Organic Chemistry 1 1st Hour Exam Student ID # Name
... 1. Draw as many skeletal structures of the isomers (constitutional isomers or stereoisomers) for a compound with the molecular formula C5H10 as possible and name each isomer according to the IUPAC nomenclature. You may use the condensed formula to draw the structure if you want. ...
... 1. Draw as many skeletal structures of the isomers (constitutional isomers or stereoisomers) for a compound with the molecular formula C5H10 as possible and name each isomer according to the IUPAC nomenclature. You may use the condensed formula to draw the structure if you want. ...
Notes
... ‐ Incomplete combustion occurs when there is not enough oxygen available to react with the hydrocarbon ‐ As a result the following products are produced ‐ Carbon monoxide ‐ Solid carbon (soot) ‐ Water vapor ‐ Carbon dioxide Hydrocarbon + (insufficient) oxygen ‐‐> xC(s) + yCO(g) + zCO2(g) + H2O(g) ‐ ...
... ‐ Incomplete combustion occurs when there is not enough oxygen available to react with the hydrocarbon ‐ As a result the following products are produced ‐ Carbon monoxide ‐ Solid carbon (soot) ‐ Water vapor ‐ Carbon dioxide Hydrocarbon + (insufficient) oxygen ‐‐> xC(s) + yCO(g) + zCO2(g) + H2O(g) ‐ ...
C h e m g u i d e ... ALCOHOLS: ESTERIFICATION
... 4. Esters can be also be made by reacting alcohols with acyl chlorides such as ethanoyl chloride, CH3COCl. a) Suggest a disadvantage of making, say, ethyl ethanoate using this reaction. b) What advantage(s) does the method have over the reaction between ethanol and ethanoic acid? c) Write the equati ...
... 4. Esters can be also be made by reacting alcohols with acyl chlorides such as ethanoyl chloride, CH3COCl. a) Suggest a disadvantage of making, say, ethyl ethanoate using this reaction. b) What advantage(s) does the method have over the reaction between ethanol and ethanoic acid? c) Write the equati ...
Hydrogenation of fatty acid methyl ester to fatty alcohol
... Natural fatty alcohols are important raw materials for surfactants and lubricants and can be produced by catalytic hydrogenation of fatty acid methyl esters (FAME). Commercial multiphase processes are necessarily operated at high pressures and high hydrogen-to-ester mole ration owing to low solubili ...
... Natural fatty alcohols are important raw materials for surfactants and lubricants and can be produced by catalytic hydrogenation of fatty acid methyl esters (FAME). Commercial multiphase processes are necessarily operated at high pressures and high hydrogen-to-ester mole ration owing to low solubili ...
South Pasadena • Chemistry Name Period Date 3 · Organic
... Draw and name isomers of substituted hydrocarbons, by moving the side group to a different carbon. ...
... Draw and name isomers of substituted hydrocarbons, by moving the side group to a different carbon. ...
Formative 3.5 2014
... Heat with acidified Cr2O72-: colour change from orange to green. Heat with acidified MnO4-: colour change from purple to colourless Benedict’s test: warm with Benedict’s solution. Colour change from blue to brick red. Fehling’s Test: Warm with Fehling’s solution (a mixture of Fehling’s A and Fehling ...
... Heat with acidified Cr2O72-: colour change from orange to green. Heat with acidified MnO4-: colour change from purple to colourless Benedict’s test: warm with Benedict’s solution. Colour change from blue to brick red. Fehling’s Test: Warm with Fehling’s solution (a mixture of Fehling’s A and Fehling ...
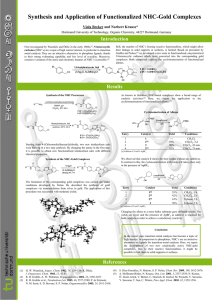
Synthesis and Application of Functionalized NHC
... Starting from 4-(Chloromethylbenzoyl)chloride, two new imidazolium salts were built up in a two step synthesis. By changing the amine in the first step, it is possible to obtain new functionalized imidazolium salts with different chemical properties. ...
... Starting from 4-(Chloromethylbenzoyl)chloride, two new imidazolium salts were built up in a two step synthesis. By changing the amine in the first step, it is possible to obtain new functionalized imidazolium salts with different chemical properties. ...
Organic Chemistry - Centennial College Libraries
... Esters are compounds that contain –COO – between two alkyl groups. They are formed from a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Amides are compounds that contain the H2NCOO— group. They are formed from ammonia and carboxylic ...
... Esters are compounds that contain –COO – between two alkyl groups. They are formed from a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Amides are compounds that contain the H2NCOO— group. They are formed from ammonia and carboxylic ...
F017006 - Fluorous Technologies
... F-PMB-OH is the fluorous equivalent of p-methoxybenzyl alcohol (PMB-OH) used in protecting alcohols in multi-step organic synthesis. Protection of an alcohol with F-PMB-OH and deprotection are achieved under traditional reaction conditions, with the advantage that products containing the F-PMB group ...
... F-PMB-OH is the fluorous equivalent of p-methoxybenzyl alcohol (PMB-OH) used in protecting alcohols in multi-step organic synthesis. Protection of an alcohol with F-PMB-OH and deprotection are achieved under traditional reaction conditions, with the advantage that products containing the F-PMB group ...
