (depends on 1 reactant) called 1st order ...
... There is very little difference in these reactions. Both have 2 steps and the same product , the same reactants. Hard to see any difference S = substitution (both will swap) N= Nucleophile (both will use the same Nu: 1 =Rate of reaction (depends on 1 reactant) called 1st order ...
11. Reactions of Alkyl Halides
... species and the rate constant of the step • The highest energy transition state point on the diagram is that for the rate determining step (which is not always the highest barrier) • This is the not the greatest difference but the absolute highest point (Figures 11.8 – the same step is rate-determin ...
... species and the rate constant of the step • The highest energy transition state point on the diagram is that for the rate determining step (which is not always the highest barrier) • This is the not the greatest difference but the absolute highest point (Figures 11.8 – the same step is rate-determin ...
Handout 7
... In conclusion, all steps included in the conversion of an aldehyde or ketone to acetal or ketal via hemiacetal or hemiketal as intermediates, are reversible. Performing the reaction in large excess of an anhydrous alcohol and a small amount of an anhydrous acid will strongly favour the formation of ...
... In conclusion, all steps included in the conversion of an aldehyde or ketone to acetal or ketal via hemiacetal or hemiketal as intermediates, are reversible. Performing the reaction in large excess of an anhydrous alcohol and a small amount of an anhydrous acid will strongly favour the formation of ...
Document
... The alcohol obtained from oxymercuration-demercuration is the same as that obtained from Markovnikov hydration, however, since no carbocation is involved in the reaction mechanism, rearrangements of the transition state do not occur. ...
... The alcohol obtained from oxymercuration-demercuration is the same as that obtained from Markovnikov hydration, however, since no carbocation is involved in the reaction mechanism, rearrangements of the transition state do not occur. ...
1b. Loss of N
... 2. Gain or loss of bonds to oxygen: Oxidations and Reductions Catalyzed by enzymes together with cofactors NAD+/NADP+ (works with dehydrogenases) --Oxidation of hydroxyl group to carbonyl or aldehyde to carboxylic acid --Oxidation of amine to imine ...
... 2. Gain or loss of bonds to oxygen: Oxidations and Reductions Catalyzed by enzymes together with cofactors NAD+/NADP+ (works with dehydrogenases) --Oxidation of hydroxyl group to carbonyl or aldehyde to carboxylic acid --Oxidation of amine to imine ...
Regents Unit 15b: Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids, & Esters
... • Contain –COOH group. • H is bonded to O. Hydrogen bonding occurs. Leads to increases in boiling point over corresponding alkane. • Also can form hydrogen bonds with water so the smaller acids are pretty soluble. ...
... • Contain –COOH group. • H is bonded to O. Hydrogen bonding occurs. Leads to increases in boiling point over corresponding alkane. • Also can form hydrogen bonds with water so the smaller acids are pretty soluble. ...
Some comments and hints for the March 9 Biochemistry
... gas phase. Also, they denature to form caramel like goos. c. The reduction of fructose creates a new tetrahedral stereocenter. This can be examined best by looking at Fischer projections of the sugars. d. The first method will convert the alcohols to methyl ethers. The second will produce silyl ethe ...
... gas phase. Also, they denature to form caramel like goos. c. The reduction of fructose creates a new tetrahedral stereocenter. This can be examined best by looking at Fischer projections of the sugars. d. The first method will convert the alcohols to methyl ethers. The second will produce silyl ethe ...
Asymmetric induction

Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.