An Overview of Organic Reactions
... relative Gibbs free energy This energy is released on the favored side of an equilibrium reaction The change in Gibbs free energy between products and reacts is written as “ΔG” If Keq > 1, energy is released to the surroundings (exergonic reaction) If Keq < 1, energy is absorbed from the surrounding ...
... relative Gibbs free energy This energy is released on the favored side of an equilibrium reaction The change in Gibbs free energy between products and reacts is written as “ΔG” If Keq > 1, energy is released to the surroundings (exergonic reaction) If Keq < 1, energy is absorbed from the surrounding ...
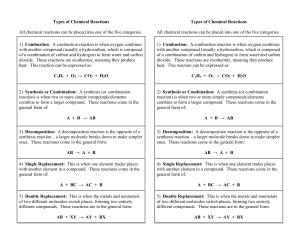
Types of Chemical Reactions
... general form of: A + BC → AC + B 5) Double Replacement: This is when the metals and nonmetals of two different molecules switch places, forming two entirely different compounds. These reactions are in the general form: ...
... general form of: A + BC → AC + B 5) Double Replacement: This is when the metals and nonmetals of two different molecules switch places, forming two entirely different compounds. These reactions are in the general form: ...
Chapter 21 aldehydes and ketones
... carbonyl carbon, but the “1” is usually omitted from the name. The ring is then numbered clockwise or counterclockwise to give the first substituent the lower number. ...
... carbonyl carbon, but the “1” is usually omitted from the name. The ring is then numbered clockwise or counterclockwise to give the first substituent the lower number. ...
Drug Design
... • The anti-cancer drug TAXOL is found in the Pacific Yew tree, but there is not a sufficient supply to meet demand. • Since Taxol is a very chiral molecule, one possibility is to make it synthetically. • The potential synthesis is very complicated and would require using several chiral auxilliaries. ...
... • The anti-cancer drug TAXOL is found in the Pacific Yew tree, but there is not a sufficient supply to meet demand. • Since Taxol is a very chiral molecule, one possibility is to make it synthetically. • The potential synthesis is very complicated and would require using several chiral auxilliaries. ...
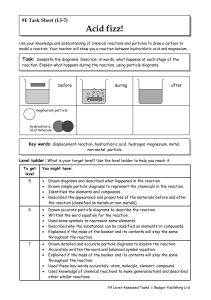
Year 9 Homework Task 9E-5 Reactions 5-7
... Acid fizz! Use your knowledge and understanding of chemical reactions and particles to draw a cartoon to model a reaction. Your teacher will show you a reaction between hydrochloric acid and magnesium. ...
... Acid fizz! Use your knowledge and understanding of chemical reactions and particles to draw a cartoon to model a reaction. Your teacher will show you a reaction between hydrochloric acid and magnesium. ...
Slide 1
... • A chiral auxilliary is a chiral molecule that is attached to the starting material during a synthesis that creates the appropriate stereo-chemical environment so that only one enantiomer is produced. ...
... • A chiral auxilliary is a chiral molecule that is attached to the starting material during a synthesis that creates the appropriate stereo-chemical environment so that only one enantiomer is produced. ...
Transition Metal Chemistry 2 2011.12.2 Ⅰ Fundamental
... (4) Role of transition metal catalysts in industrial acetic acid synthesis. Acetic acid is one of the most important chemicals and was produced by (destructive distillation of coal. History of acetic acid production revealed importance of transition metal catalysts. (4-1) Hydration of acetylene---M ...
... (4) Role of transition metal catalysts in industrial acetic acid synthesis. Acetic acid is one of the most important chemicals and was produced by (destructive distillation of coal. History of acetic acid production revealed importance of transition metal catalysts. (4-1) Hydration of acetylene---M ...
Study Guide for Exam 2 Chapter 12
... From their structural or line-angle formulas, write names of alkenes and alkynes. This includes cycloalkenes and compounds with more than one double bond. Where geometry is shown, identify cis and trans isomers From their names, draw condensed structural or line-angle formulas of alkenes and alkynes ...
... From their structural or line-angle formulas, write names of alkenes and alkynes. This includes cycloalkenes and compounds with more than one double bond. Where geometry is shown, identify cis and trans isomers From their names, draw condensed structural or line-angle formulas of alkenes and alkynes ...
FUNCTIONAL GROUPS
... • C-N, N-H, C=O bonds are polar, so molecules are usually polar • Primary and secondary amides experience hydrogen bonding • Soluble in water and other polar solvents, solubility decreases as the number of carbons increases • Primary amides have higher melting and boiling points than analogous ...
... • C-N, N-H, C=O bonds are polar, so molecules are usually polar • Primary and secondary amides experience hydrogen bonding • Soluble in water and other polar solvents, solubility decreases as the number of carbons increases • Primary amides have higher melting and boiling points than analogous ...
Organic Reactions
... • Addition of Halogen – homolytic fission: molecule breaks evenly • Free Radical formed – Free radical is a molecule with an unpaired electron ...
