Bohr model
... • With the increase of grid potential, more electrons move to the plate and the current rises accordingly. • For mercury atoms, when V=4.9V, the electrons make inelastic collision and leave the atom jump to a high orbit (n=2). The original electrons move off with little energy and could not reach th ...
... • With the increase of grid potential, more electrons move to the plate and the current rises accordingly. • For mercury atoms, when V=4.9V, the electrons make inelastic collision and leave the atom jump to a high orbit (n=2). The original electrons move off with little energy and could not reach th ...
The true nature of the atom?
... Newtonian physics just doesn’t cut it The behavior of our everyday world can be described by classical, Newtonian, physics. However, at the end of the 1800s it was clear that Newtonian physics didn’t accurately describe the behavior of light and matter at the atomic scale. For example: Why atoms do ...
... Newtonian physics just doesn’t cut it The behavior of our everyday world can be described by classical, Newtonian, physics. However, at the end of the 1800s it was clear that Newtonian physics didn’t accurately describe the behavior of light and matter at the atomic scale. For example: Why atoms do ...
The role of atomic radius in ion channel selectivity :
... 2. Count the total number of valence electrons. If there is a negative ion, add the absolute value of total charge to the count of valence electrons; if positive ion, subtract. 3. Count the total # of e-s needed for each atom to have a full valence shell. 4. Subtract the number in step 2 (valence ...
... 2. Count the total number of valence electrons. If there is a negative ion, add the absolute value of total charge to the count of valence electrons; if positive ion, subtract. 3. Count the total # of e-s needed for each atom to have a full valence shell. 4. Subtract the number in step 2 (valence ...
1. Define the vocabulary on page 88. Section 1
... 3. All forms of electromagnetic radiation move at a constant speed of _____________ through a vacuum. 4. _________ is the distance between corresponding points on adjacent waves. 5. What is the symbol for wavelength? 6. Frequency is defined as _______________________________________. 7. What is the ...
... 3. All forms of electromagnetic radiation move at a constant speed of _____________ through a vacuum. 4. _________ is the distance between corresponding points on adjacent waves. 5. What is the symbol for wavelength? 6. Frequency is defined as _______________________________________. 7. What is the ...
Chemistry I Midterm Exam
... In solving the Schrödinger equation for a particle constrained in a box of size L (x = 0 to L), the allowed wavefunctions have the form (x) = A sin kx + B cos kx. (a) What are the boundary conditions and normalization that can be used to find A, B, and k?? (b) Sketch the wavefunction for the 1st-ex ...
... In solving the Schrödinger equation for a particle constrained in a box of size L (x = 0 to L), the allowed wavefunctions have the form (x) = A sin kx + B cos kx. (a) What are the boundary conditions and normalization that can be used to find A, B, and k?? (b) Sketch the wavefunction for the 1st-ex ...
Chemistry—Chapter 13: Electrons in Atoms
... 3) What are the types of sublevels and number of orbitals in the following energy levels? a. n = 1 d. n = 4 b. n = 2 e. n = 5 c. n = 3 f. n = 6 II. Electron Arrangement in Atoms 4. Write a complete electron configuration of each atom, including orbital notations. Give the quantum numbers for the hig ...
... 3) What are the types of sublevels and number of orbitals in the following energy levels? a. n = 1 d. n = 4 b. n = 2 e. n = 5 c. n = 3 f. n = 6 II. Electron Arrangement in Atoms 4. Write a complete electron configuration of each atom, including orbital notations. Give the quantum numbers for the hig ...
The Periodic Table OL Page 1 of 2 G. Galvin Name: Periodic Table
... -define atomic number (Z) and mass number (A) -define relative atomic mass (Ar) using 12C scale -define isotope -describe the composition of isotopes using hydrogen and carbon as an example -describe the organisation of particles in atoms of elements numbers 1-20 -classify the first twenty elem ...
... -define atomic number (Z) and mass number (A) -define relative atomic mass (Ar) using 12C scale -define isotope -describe the composition of isotopes using hydrogen and carbon as an example -describe the organisation of particles in atoms of elements numbers 1-20 -classify the first twenty elem ...
Constructive Interference
... exist in stable configurations around nuclei Wavefunctions and energies for these configurations determine most properties of matter ...
... exist in stable configurations around nuclei Wavefunctions and energies for these configurations determine most properties of matter ...
Glowing Tubes for Signs, Television Sets, and Computers
... passes between the electrodes. The fast-moving particles excite the gas in the tube, causing a glow between the plates. ...
... passes between the electrodes. The fast-moving particles excite the gas in the tube, causing a glow between the plates. ...
Seeing Atoms and Electrons in Motion - The Munich
... (b) Compressing single-electron wavepackets with laser fields for reaching attosecond+picometer resolution in electron diffraction. (c) Electron microscopy/spectroscopy of electromagnetic resonances and quantum interferences at plasmonic subwavelength structures. Our research is located at the Max-P ...
... (b) Compressing single-electron wavepackets with laser fields for reaching attosecond+picometer resolution in electron diffraction. (c) Electron microscopy/spectroscopy of electromagnetic resonances and quantum interferences at plasmonic subwavelength structures. Our research is located at the Max-P ...
CHEMISTRY MIDTERM REVIEW
... 26. Why is mass not conserved in a nuclear reaction, yet it is in a chemical reaction? Unit 3 – Electronic Structure and Periodicity 27. Define the following: atomic orbital energy level sublevel quantum ionization energy atomic radius electronegativity 28. List all the types of electromagnetic radi ...
... 26. Why is mass not conserved in a nuclear reaction, yet it is in a chemical reaction? Unit 3 – Electronic Structure and Periodicity 27. Define the following: atomic orbital energy level sublevel quantum ionization energy atomic radius electronegativity 28. List all the types of electromagnetic radi ...
Vocabulary Terms Defined
... specific energy difference. These collections of different transitions, leading to different radiated wavelengths, make up an emission spectrum. Each element's emission spectrum is unique. Therefore, spectroscopy can be used to identify the elements in matter of unknown composition. Similarly, the e ...
... specific energy difference. These collections of different transitions, leading to different radiated wavelengths, make up an emission spectrum. Each element's emission spectrum is unique. Therefore, spectroscopy can be used to identify the elements in matter of unknown composition. Similarly, the e ...
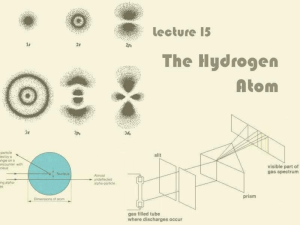
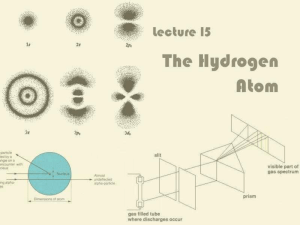
Lecture 15: The Hydrogen Atom
... It only absorbs or emits photons with precisely the right energies dictated by energy conservation ...
... It only absorbs or emits photons with precisely the right energies dictated by energy conservation ...
File
... b. atomic absorption spectra c. atomic emission spectra d. the deflection of cathode rays by an electric field e. absorption of beta particles 3. Rutherford's gold foil experiment showed that the atom is mostly empty space because a. some alpha particles were reflected right back b. some alpha parti ...
... b. atomic absorption spectra c. atomic emission spectra d. the deflection of cathode rays by an electric field e. absorption of beta particles 3. Rutherford's gold foil experiment showed that the atom is mostly empty space because a. some alpha particles were reflected right back b. some alpha parti ...