Experiment #3: Asymmetric Synthesis – Use of a Chiral Manganese
... mono-(+)-tartrate. In a 150 mL beaker, L-(+)-Tartaric acid (7.5 g, 0.05 mol) is dissolved in 25 mL of distilled water. The solution is stirred as 11.4 g (12.2 mL, 0.10 mol) of 1,2diaminocyclohexane (a mixture of cis and trans isomers) is added slowly in one portion. (Note: The addition of the diamin ...
... mono-(+)-tartrate. In a 150 mL beaker, L-(+)-Tartaric acid (7.5 g, 0.05 mol) is dissolved in 25 mL of distilled water. The solution is stirred as 11.4 g (12.2 mL, 0.10 mol) of 1,2diaminocyclohexane (a mixture of cis and trans isomers) is added slowly in one portion. (Note: The addition of the diamin ...
Carbon Chemistry
... Functional Groups / Characteristics Organic molecules have different properties as a result of their structures which is dependent on their functional groups. If the functional group is the variable portion of the molecule = R Group Hydroxyl group – attract water, helping to dissolve organic co ...
... Functional Groups / Characteristics Organic molecules have different properties as a result of their structures which is dependent on their functional groups. If the functional group is the variable portion of the molecule = R Group Hydroxyl group – attract water, helping to dissolve organic co ...
Year 9 Homework Task 9E-5 Reactions 5-7
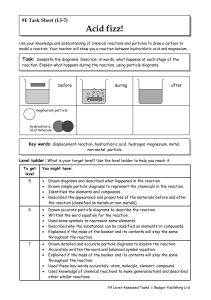
... Task: Complete the diagrams. Describe, in words, what happens at each stage of the reaction. Explain what happens during the reaction, using particle diagrams. ...
... Task: Complete the diagrams. Describe, in words, what happens at each stage of the reaction. Explain what happens during the reaction, using particle diagrams. ...
بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
... 6 – There are 3 significant figures in the number 20.031. 7 – Nonmetals react with each other to form ionic compounds 8 –In osmosis, the solvent passes from the concentrated to the dilute solution ...
... 6 – There are 3 significant figures in the number 20.031. 7 – Nonmetals react with each other to form ionic compounds 8 –In osmosis, the solvent passes from the concentrated to the dilute solution ...
Michael Carney - University of Wisconsin
... First published as an Advance Article on the web 16th April 2007 DOI: 10.1039/b702197f This report describes the synthesis and characterization of metal halide complexes (M = Mn, Fe, Co) supported by a new family of pendant donor-modified a-diimine ligands. The donor (N, O, P, S) substituent is link ...
... First published as an Advance Article on the web 16th April 2007 DOI: 10.1039/b702197f This report describes the synthesis and characterization of metal halide complexes (M = Mn, Fe, Co) supported by a new family of pendant donor-modified a-diimine ligands. The donor (N, O, P, S) substituent is link ...
Chapter 3. The Concept of Protecting Functional Groups
... benzylidene and ethylidene derivatives, respectively. ...
... benzylidene and ethylidene derivatives, respectively. ...
Episode 21
... 4. When was nylon first developed? Why was its development so essential? Before World War II. A substitute for silk. 5. What was the first organic synthesis? Wöhler's synthesis of urea. 6. What is a hydrocarbon? A compound formed only of hydrogen and carbon atoms. 7. What is meant by an isomer? Two ...
... 4. When was nylon first developed? Why was its development so essential? Before World War II. A substitute for silk. 5. What was the first organic synthesis? Wöhler's synthesis of urea. 6. What is a hydrocarbon? A compound formed only of hydrogen and carbon atoms. 7. What is meant by an isomer? Two ...
Episode 21
... 4. When was nylon first developed? Why was its development so essential? Before World War II. A substitute for silk. 5. What was the first organic synthesis? Wöhler's synthesis of urea. 6. What is a hydrocarbon? A compound formed only of hydrogen and carbon atoms. 7. What is meant by an isomer? Two ...
... 4. When was nylon first developed? Why was its development so essential? Before World War II. A substitute for silk. 5. What was the first organic synthesis? Wöhler's synthesis of urea. 6. What is a hydrocarbon? A compound formed only of hydrogen and carbon atoms. 7. What is meant by an isomer? Two ...
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
... The tetrahedral intermediate loses HCl in a single step, one in which the H+ is transferred to a second molecule of alcohol and the Cl comes off as Cl-. It is important to notice that the neutral alcohol oxygen serves as the nucleophile. The O-H bond is not broken until after the C-O bond is formed. ...
... The tetrahedral intermediate loses HCl in a single step, one in which the H+ is transferred to a second molecule of alcohol and the Cl comes off as Cl-. It is important to notice that the neutral alcohol oxygen serves as the nucleophile. The O-H bond is not broken until after the C-O bond is formed. ...
UNIVERSITAT ROVIRA I VIRGILI
... different reaction media. It was found that the polyketone products produced with the phosphine catalysts show number-average molecular weights up to five times bigger than those obtained with the diphosphonium-diphosphine catalysts. The results have been interpreted in terms of faster chain-transfe ...