... • Addition of Halogen – homolytic fission: molecule breaks evenly • Free Radical formed – Free radical is a molecule with an unpaired electron ...
Final Exam Review Sheet Chemistry 110a/1998
... The final exam questions will seek an integrated understanding of the material found in chapters 1-13. You will be allowed to use the following when working your final exam: a calculator, molecular models, 13 pieces of unlined white 8.5 x 11 inch paper on which you may hand-write any information to ...
... The final exam questions will seek an integrated understanding of the material found in chapters 1-13. You will be allowed to use the following when working your final exam: a calculator, molecular models, 13 pieces of unlined white 8.5 x 11 inch paper on which you may hand-write any information to ...
Wed March 3 lecture
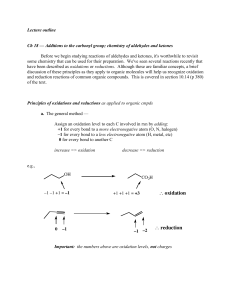
... Ch 18 — Additions to the carbonyl group; chemistry of aldehydes and ketones Before we begin studying reactions of aldehydes and ketones, it's worthwhile to revisit some chemistry that can be used for their preparation. We've seen several reactions recently that have been described as oxidations or r ...
... Ch 18 — Additions to the carbonyl group; chemistry of aldehydes and ketones Before we begin studying reactions of aldehydes and ketones, it's worthwhile to revisit some chemistry that can be used for their preparation. We've seen several reactions recently that have been described as oxidations or r ...
organic synthesis
... the nucleophile can attack from above and below there is an equal chance of each possibility a mixture of optically active isomers is produced only occurs if different groups are attached to the carbonyl group ...
... the nucleophile can attack from above and below there is an equal chance of each possibility a mixture of optically active isomers is produced only occurs if different groups are attached to the carbonyl group ...
File
... • contain the carbonyl group, C=O • carbonyl group polar as O greater electronegativity than C • when naming, carbon chain must include carbonyl group • number carbons from end closest to carbonyl group e.g. ...
... • contain the carbonyl group, C=O • carbonyl group polar as O greater electronegativity than C • when naming, carbon chain must include carbonyl group • number carbons from end closest to carbonyl group e.g. ...
Chapter 4
... Compute the amount of product produced or reactant consumed by two or more simultaneous reactions. ...
... Compute the amount of product produced or reactant consumed by two or more simultaneous reactions. ...
Carbonyl compounds
... Propanone with a boiling point 56°C is widely used as an inexpensive solvent in both the laboratory and industry. In industry, for example, propanone is used as a solvent for plastics, varnishes and grease. Organic Syntheses Carbonyl compounds are also used in the laboratory and in industry to synth ...
... Propanone with a boiling point 56°C is widely used as an inexpensive solvent in both the laboratory and industry. In industry, for example, propanone is used as a solvent for plastics, varnishes and grease. Organic Syntheses Carbonyl compounds are also used in the laboratory and in industry to synth ...
Chapter 23
... • contains –CO– (carbonyl group) -- between two other groups polar but cannot form strong hydrogen bonds with each other; however can form strong hydrogen bonds with water. • naming: 1. Identify the longest chain that includes the carbonyl group 2. Change the –e ending to -one 3. Number to give the ...
... • contains –CO– (carbonyl group) -- between two other groups polar but cannot form strong hydrogen bonds with each other; however can form strong hydrogen bonds with water. • naming: 1. Identify the longest chain that includes the carbonyl group 2. Change the –e ending to -one 3. Number to give the ...
اســـم المـــدرس: د
... How you can synthesize the following compound from the given starting material A) m-dibromobenzene from benzene ...
... How you can synthesize the following compound from the given starting material A) m-dibromobenzene from benzene ...
Ketones - WordPress.com
... red/orange when heated with an aldehyde. Ketones cannot be oxidised any further, so the solution remains blue. ...
... red/orange when heated with an aldehyde. Ketones cannot be oxidised any further, so the solution remains blue. ...
Q 1: Molecular formula of BHA is
... ( A) In alcohols - OH group always present at the end of the chain. ( B) Alcohols may contain one or more groups. ( C) butane-1-ol has higher boiling point than 2-methyl ...
... ( A) In alcohols - OH group always present at the end of the chain. ( B) Alcohols may contain one or more groups. ( C) butane-1-ol has higher boiling point than 2-methyl ...
Organic Chemistry Lecture Outline Carbonyl
... substitution reactions. Carbonyl groups bonded to large, bulky substituents (eg., tertiary carbons) react slower with nucleophiles than carbonyl groups with smaller, less bulky substituents. Electronic Effects Electronic effects influence the reactivity of the electrophilic carbonyl carbon in nucleo ...
... substitution reactions. Carbonyl groups bonded to large, bulky substituents (eg., tertiary carbons) react slower with nucleophiles than carbonyl groups with smaller, less bulky substituents. Electronic Effects Electronic effects influence the reactivity of the electrophilic carbonyl carbon in nucleo ...
Asymmetric induction

Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.