* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exam 3 Review Sheet
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
California Green Chemistry Initiative wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Supramolecular catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Resonance (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Photoredox catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis of doxorubicin wikipedia , lookup
Bioorthogonal chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Stille reaction wikipedia , lookup
Natural product wikipedia , lookup
Acid–base reaction wikipedia , lookup
Green chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Process chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Aromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen-bond catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Inorganic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Aromatization wikipedia , lookup
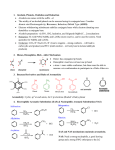
Chemistry 213 Clark College Exam 3 Review Sheet The following questions have been pulled from various exams and review sheets from some of my previous classes. The review is not complete! Make sure you study the assigned homeworks, go through suggested problems and read through the Chapter Notes and your lecture notes. Topic Outline You should feel comfortable with the following topics: Ch. 16 and 17: Aromatic Compounds • Concepts of aromaticity: MO diagrams, Hückel Rules for Aromaticity, resonance structures • Reactions at the benzylic position: o Addition of Br or Cl with NBS/NCS in the presence of peroxide. o Oxidation of a benzylic C-H with chromic acid or potassium permanganate. • Nomenclature – common derivatives, o/m/p usage. • Electrophilic Aromatic subsitution reactions. o General mechanism, high energy intermediate. o Generation of electrophile mechanisms. o Halogenation: X2, FeX3. o Sulfonation: H2SO4. o Nitration: HNO3, H2SO4. Can be followed by H2/Ni reduction of nitro to an amine o Friedel-Crafts alkylation: R-Cl, AlCl3. Watch for carbocation rearrangements! o Friedel-Crafts acylation: acid chloride, AlCl3 Can be followed by Wolff-Kishner (N2H4, KOH) or Clemmenson (Zn(Hg), HCl) reduction to eliminate oxygen. • Addition of the second and third groups o ortho/para vs. meta directors. Resonance structures, inductive effects. Activating the ring. • Synthesis of substituted benzenes, order of reaction for directing effects. • Reactions of phenol: o Kolbe carboxylation (plus mechanism) Ch. 18 Aldehydes and Ketones • Nomenclature of aldehydes and ketones, proper hierarchy in naming. • Reactions of carbon nucleophiles with aldehydes and ketones, reactions and mechanisms. o Grignard, lithium, alkyne, and cyanide nucleophiles to form alcohols. o Wittig reagents to form alkenes. • Nitrogen nucleophiles, reactions and mechanisms – acid catalysts, resonance structures and equilibrium arrows. o 1° amines to make imines o 2° amines to make enamines • Oxygen nucleophiles, reactions and mechanisms – use of acid catalysts o Acetal formation o Use of ethylene glycol (1,2-ethanediol) as a protecting group. • Reductions of aldehydes and ketones. o Understand the differences in the mechanisms/use of the various reducing agents – polar vs. nonpolar reagents, hydride reagent mechanisms. o Selectively reducing aldehydes/ketones, alkenes • Oxidation of alcohols and aldehydes to either aldehydes, ketones or carboxylic acids. o PCC/pyridine, chromic acid (H2CrO4), Tollens’ test (Ag(NH3)2+). Exam 1 Review Spring 2008 Page 1 of 6 Chemistry 213 Clark College Review Problems 1. Which of the following compounds are aromatic? O H As OH 2. Predict the product(s). Predict the product(s) of the reactions below. O Zn(Hg), HCl, ! Cl2 FeCl3 NO2 1) KMnO4, ! 2) H+ 1) NaOH 2) CO2 3) H+ OH H3CO Cl O2N AlCl3 NH2 O Cl 1) AlCl3 2) H2O O NBS, ! O-O OH 1) NaOH 2) CO2 3) HCl Br Exam 1 Review Spring 2008 Page 2 of 6 Chemistry 213 Clark College 3. Name the following molecules. O O O O H H3C Cl F HO 4. More “predict the products”. O H+ OH O N O H H+ H 1) 2) H3O+ O O EtNH2 H+ Exam 1 Review Spring 2008 Page 3 of 6 Chemistry 213 Clark College 5. “Road Map”. Fill in the products or provide the reagents of each step of the synthetic sequences. Some molecular formulas are given to help you stay on track. OH SOCl2 pyridine AlCl3 C14H20 1) BH3 2) OH-, H2O2, H2O AlCl3 SOCl2 pyridine C14H20 H Br O OH OH O H 1) BrMg 2) H3O+ A H2CrO4 OH HO B H+ C 1) Hg(OAc)2, H2O 2) NaBH4 D SOCl2 pyr G C12H21N Exam 1 Review Spring 2008 H+ F CH3NH2 DMSO E Page 4 of 6 Chemistry 213 Clark College 6. Provide the mechanisms for the following reactions. O H2SO4 HO C5H10O3 H cat. N O NH2 H+ HO 7. Methoxypyridine can form two different monochlorinated products. OCH3 Cl2 FeCl3 Two isomeric products, C6H6ClNO N a. Give the structures of both products and label them “A” and “B”. b. Predict the major product. c. Explain why the product you chose for part (b) should be the major product. 8. Synthesis. Make the following compounds from benzene. NH2 Br 4 steps Br 3 or 4 steps 9. Give the complete mechanism for the electrophilic bromination of benzene using Br2 and FeBr3. Include the formation of the electrophile. 10. NMR. Phenol undergoes a Friedel-Crafts reaction with t-butyl chloride in the presence of aluminum chloride. Only one product is formed, and NMR data for the product is shown below. With this information, give the identity of this product. OH Cl AlCl3 C10H14 NMR: d = 7.2 ppm, 2H, d 6.9 ppm, 2H, d 1.5 ppm, 1H, broad 1.3 pmm, 9H, s 11. Rank the following substituted benzene derivatives with respect to their reactivity toward the electrophilic nitronium cation (1 = fastest, 5 = slowest). Exam 1 Review Spring 2008 Page 5 of 6 Chemistry 213 Clark College OCH3 OCH3 O NO2 O Exam 1 Review Spring 2008 Page 6 of 6