File
... using a large excess of concentrated acid (HCl and zinc chloride) • we can distinguish between 1°, 2° and 3° alcohols by their different rates of reaction using the Lucas Test • order of reactivity: – tertiary > secondary > primary ...
... using a large excess of concentrated acid (HCl and zinc chloride) • we can distinguish between 1°, 2° and 3° alcohols by their different rates of reaction using the Lucas Test • order of reactivity: – tertiary > secondary > primary ...
Chapter 4-Carbon & Diversity of Life
... Can be bonded to the carbon or a different atom Referred to as Methylated Compounds Addition of a methyl group to DNA effects gene expression and arrangement of methyl groups in sex hormones affects their shape and funtion Ex: 5-Methyl cytidine (part of DNA that has been modified by adding a methyl ...
... Can be bonded to the carbon or a different atom Referred to as Methylated Compounds Addition of a methyl group to DNA effects gene expression and arrangement of methyl groups in sex hormones affects their shape and funtion Ex: 5-Methyl cytidine (part of DNA that has been modified by adding a methyl ...
- professional publication
... Reaction. Mechanism and Stereochemistry of S N2 reaction, Mechanism and Stereochemistry of SN1 Reaction. Rearrangement of Carbocation, S N2 versus SN1 Reactions, Reactivity of Alkyl Halides in SN1 and SN2, Factors Affecting SN1 and SN2. ...
... Reaction. Mechanism and Stereochemistry of S N2 reaction, Mechanism and Stereochemistry of SN1 Reaction. Rearrangement of Carbocation, S N2 versus SN1 Reactions, Reactivity of Alkyl Halides in SN1 and SN2, Factors Affecting SN1 and SN2. ...
blank lecture 11
... PHYSICAL PROPERTIES (continued) • Because of the polarity of the C=O group, these groups can interact, but the attraction is not as strong as hydrogen bonding. • This makes the boiling point of aldehydes and ketones ___________ than alkanes, but _________ than alcohols. ...
... PHYSICAL PROPERTIES (continued) • Because of the polarity of the C=O group, these groups can interact, but the attraction is not as strong as hydrogen bonding. • This makes the boiling point of aldehydes and ketones ___________ than alkanes, but _________ than alcohols. ...
Practical and selective aerobic oxidation of alcohols to
... states, supported on a variety of metarials.11-15 In this work, Ru/Al2O3 was chosen as it is commercially available at a reasonable cost, thus accessible to most synthetic laboratories. The use of this catalyst for the selective oxidation of alcohols to carbonyl compounds was first proposed by Mizun ...
... states, supported on a variety of metarials.11-15 In this work, Ru/Al2O3 was chosen as it is commercially available at a reasonable cost, thus accessible to most synthetic laboratories. The use of this catalyst for the selective oxidation of alcohols to carbonyl compounds was first proposed by Mizun ...
Sample 3 - University of Puget Sound
... between stable ecosystems and global welfare.1 Since chemical processes rely on fossil fuels as a source of energy and primary feedstock, reducing this fuel dependence poses a serious challenge for the chemical industry.1 The need to reduce energy consumption is driving many chemistry related fields ...
... between stable ecosystems and global welfare.1 Since chemical processes rely on fossil fuels as a source of energy and primary feedstock, reducing this fuel dependence poses a serious challenge for the chemical industry.1 The need to reduce energy consumption is driving many chemistry related fields ...
Ruthenium(II) Complexes Bearing a Pyridyl-Supported Pyrazolyl
... obtained by Claisen condensation of 4 with 3,3-dimethyl-2butone followed by reacting with hydrazine hydrate. The ligand precursor 6 was efficiently prepared by the reaction of 5 with 1-iodobutane in refluxing acetonitrile. When the tert-butyl group in 5 was substituted by a methyl group, the corresp ...