... different reaction media. It was found that the polyketone products produced with the phosphine catalysts show number-average molecular weights up to five times bigger than those obtained with the diphosphonium-diphosphine catalysts. The results have been interpreted in terms of faster chain-transfe ...
chemistry pretest - the Biology Scholars Program Wiki
... Below are 20 questions that represent some of the major concepts you have encountered in Chem105/205 (Chem120) and Chem211/212. Concepts surveyed in this pretest establish the foundations for the chemistry component of the biochemistry course. Since for most of you it has been a while since you have ...
... Below are 20 questions that represent some of the major concepts you have encountered in Chem105/205 (Chem120) and Chem211/212. Concepts surveyed in this pretest establish the foundations for the chemistry component of the biochemistry course. Since for most of you it has been a while since you have ...
Chem+174–Lecture+12a..
... to ligands like CO, CN-, etc. Tolman observed for Ni(CO)3L that the carbonyl stretching frequency decreases as the donor ability of the R-group increases (i.e., PCy3 (2056 cm-1) vs. P(OMe)3 (2070 cm-1) vs. ...
... to ligands like CO, CN-, etc. Tolman observed for Ni(CO)3L that the carbonyl stretching frequency decreases as the donor ability of the R-group increases (i.e., PCy3 (2056 cm-1) vs. P(OMe)3 (2070 cm-1) vs. ...
슬라이드 1
... Isotope effects indicate that the collapse of the adduct by reductive elimination is the rate determining step. The more easily reduced, the more reactive is the compound toward cuprate reagents. Compounds such as a,b-unsaturated esters and nitriles, which are not as easily reduced as the correspond ...
... Isotope effects indicate that the collapse of the adduct by reductive elimination is the rate determining step. The more easily reduced, the more reactive is the compound toward cuprate reagents. Compounds such as a,b-unsaturated esters and nitriles, which are not as easily reduced as the correspond ...
22-2 Alcohols, Ethers, and Amines
... • To name ethers say the first alphabetical R followed by the second alphabetical R then the word ether. • If both are identical, say di- the R group with ...
... • To name ethers say the first alphabetical R followed by the second alphabetical R then the word ether. • If both are identical, say di- the R group with ...
Class X Chemistry-Carbon and its compounds
... (d) C2H5OH + Na (e) CH3COOH + NaOH 16. An organic compound with molecular formula C2H4O2 produces brisk effervescence on addition of sodium carbonate/bicarbonate. (a) Identify the organic compound. (b) Name the gas evolved. (c) How will you test this gas? (d) Write a chemical equation for the above ...
... (d) C2H5OH + Na (e) CH3COOH + NaOH 16. An organic compound with molecular formula C2H4O2 produces brisk effervescence on addition of sodium carbonate/bicarbonate. (a) Identify the organic compound. (b) Name the gas evolved. (c) How will you test this gas? (d) Write a chemical equation for the above ...
Organic 2 PPT
... ether is the one commonly called just “ether” –was the first reliable general anesthetic –dangerous- highly flammable, also causes nausea ethers are fairly soluble in water Alcohol used for fuel in the future? ...
... ether is the one commonly called just “ether” –was the first reliable general anesthetic –dangerous- highly flammable, also causes nausea ethers are fairly soluble in water Alcohol used for fuel in the future? ...
Chapter 11: Reactions at an sp3 Hybridized Carbon III
... • In this case, however, the stability of tertiary carbocation which results from H– shifting and substituting for CH3OH makes this reaction work with HCl • If tertiary carbocations can be formed then HCl is strong enough to cleave ethers ...
... • In this case, however, the stability of tertiary carbocation which results from H– shifting and substituting for CH3OH makes this reaction work with HCl • If tertiary carbocations can be formed then HCl is strong enough to cleave ethers ...
CH 6
... • Markovnikov observed in the 19th century that in the addition of HX to alkene, the H attaches to the carbon with the most H’s and X attaches to the other end (to the one with the most alkyl substituents) – This is Markovnikov’s rule ...
... • Markovnikov observed in the 19th century that in the addition of HX to alkene, the H attaches to the carbon with the most H’s and X attaches to the other end (to the one with the most alkyl substituents) – This is Markovnikov’s rule ...
OCR_Organic_Chemistry_AS_summary
... Formulae of organic molecules • Structural formulae – the minimal detail that shows the arrangement of atoms, e.g. CH3CH3 for ethane • Displayed formulae – shows the relative position of all atoms and bonds between them, e.g. ethene • Skeleton formulae – the simplest representation of organic molec ...
... Formulae of organic molecules • Structural formulae – the minimal detail that shows the arrangement of atoms, e.g. CH3CH3 for ethane • Displayed formulae – shows the relative position of all atoms and bonds between them, e.g. ethene • Skeleton formulae – the simplest representation of organic molec ...
Document
... 1979 Nobel Prize in Chemistry: Georg Wittig (Wittig Reaction) and H.C. Brown (Hydroboration) ...
... 1979 Nobel Prize in Chemistry: Georg Wittig (Wittig Reaction) and H.C. Brown (Hydroboration) ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.