Notes - Organization of Matter
... mixed and cannot be visibly distinguished. The particles of the substances are so small that they cannot be easily seen. Another name for a homogeneous mixture is a ...
... mixed and cannot be visibly distinguished. The particles of the substances are so small that they cannot be easily seen. Another name for a homogeneous mixture is a ...
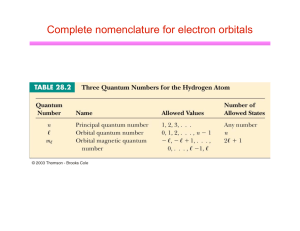
Which scientist developed the quantum mechanical model of the
... Which of the following states that no more than two electrons can occupy an atomic orbital and that two electrons in the same orbital must have opposite spins? A) B) C) D) ...
... Which of the following states that no more than two electrons can occupy an atomic orbital and that two electrons in the same orbital must have opposite spins? A) B) C) D) ...
Chapter 6.8 - Periodic Trends
... b. the properties of elements can be expressed mathematically as a function of atomic number c. when making the periodic table, elements must be placed in rows periods and families d. the properties of elements are found to be a repeating function of the atomic number The book states that chemical p ...
... b. the properties of elements can be expressed mathematically as a function of atomic number c. when making the periodic table, elements must be placed in rows periods and families d. the properties of elements are found to be a repeating function of the atomic number The book states that chemical p ...
Chapter 7 Student Learning Map
... photoelectric effect in describing the behavior of the electron and light? ...
... photoelectric effect in describing the behavior of the electron and light? ...
Physical Science
... What is a covalent bond – shared electrons, gaining stability, octet rule, Single, Double, Triple Bonds Naming covalent molecules – greek prefixes, name to formula and formula to name, Naming Acids Coordinate Covalent Bonds, exceptions to the octet rule Electronegativity and Polarity – polar ...
... What is a covalent bond – shared electrons, gaining stability, octet rule, Single, Double, Triple Bonds Naming covalent molecules – greek prefixes, name to formula and formula to name, Naming Acids Coordinate Covalent Bonds, exceptions to the octet rule Electronegativity and Polarity – polar ...
For a “black body” - The University of Sheffield
... form, different elements composed of different atoms, atoms can ...
... form, different elements composed of different atoms, atoms can ...
Part 1 Electron Arrangement
... electrons could be particles yet they gave off waves of light. • De Broglie suggested that electrons could be considered waves confined to space around a nucleus only at specific frequencies. • Diffraction experiments proved that electron beams can interfere with each other and produce areas of low ...
... electrons could be particles yet they gave off waves of light. • De Broglie suggested that electrons could be considered waves confined to space around a nucleus only at specific frequencies. • Diffraction experiments proved that electron beams can interfere with each other and produce areas of low ...
constructive - Purdue Physics
... where, for example, a nucleon changes orbit emitting a photon, the same as for atoms. The photon in this context is called a gamma ray and has E~ 1 MeV. These photons are actually the most dangerous products of nuclear decays and are responsible for the “danger radioactivity signs”. Alpha particles ...
... where, for example, a nucleon changes orbit emitting a photon, the same as for atoms. The photon in this context is called a gamma ray and has E~ 1 MeV. These photons are actually the most dangerous products of nuclear decays and are responsible for the “danger radioactivity signs”. Alpha particles ...
3.3 Review Name________________________________ Period_______Date_____________________
... contribution to the quantum theory listed below. Each name may be used more than once. Planck ...
... contribution to the quantum theory listed below. Each name may be used more than once. Planck ...
Document
... contribution to the quantum theory listed below. Each name may be used more than once. Planck ...
... contribution to the quantum theory listed below. Each name may be used more than once. Planck ...
Chemistry Fall-2016 Final
... AL. one of the Group B (Groups 3-12) elements that is usually displayed in the main body of the periodic table ...
... AL. one of the Group B (Groups 3-12) elements that is usually displayed in the main body of the periodic table ...
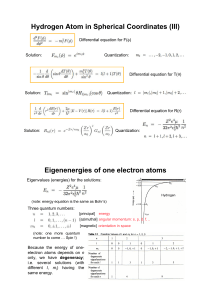
7.1 Variational Principle
... a, we would expect that the electron wf is not changed very much near the first proton. On the other hand, we would like to treat the two protons on an equal footing. This suggest that the trial wf take the form ψ = A[ψg (r1) + ψg (r2)]. ...
... a, we would expect that the electron wf is not changed very much near the first proton. On the other hand, we would like to treat the two protons on an equal footing. This suggest that the trial wf take the form ψ = A[ψg (r1) + ψg (r2)]. ...
physics - Keith E. Holbert
... Application of the conservation of energy gives the Q value of the reaction. This Q represents the change in rest mass energies (or equivalently the change in kinetic energies) of the particles: ...
... Application of the conservation of energy gives the Q value of the reaction. This Q represents the change in rest mass energies (or equivalently the change in kinetic energies) of the particles: ...
Chapter 2 Part 1 ppt
... corresponding to an atomic orbital • The conditions for a physically realistic solution: -One value for electron density/point -Continuous (does not change abruptly) -Must approach zero as r approaches infinity ...
... corresponding to an atomic orbital • The conditions for a physically realistic solution: -One value for electron density/point -Continuous (does not change abruptly) -Must approach zero as r approaches infinity ...
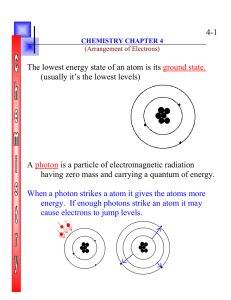
4-1 The lowest energy state of an atom is its ground state. (usually
... When a photon strikes a atom it gives the atoms more energy. If enough photons strike an atom it may cause electrons to jump levels. ...
... When a photon strikes a atom it gives the atoms more energy. If enough photons strike an atom it may cause electrons to jump levels. ...
Chemistry Semester One Exam Review Name:
... a. Chemical property – b. Chemical change – c. Physical property – d. Physical change – ...
... a. Chemical property – b. Chemical change – c. Physical property – d. Physical change – ...