... obtained by Claisen condensation of 4 with 3,3-dimethyl-2butone followed by reacting with hydrazine hydrate. The ligand precursor 6 was efficiently prepared by the reaction of 5 with 1-iodobutane in refluxing acetonitrile. When the tert-butyl group in 5 was substituted by a methyl group, the corresp ...
Name: Chem 22 Final exam Spring `00 What product is formed when
... a) Thiols have a pka values of about 16, and they are stronger acids than alcohols. b) Thiols have a pka values of about 16, and they are weaker acids than alcohols c) Thiols have a pka values of about 10, and they are stronger acids than alcohols d) Thiols do not have a pka values. e) Thiols have a ...
... a) Thiols have a pka values of about 16, and they are stronger acids than alcohols. b) Thiols have a pka values of about 16, and they are weaker acids than alcohols c) Thiols have a pka values of about 10, and they are stronger acids than alcohols d) Thiols do not have a pka values. e) Thiols have a ...
C h e m g u i d e ... ALCOHOLS: THE REACTION WITH SODIUM
... a) Why is it important to test the pH of the liquid before adding the sodium? b) What would you observe if the liquid was actually an alcohol? c) Observing this isn’t enough to be sure that you have an alcohol. What else might cause the result you described in part (b)? d) Suppose you added a small ...
... a) Why is it important to test the pH of the liquid before adding the sodium? b) What would you observe if the liquid was actually an alcohol? c) Observing this isn’t enough to be sure that you have an alcohol. What else might cause the result you described in part (b)? d) Suppose you added a small ...
Chapter 17 Aldehydes and Ketones
... The most common laboratory reagent for the reduction of an aldehyde or ketone is sodium borohydride, NaBH4. • This reagent contains hydrogen in the form of hydride ion, H:-. • In a reduction by sodium borohydride, hydride ion adds to the partially positive carbonyl carbon which leaves a negative cha ...
... The most common laboratory reagent for the reduction of an aldehyde or ketone is sodium borohydride, NaBH4. • This reagent contains hydrogen in the form of hydride ion, H:-. • In a reduction by sodium borohydride, hydride ion adds to the partially positive carbonyl carbon which leaves a negative cha ...
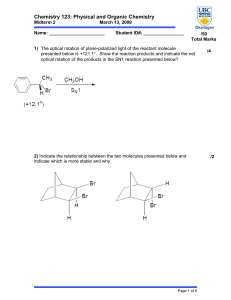
Chemistry 123: Physical and Organic Chemistry
... 17) CO2 is a greenhouse gas because…. (A) It absorbs infrared radiation (B) It has a high entropy (C) It makes plants grow better in a greenhouse (D) It has a high enthalpy of formation 18) Carbon dating is possible due to; (A) open minded rate laws (B) Irradiation of N2(g) by cosmic radiation (C) N ...
... 17) CO2 is a greenhouse gas because…. (A) It absorbs infrared radiation (B) It has a high entropy (C) It makes plants grow better in a greenhouse (D) It has a high enthalpy of formation 18) Carbon dating is possible due to; (A) open minded rate laws (B) Irradiation of N2(g) by cosmic radiation (C) N ...
Exam practice answers
... The N in NH3 is −3 and the N in HNO3 is +5 . An increase in oxidation number involves a loss of electrons, which is oxidation (OILRIG). (ii) Le Chatelier’s principle states that if a closed system under equilibrium is subject to a change, the system will move in such a way as to minimise the effect ...
... The N in NH3 is −3 and the N in HNO3 is +5 . An increase in oxidation number involves a loss of electrons, which is oxidation (OILRIG). (ii) Le Chatelier’s principle states that if a closed system under equilibrium is subject to a change, the system will move in such a way as to minimise the effect ...
In hydrogenation and hydrogenolysis chemical reactions
... Besenbacher and his colleagues have one of the world's fastest scanning tunneling microscopes, which has atomic-scale resolution. With it, they could see how quickly hydrogen atoms diffused across iron oxide in the presence of water. To explain the fundamental mechanisms of how that happened, Mavrik ...
