The Address of the Electrons
... ¡ Each requires a different amount of energy for an e- to remain ¡ Lowest energy is s ¡ Highest energy is f Described ...
... ¡ Each requires a different amount of energy for an e- to remain ¡ Lowest energy is s ¡ Highest energy is f Described ...
Molecules Molecular Bonding
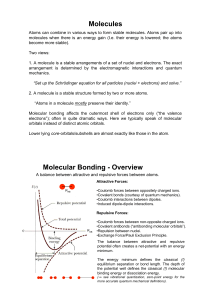
... The energy minimum defines the classical (!) equilibrium separation or bond length. The depth of the potential well defines the classical (!) molecular binding energy or dissociation energy. (! see vibrational quantization, zero-point energy for the more accurate quantum mechanical definitions). ...
... The energy minimum defines the classical (!) equilibrium separation or bond length. The depth of the potential well defines the classical (!) molecular binding energy or dissociation energy. (! see vibrational quantization, zero-point energy for the more accurate quantum mechanical definitions). ...
Atomic and Molecular Spectroscopy
... o Hydrogen energy levels o Fine structure o Spin-orbit coupling o Nuclear moments and hyperfine structure ...
... o Hydrogen energy levels o Fine structure o Spin-orbit coupling o Nuclear moments and hyperfine structure ...
Atomic Structure
... – Absorb energy to go to excited state; emits light/energy when comes back down ...
... – Absorb energy to go to excited state; emits light/energy when comes back down ...
Primary electrons make random elastic and inelastic collision either
... Signals such as secondary electrons (SE) and Auger electrons come from only a very tiny portion of the total interaction volume, since they lack the energy to travel large distances… Only these SE electrons that originated within a few nanometer of the surface are able to escape from sample…. SE has ...
... Signals such as secondary electrons (SE) and Auger electrons come from only a very tiny portion of the total interaction volume, since they lack the energy to travel large distances… Only these SE electrons that originated within a few nanometer of the surface are able to escape from sample…. SE has ...
Powerpoint handout
... Bohr derived a more general formula to predict the observed energies of light: Each electron’s energy is determined by which level it is in. The levels are designated by whole numbers, n. ...
... Bohr derived a more general formula to predict the observed energies of light: Each electron’s energy is determined by which level it is in. The levels are designated by whole numbers, n. ...
First Semester Final - Review Questions
... 37. Describe the different amounts and kinds of damage in matter produced by the different penetrations of each type of radioactive decay. 38. How does the energy release in a nuclear reaction compare to the energy release in a chemical reaction. Investigation and Experimentation 39. What is the pur ...
... 37. Describe the different amounts and kinds of damage in matter produced by the different penetrations of each type of radioactive decay. 38. How does the energy release in a nuclear reaction compare to the energy release in a chemical reaction. Investigation and Experimentation 39. What is the pur ...
Quantum Theory Historical Reference
... Determined alpha particles to be positively charged. Gold foil experiment proved existence of positively charged and extremely dense nucleus surrounded by clouds of electrons at relatively large distances from the nuclei – Rutherford model. Nuclear diameter approximately 10-5 nm or 10-14m. 8. H.G.J ...
... Determined alpha particles to be positively charged. Gold foil experiment proved existence of positively charged and extremely dense nucleus surrounded by clouds of electrons at relatively large distances from the nuclei – Rutherford model. Nuclear diameter approximately 10-5 nm or 10-14m. 8. H.G.J ...
Quiz 1 Key
... hydrogen had only certain colors and thus certain wavelengths present. Because wavelength is related to energy, this indicated that there were only certain energies of light emitted. This indicated that there were only defined energy levels for an excited atom and the electrons could only be at cert ...
... hydrogen had only certain colors and thus certain wavelengths present. Because wavelength is related to energy, this indicated that there were only certain energies of light emitted. This indicated that there were only defined energy levels for an excited atom and the electrons could only be at cert ...
