Topic 10 IB Chemistry Definitions
... increased intermolecular forces. Often, long carbon chains can negate the effect of a polar end molecule is non-polar. Addition of water. Ethanol can be formed from addition of water to ...
... increased intermolecular forces. Often, long carbon chains can negate the effect of a polar end molecule is non-polar. Addition of water. Ethanol can be formed from addition of water to ...
2.10 Organic synthesis – Oxidation of alcohols
... • The reaction will proceed at a constant temperature (i.e. the solvent's boiling point.). •Any vapours given off are cooled back to liquid, and fall back into the reaction vessel • Useful for performing chemical reactions under controlled conditions that require substantial time for completion. ...
... • The reaction will proceed at a constant temperature (i.e. the solvent's boiling point.). •Any vapours given off are cooled back to liquid, and fall back into the reaction vessel • Useful for performing chemical reactions under controlled conditions that require substantial time for completion. ...
Chapter 17 - Ellis Benjamin
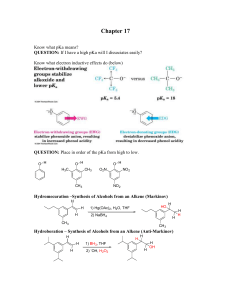
... Chapter 17 Know what pKa means? QUESTION: If I have a high pKa will I dissociates easily? Know what electron inductive effects do (below) ...
... Chapter 17 Know what pKa means? QUESTION: If I have a high pKa will I dissociates easily? Know what electron inductive effects do (below) ...
Nugget
... involving fully characterized mononuclear Ru(II) complexes, with overall retention of the metal oxidation state, has been demonstrated; O-O bond formation is intramolecular and involves a single metal center. Science 2009, 324, 74 ...
... involving fully characterized mononuclear Ru(II) complexes, with overall retention of the metal oxidation state, has been demonstrated; O-O bond formation is intramolecular and involves a single metal center. Science 2009, 324, 74 ...
Exam 4
... 3) The sum of the masses of two hydrogen atoms (mass number 1) and two neutrons is 4.0330. Why does this differ from the mass of a helium atom (4.0026)? a) Some hydrogen atoms are heavier than others b) The difference is the binding energy of the helium nucleus c) The difference is the experimental ...
... 3) The sum of the masses of two hydrogen atoms (mass number 1) and two neutrons is 4.0330. Why does this differ from the mass of a helium atom (4.0026)? a) Some hydrogen atoms are heavier than others b) The difference is the binding energy of the helium nucleus c) The difference is the experimental ...
REACTIONS OF ALCOHOLS
... resulting alkyl halides • Tertiary Alcohol→ turns cloudy immediately (the alkyl halide is not soluble in water and precipitates out) • Secondary Alcohol → turns cloudy after 5 minutes • Primary Alcohol → takes much longer than 5 minutes to turn cloudy ...
... resulting alkyl halides • Tertiary Alcohol→ turns cloudy immediately (the alkyl halide is not soluble in water and precipitates out) • Secondary Alcohol → turns cloudy after 5 minutes • Primary Alcohol → takes much longer than 5 minutes to turn cloudy ...
Study Guide for Exam 2 Chapter 12
... Describe the physical properties of alcohols, thiols, and ethers. Know the attractive forces between these molecules, their relative strengths, and their effects on solubility in water and melting and boiling points. Be able to complete chemical equations for characteristic reactions of alcohols (ac ...
... Describe the physical properties of alcohols, thiols, and ethers. Know the attractive forces between these molecules, their relative strengths, and their effects on solubility in water and melting and boiling points. Be able to complete chemical equations for characteristic reactions of alcohols (ac ...
Workshop 5
... Consider the chlorination of methane. The initiation step involves the dissociation of Cl2 using either light or heat. Alternatively, tetramethyl lead ((CH3)4Pb) can be added to initiate this same reaction at a lower temperature. The Pb-C bond energy in (CH3)4Pb is 49 kcal/mol. a. Show the initiatio ...
... Consider the chlorination of methane. The initiation step involves the dissociation of Cl2 using either light or heat. Alternatively, tetramethyl lead ((CH3)4Pb) can be added to initiate this same reaction at a lower temperature. The Pb-C bond energy in (CH3)4Pb is 49 kcal/mol. a. Show the initiatio ...
1) What is a biochemical cycle? 2) Oxygen is released as a waste
... 2) Oxygen is released as a waste product by plants during the process of Animals takes in this oxygen and release it as ...
... 2) Oxygen is released as a waste product by plants during the process of Animals takes in this oxygen and release it as ...
Organic Reactions Note – Student
... carbon atoms and in presence of OH- ion (basic solution) Dehydration Reactions ...