... Besenbacher and his colleagues have one of the world's fastest scanning tunneling microscopes, which has atomic-scale resolution. With it, they could see how quickly hydrogen atoms diffused across iron oxide in the presence of water. To explain the fundamental mechanisms of how that happened, Mavrik ...
Chem 3.5 Answers #3
... The presence of the OH group on propanol allows hydrogen bonding to occur between propanol molecules. The attractions between propane molecules are weak Van der Waals forces and so the energy needed to separate its molecules from each other is much less giving a lower B. Pt. The OH bond allows the a ...
... The presence of the OH group on propanol allows hydrogen bonding to occur between propanol molecules. The attractions between propane molecules are weak Van der Waals forces and so the energy needed to separate its molecules from each other is much less giving a lower B. Pt. The OH bond allows the a ...
TM - Intro to Organi..
... – Propane (C3H8) – a fuel for heating homes and cooking. – Octane (C8H18) – a fuel used for automobile combustion – Dodecadecane (C20H42) – solid wax used for making candles and as a lubricant All of these are straight-chained hydrocarbons (CnH2n+2). ...
... – Propane (C3H8) – a fuel for heating homes and cooking. – Octane (C8H18) – a fuel used for automobile combustion – Dodecadecane (C20H42) – solid wax used for making candles and as a lubricant All of these are straight-chained hydrocarbons (CnH2n+2). ...
Organic Tutorial 1st Year HT01
... 3. "Mechanisms of organic reactions", H.Maskill, OUP Primer No 45. Introduction Nucleophilic attack at carbonyl compounds was covered in a previous tutorial. This tutorial aims to cover another major function of carbonyl compounds: enolisation and subsequent reaction. A proton a to a carbonyl centre ...
... 3. "Mechanisms of organic reactions", H.Maskill, OUP Primer No 45. Introduction Nucleophilic attack at carbonyl compounds was covered in a previous tutorial. This tutorial aims to cover another major function of carbonyl compounds: enolisation and subsequent reaction. A proton a to a carbonyl centre ...
4.5 Topic Checklist Carbonyl Compounds
... basis of a simple chemical test to distinguish between aldehydes and ketones (e.g. Fehling’s solution and Tollens’ reagent) appreciate the hazards of synthesis using HCN/KCN know that aldehydes can be reduced to primary alcohols and ketones to secondary alcohols using reducing agents such as NaBH4. ...
... basis of a simple chemical test to distinguish between aldehydes and ketones (e.g. Fehling’s solution and Tollens’ reagent) appreciate the hazards of synthesis using HCN/KCN know that aldehydes can be reduced to primary alcohols and ketones to secondary alcohols using reducing agents such as NaBH4. ...
Dr. György Keglevich e-mail: Title of the
... 1: The use of the microwave technique in the synthesis of P-esters and P-oxides Consultant: Dr. Nóra Zs. Kiss Assistant Professor The purpose is to synthesize phosphoric-, phosphonic and phosphinic ester, as well as phosphine oxide intermediates by MW-assisted direct esterification, alkylating ester ...
... 1: The use of the microwave technique in the synthesis of P-esters and P-oxides Consultant: Dr. Nóra Zs. Kiss Assistant Professor The purpose is to synthesize phosphoric-, phosphonic and phosphinic ester, as well as phosphine oxide intermediates by MW-assisted direct esterification, alkylating ester ...
Synthesis of Ligands for the Functionalization of Magnetic
... ligands attached to iron nanoparticles is the best choice for catalyzing the Mukaiyama-Aldol reaction. The synthesis of the ligand portion of the project has faced many problems. For instance, in step 1, the heating required is evaporating the small reaction solution, and NMR analysis has been showi ...
... ligands attached to iron nanoparticles is the best choice for catalyzing the Mukaiyama-Aldol reaction. The synthesis of the ligand portion of the project has faced many problems. For instance, in step 1, the heating required is evaporating the small reaction solution, and NMR analysis has been showi ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.