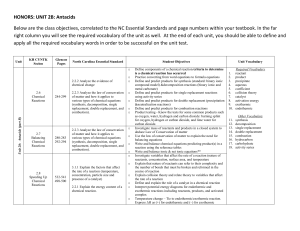
HONORS: UNIT 2B: Antacids Below are the class objectives
... Below are the class objectives, correlated to the NC Essential Standards and page numbers within your textbook. In the far right column you will see the required vocabulary of the unit as well. At the end of each unit, you should be able to define and apply all the required vocabulary words in order ...
... Below are the class objectives, correlated to the NC Essential Standards and page numbers within your textbook. In the far right column you will see the required vocabulary of the unit as well. At the end of each unit, you should be able to define and apply all the required vocabulary words in order ...
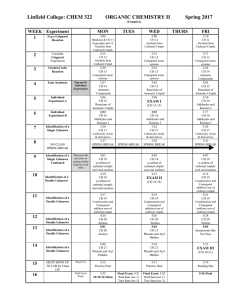
O V O O RO OH t-BuOOH, CH2Cl2, Ti(OPr-i)4(cat), 20 oC (L)
... These are not actually enantiomers of each other, but rather diastereomers, because the chirality of the C bearing the ethyl is the same in each case ((R)-). For the dihydroxylations, however, they function as the complementary systems to get enantiomeric products; the unofficial term pseudoenantiom ...
... These are not actually enantiomers of each other, but rather diastereomers, because the chirality of the C bearing the ethyl is the same in each case ((R)-). For the dihydroxylations, however, they function as the complementary systems to get enantiomeric products; the unofficial term pseudoenantiom ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034 PART-A
... ‘Aryldiazonium salt involves both in electrophilic and nucleophilic substitutions’. Justify. What is first order asymmetric transformation? Give an example. How do inductive and field effects affect the second substitution in aromatic systems? In 4-t-butylcyclohexanecarboxylic acid, trans form is mo ...
... ‘Aryldiazonium salt involves both in electrophilic and nucleophilic substitutions’. Justify. What is first order asymmetric transformation? Give an example. How do inductive and field effects affect the second substitution in aromatic systems? In 4-t-butylcyclohexanecarboxylic acid, trans form is mo ...
Lecture syllabus - Linfield College
... The course work consists of participation in 1) lectures, where facts and governing principles are discussed and where problems are worked out; and 2) in laboratory sessions, where common synthetic and analytical techniques are used to illustrate and expand upon principles taught in lecture. There i ...
... The course work consists of participation in 1) lectures, where facts and governing principles are discussed and where problems are worked out; and 2) in laboratory sessions, where common synthetic and analytical techniques are used to illustrate and expand upon principles taught in lecture. There i ...
Slide 1 - Alfred State College intranet site
... Formaldehyde (CH2═O) is the simplest aldehyde: •It is sold as formalin, a 37% aqueous solution used to preserve biological specimens. ...
... Formaldehyde (CH2═O) is the simplest aldehyde: •It is sold as formalin, a 37% aqueous solution used to preserve biological specimens. ...
Chapter 8. CARBONYL COMPOUNDS
... (mostly a proton) within a molecule and is accompanied by redistribution of electron density. Theoretically, any carbonyl compound having an α-hydrogen can exist as a tautomeric mixture. However, simple aldehydes and ketones exist mainly in the keto form. In acetone, for example, the enol form amoun ...
... (mostly a proton) within a molecule and is accompanied by redistribution of electron density. Theoretically, any carbonyl compound having an α-hydrogen can exist as a tautomeric mixture. However, simple aldehydes and ketones exist mainly in the keto form. In acetone, for example, the enol form amoun ...
Answers
... 5. These two metabolic reactions may occur in either direction. In which direction are they additions? What was added in each case? In which direction are they eliminations? Do they follow an acidic or basic elimination? (Hint: look at the structure of the starting alcohol.) addition of H2O ...
... 5. These two metabolic reactions may occur in either direction. In which direction are they additions? What was added in each case? In which direction are they eliminations? Do they follow an acidic or basic elimination? (Hint: look at the structure of the starting alcohol.) addition of H2O ...