Isomer - Fort Bend ISD / Homepage
... • Contributes to the diversity of organic compounds. • Hydrocarbons are: – composed of hydrogen and carbon. – excellent fuels because the covalent bond between the carbon and hydrogen contain a lot of energy. – composed of partially decomposed organisms. – Hydrophobic because they are long chains of ...
... • Contributes to the diversity of organic compounds. • Hydrocarbons are: – composed of hydrogen and carbon. – excellent fuels because the covalent bond between the carbon and hydrogen contain a lot of energy. – composed of partially decomposed organisms. – Hydrophobic because they are long chains of ...
Organic Chemistry - WilsonSCH4U1-07-2015
... products: alkyl halide + water • This reaction is a qualitative test for the different types of alcohols because the rate of the reaction differs greatly for a primary, secondary and tertiary alcohol due to the solubility of the resulting alkyl halides ...
... products: alkyl halide + water • This reaction is a qualitative test for the different types of alcohols because the rate of the reaction differs greatly for a primary, secondary and tertiary alcohol due to the solubility of the resulting alkyl halides ...
9 carbene complexes in olefin metathesis and ring
... demanding applications such as automotive hoses and gaskets and as rollers for printing presses. The product is made by treatment of cyclooctene with a Ziegler-type catalyst prepared from WCl6, excess EtAlCl2, and an activator such as ethanol, 2,6-dit-butyl-4-methylphenol, or an allyl aryl ether. Or ...
... demanding applications such as automotive hoses and gaskets and as rollers for printing presses. The product is made by treatment of cyclooctene with a Ziegler-type catalyst prepared from WCl6, excess EtAlCl2, and an activator such as ethanol, 2,6-dit-butyl-4-methylphenol, or an allyl aryl ether. Or ...
Reductions of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives - IDC
... As a rule, the carbonyl group does not add hydrogen as readily as do the carbon-carbon double and triple bonds. Thus, it is fairly easy to reduce an alkene or alkyne function without affecting any carbonyl functions in the same molecule. By using a platinum catalyst and increased temperature and pre ...
... As a rule, the carbonyl group does not add hydrogen as readily as do the carbon-carbon double and triple bonds. Thus, it is fairly easy to reduce an alkene or alkyne function without affecting any carbonyl functions in the same molecule. By using a platinum catalyst and increased temperature and pre ...
Dehydration of 3,3-dimethyl-2-butanol to make alkenes March 1 & 3
... Elimination Reactions Let’s Review: – Elimination reaction: a fundamental organic reaction Two species are eliminated from a substrate Elimination mean’s they are gone, gone, gone – NOT a substitution ...
... Elimination Reactions Let’s Review: – Elimination reaction: a fundamental organic reaction Two species are eliminated from a substrate Elimination mean’s they are gone, gone, gone – NOT a substitution ...
File
... Catalysed by: NiL4 where L = P[O(o-tolyl)]3 Addition of H-C≡N to double bonds catalysed by Ni, Cu and Pd complexes Strong donor phosphines do not give turnover Reaction tends to isomerise internal alkenes to give terminal products Most important hydrocyanation is hydrocyanation of butadiene to give ...
... Catalysed by: NiL4 where L = P[O(o-tolyl)]3 Addition of H-C≡N to double bonds catalysed by Ni, Cu and Pd complexes Strong donor phosphines do not give turnover Reaction tends to isomerise internal alkenes to give terminal products Most important hydrocyanation is hydrocyanation of butadiene to give ...
Unit 4_Carbonyl and carboxylic acid questions
... 6. The oxidation of an alkene with trioxygen (ozone), followed by hydrolysis (process is called ozonolysis) gives 2 carbonyl compounds: ...
... 6. The oxidation of an alkene with trioxygen (ozone), followed by hydrolysis (process is called ozonolysis) gives 2 carbonyl compounds: ...
CARBONYL COMPOUNDS
... and HCHO (MR = 30) and put these compounds in order with respect to increasing boiling point. C2H6 CH3OH HCHO Methanal is a gas, other important carbonyl compounds are …………………... Early members are soluble in water due to ……………….. ………………. between hydrogen from water and oxygen from the carboxylic gro ...
... and HCHO (MR = 30) and put these compounds in order with respect to increasing boiling point. C2H6 CH3OH HCHO Methanal is a gas, other important carbonyl compounds are …………………... Early members are soluble in water due to ……………….. ………………. between hydrogen from water and oxygen from the carboxylic gro ...
Slide 1
... Monoalkyl esters of long chain fatty acids derived from renewable lipid feedstocks3 Produced from renewable vegetable oils, waste cooking oil, animal fat and non-edible oils ...
... Monoalkyl esters of long chain fatty acids derived from renewable lipid feedstocks3 Produced from renewable vegetable oils, waste cooking oil, animal fat and non-edible oils ...
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
... • Can aldehydes and ketones set up hydrogen bonds with each other? • Can they set them up with water? ...
... • Can aldehydes and ketones set up hydrogen bonds with each other? • Can they set them up with water? ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.