... carbon atoms and in presence of OH- ion (basic solution) Dehydration Reactions ...
Slide 1
... presence of base or by heating a mixture of the reactants at high temperatures ranging from 150-220°C in the absence of catalyst.(1) ...
... presence of base or by heating a mixture of the reactants at high temperatures ranging from 150-220°C in the absence of catalyst.(1) ...
Markovnikov`s Rule
... Explain why the H-rich get H-richer (them that has the Hs gits the H). Hint: it might be easier if you ignore the Hs. Then again, it might not. ...
... Explain why the H-rich get H-richer (them that has the Hs gits the H). Hint: it might be easier if you ignore the Hs. Then again, it might not. ...
Chapter 4_part 1
... The parent name is that of the longest chain that contains the C=C. Number the chain from the end that gives the lower numbers to the carbons of the C=C. Locate the C=C by the number of its first carbon. Use the ending -ene to show the presence of the C=C Branched-chain alkenes are named i ...
... The parent name is that of the longest chain that contains the C=C. Number the chain from the end that gives the lower numbers to the carbons of the C=C. Locate the C=C by the number of its first carbon. Use the ending -ene to show the presence of the C=C Branched-chain alkenes are named i ...
HONORS: UNIT 2B: Antacids Below are the class objectives
... Define components of a chemical reaction/criteria to determine is a chemical reaction has occurred Practice converting from word equations to formula equations Define and predict products for synthesis (standard: binary ionic compound model) &decomposition reactions (binary ionic and metal carbonate ...
... Define components of a chemical reaction/criteria to determine is a chemical reaction has occurred Practice converting from word equations to formula equations Define and predict products for synthesis (standard: binary ionic compound model) &decomposition reactions (binary ionic and metal carbonate ...
Unit 5 Study Guide
... 14. Which element can replace copper in a single replacement reaction? a. Mg c. Neither b. Pb d. Both 15. Which of the following displacement reactions will NOT occur? a) CuSO4(aq) + Zn(s) ---> Cu(s) + ZnSO4(aq) b) 2NaNO3(aq) + Zn(s) ---> 2Na(s) + Zn(NO3)2(aq) c) 2AgNO3(aq) + Zn(s) ---> 2Ag(s) + Zn( ...
... 14. Which element can replace copper in a single replacement reaction? a. Mg c. Neither b. Pb d. Both 15. Which of the following displacement reactions will NOT occur? a) CuSO4(aq) + Zn(s) ---> Cu(s) + ZnSO4(aq) b) 2NaNO3(aq) + Zn(s) ---> 2Na(s) + Zn(NO3)2(aq) c) 2AgNO3(aq) + Zn(s) ---> 2Ag(s) + Zn( ...
snc 2do unit: chemistry unit test review questions
... D) carbon monoxide E) rubidium oxide F) nitric acid G) copper (II) sulphide H) aluminum sulphate I) silicon dioxide J) phosphorus pentachloride 3. What do the elements in the same group all have in common? 4. Aluminum and oxygen react to form a compound. a) What is the name of the compound formed? b ...
... D) carbon monoxide E) rubidium oxide F) nitric acid G) copper (II) sulphide H) aluminum sulphate I) silicon dioxide J) phosphorus pentachloride 3. What do the elements in the same group all have in common? 4. Aluminum and oxygen react to form a compound. a) What is the name of the compound formed? b ...
A Summary of Organometallic Chemistry
... Althought the oxidative addition of X–Y to M gives a complex that formally results from the insertion of a metal atom into the covalent X–Y-bond, the term “insertion” (Einschiebung) is reserved for reactions in which a molecule (which must possess a multiple bond) is inserted into a metal-ligand bon ...
... Althought the oxidative addition of X–Y to M gives a complex that formally results from the insertion of a metal atom into the covalent X–Y-bond, the term “insertion” (Einschiebung) is reserved for reactions in which a molecule (which must possess a multiple bond) is inserted into a metal-ligand bon ...
Organometallic Chemistry
... Chain-end control mechanism: the polymer chain determines the stereospecificity of the final polymer. ...
... Chain-end control mechanism: the polymer chain determines the stereospecificity of the final polymer. ...
Organic Synthesis
... Most synthesis problems which we see in the lab are not quite so straight forward as the one above. Usually, we have a target compound, but no specific starting material. Instead, we try to come up with a synthesis from “readily available materials”. What do we mean by that? It may simply mean, “wh ...
... Most synthesis problems which we see in the lab are not quite so straight forward as the one above. Usually, we have a target compound, but no specific starting material. Instead, we try to come up with a synthesis from “readily available materials”. What do we mean by that? It may simply mean, “wh ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.