* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organic Chemistry - Centennial College Libraries
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
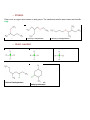
Organic Chemistry NOMENCLATURE -Hydrocarbonsorganic compounds that contain carbon and hydrogen only Saturated - only C-C and C-H bonds - alkanes - cycloalkanes Unsaturated - carbon-carbon double and triple bonds - alkenes - alkynes ALKANES are saturated hydrocarbons. They are specified by the parent name and suffix ane. Figure 1: The most common parent names. Source: http://www.wavesignal.com/o_chem/images/Stereo5.jpg NOTE: Alkanes with 3 or more carbons have constitutional isomers (compounds that have the same molecular formula but connect differently) o ACYCLIC ALKANES Example 1: Name the following 1) Find the longest chain and number the carbon atoms in the chain. Start numbering at the end which has the closest branch. 2) Identify substituents if present and place them in alphabetic order. For alkyl groups: parent + yl Answer: 4-ethyl-3-methylheptane o CYCLOALKANES Example 2: Name the following 1) Find parent chain and number the ring ** Number different substituents in such a way that they have the lowest corresponding location number possible Answer: 1-isobutyl-2-methylcyclohexane ALKENES & ALKYNES Alkenes are hydrocarbons that contain carbon—carbon double bond, whereas alkynes contain carbon – carbon triple bonds. o ISOMERS Geometric isomers (in which atoms are joined to one another in the same way but atoms occupy different relative positions in space). They are two very distinct compounds. Constitutional isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula, but the atoms are connected in different ways. COMPOUNDS THAT CONTAIN OXYGEN, HALOGEN or SULFUR o ALCOHOLS Alcohols have –OH as the functional group present. They take the suffix ol. Nomenclature rules: 1) determine the longest chain with –OH attached 2) OH suffix must get the lowest number 3) Number the chain in the direction that will give the substituent the lowest possible number 4) If more than one, write the substituents in order 2-ethyl-1-pentanol 3,3-dimethylcyclohexanol 2-ethyl-4-methylcyclopentanol o ETHERS Ethers have an oxygen atom between to alkyl groups. The substituents take the parent name and the suffix oxy. 2-methoxypentane 1-ethoxy-2-ethylbutane 2-butoxy-3-methylpentane o ALKYL HALIDES Primary alkyl halide Secondary alkyl halide Alkyl halides are named as substituted alkanes: 3-chloro-5-methyloctane 4-bromo-3-chloro-1methylcyclohexane Tertiary alkyl halide ALDEHYDES & KETONES They both contain C=O (carbonyl) functional group. Aldehydes contain a carbonyl group with at least one Hydrogen atom attached to it. Ketones contain a carbonyl group with two hydrocarbons attached to it. ALDEHYDE KETONE ethanal 2-butanone CARBOXYLIC ACIDS, ESTERS & AMIDES Carboxylic acids are compounds that contain the carboxyl group –COOH. Esters are compounds that contain –COO – between two alkyl groups. They are formed from a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Amides are compounds that contain the H2NCOO— group. They are formed from ammonia and carboxylic acids. CARBOXYLIC ACID ESTER AMIDE Ethanoic acid Ethyl acetate acetamide