Review Exam #1 - Seattle Central College
... Characteristics (Electrons have Mass and Momentum) Electromagnetic Radiation (Light) has Both Wave Characteristics (Waves can be Diffracted by Crystals) and Particle Characteristics (Photons have Momentum, but No Mass) Emission spectra of elements demonstrate that the energy of electrons is quantize ...
... Characteristics (Electrons have Mass and Momentum) Electromagnetic Radiation (Light) has Both Wave Characteristics (Waves can be Diffracted by Crystals) and Particle Characteristics (Photons have Momentum, but No Mass) Emission spectra of elements demonstrate that the energy of electrons is quantize ...
Quantum Notes
... • The wave model of light cannot explain all of light’s characteristics; Albert Einstein proposed in 1905 that light has a dual nature (wave-like and particle-like) • Matter can gain or lose energy only in small, specific amounts called quanta •A quantum is the minimum amount of energy that can be g ...
... • The wave model of light cannot explain all of light’s characteristics; Albert Einstein proposed in 1905 that light has a dual nature (wave-like and particle-like) • Matter can gain or lose energy only in small, specific amounts called quanta •A quantum is the minimum amount of energy that can be g ...
Transparancies for Revision Lecture - University of Manchester
... In a magnetic field E will depend upon other quantum numbers (ml,ms), for Zeeman effect this is: ...
... In a magnetic field E will depend upon other quantum numbers (ml,ms), for Zeeman effect this is: ...
Chapter 4-Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms
... Chapter 6-Electronic Structure of Atoms Key Concepts: -The atoms of each element have unique structures arising from interactions between electrons and the nucleus. -Atoms are so small that they are difficult to directly study. Atomic models are constructed to explain collections of experimental dat ...
... Chapter 6-Electronic Structure of Atoms Key Concepts: -The atoms of each element have unique structures arising from interactions between electrons and the nucleus. -Atoms are so small that they are difficult to directly study. Atomic models are constructed to explain collections of experimental dat ...
Exam sample
... 5. The hydrogen emission spectrum includes light with a wavelength of 434 nanometers. This is caused by an electron moving from: a. the n = 3 state to the n = 2 state. b. the n = 4 state to the n = 2 state. c. the n = 5 state to the n = 2 state. d. the n = 6 state to the n = 2 state. 6. “It is impos ...
... 5. The hydrogen emission spectrum includes light with a wavelength of 434 nanometers. This is caused by an electron moving from: a. the n = 3 state to the n = 2 state. b. the n = 4 state to the n = 2 state. c. the n = 5 state to the n = 2 state. d. the n = 6 state to the n = 2 state. 6. “It is impos ...
Thursday, 1/29/09 - Liberty Union High School District
... frequency was required to eject electron from metal •Problem-wave theory of light predicted light of any frequency could eject electron ...
... frequency was required to eject electron from metal •Problem-wave theory of light predicted light of any frequency could eject electron ...
Modern Model of the Atom Student Notes and Assignment
... CONFIGURATIONS. The rules that govern the way the electrons fill the atomic orbitals are: 1. AUFBAU PRINCIPLE - electrons enter orbitals of the lowest energy levels first 2. PAULI EXCLUSION PRINCIPLE - an atomic orbital may hold at most two electrons. Each must have an opposite spin. 3. HUND’S RULE ...
... CONFIGURATIONS. The rules that govern the way the electrons fill the atomic orbitals are: 1. AUFBAU PRINCIPLE - electrons enter orbitals of the lowest energy levels first 2. PAULI EXCLUSION PRINCIPLE - an atomic orbital may hold at most two electrons. Each must have an opposite spin. 3. HUND’S RULE ...
nuclear chemistry - La Salle High School
... VI. Nuclear Stability A. The nucleus of an atom is stable if it does NOT change into another nuclide without adding outside energy. B. Look at each element, determine what nuclides of the elements are stable, plot stable nuclides on graph. No. of protons x axis No. of neutrons y-axis ...
... VI. Nuclear Stability A. The nucleus of an atom is stable if it does NOT change into another nuclide without adding outside energy. B. Look at each element, determine what nuclides of the elements are stable, plot stable nuclides on graph. No. of protons x axis No. of neutrons y-axis ...