Substitution reactions of carbonyl compounds at the α
... 2) Saponiofication and decarboxylation can occur in one step - provided the temperature is high enough (usually, 110 - 120°C will do it). 3) Note that all esters in the molecule are saponified, but only the 1,3dicarbonyl compounds can undergo decarboxylation. 4) As you’ll see in lecture, many differ ...
... 2) Saponiofication and decarboxylation can occur in one step - provided the temperature is high enough (usually, 110 - 120°C will do it). 3) Note that all esters in the molecule are saponified, but only the 1,3dicarbonyl compounds can undergo decarboxylation. 4) As you’ll see in lecture, many differ ...
F324 summary - Macmillan Academy
... Benzene • Benzene, C6H6, consists of a sigma-bonded framework of carbon and hydrogen atoms. • Above and below the plane of atoms is a p-bond, which consists of a delocalised electron cloud. • The Kekule structure of benzene assumes that all the bonds are localised i.e. cannot move. However, evidenc ...
... Benzene • Benzene, C6H6, consists of a sigma-bonded framework of carbon and hydrogen atoms. • Above and below the plane of atoms is a p-bond, which consists of a delocalised electron cloud. • The Kekule structure of benzene assumes that all the bonds are localised i.e. cannot move. However, evidenc ...
2d Oxidation of Food Homework
... alcohol by volume. This can be calculated from measurements taken using an instrument called a hydrometer. The hydrometer is floated in the liquid sample, before and after fermentation, to measure its specific gravity. %alcohol by volume = change in specific gravity of liquid x ƒ Where ƒ is a conver ...
... alcohol by volume. This can be calculated from measurements taken using an instrument called a hydrometer. The hydrometer is floated in the liquid sample, before and after fermentation, to measure its specific gravity. %alcohol by volume = change in specific gravity of liquid x ƒ Where ƒ is a conver ...
Ch 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I
... Nucleophilic Addition to the CarbonOxygen Double Bond • The most characteristic reaction of aldehydes and ketones is nucleophilic addition to the carbon-oxygen double bond • Examples: • Because the carbonyl is trigonal planar, the nucleophilic attack may occur from the top or the bottom, so therefo ...
... Nucleophilic Addition to the CarbonOxygen Double Bond • The most characteristic reaction of aldehydes and ketones is nucleophilic addition to the carbon-oxygen double bond • Examples: • Because the carbonyl is trigonal planar, the nucleophilic attack may occur from the top or the bottom, so therefo ...
Final Exam from 2006 - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State
... Drugs A and B below (Sertraline, the active ingredient in Zoloft) were synthesized in a lab. The amine group in compound A was neutralized with HCl to produce structure B, an ammonium ...
... Drugs A and B below (Sertraline, the active ingredient in Zoloft) were synthesized in a lab. The amine group in compound A was neutralized with HCl to produce structure B, an ammonium ...
EXPERIMENT 6: Reactions of Carbonyl Compounds: Qualitative
... steam distillation in the presence of dilute acid. The most commonly used for identification are the 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazones since simple carbonyl compounds give very colourful, highly crystalline solids. These solid derivatives can also be prepared very rapidly, which makes them an extremely us ...
... steam distillation in the presence of dilute acid. The most commonly used for identification are the 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazones since simple carbonyl compounds give very colourful, highly crystalline solids. These solid derivatives can also be prepared very rapidly, which makes them an extremely us ...
2015 CH 420 Take Home Quiz 3 March 24
... the aromatic pyrazole ring. Note the regioselectivity (one could “flip” either substrate horizontally to see the other theoretical product). In the boxes above, draw an arrow to the more nucleophilic nitrogen atom in the hydrazine substrate. In addition, circle the most electrophilic carbonyl in the ...
... the aromatic pyrazole ring. Note the regioselectivity (one could “flip” either substrate horizontally to see the other theoretical product). In the boxes above, draw an arrow to the more nucleophilic nitrogen atom in the hydrazine substrate. In addition, circle the most electrophilic carbonyl in the ...
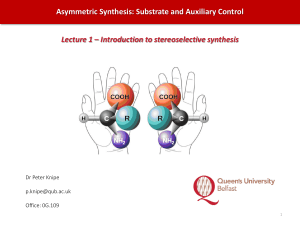
Asymmetric induction

Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.