Chem 121 QU 78 Due in lecture
... What are valence electrons?↑ →_________________________________________________________________ 34a Compare cation and atomic radii. ↑ →__________________________________________________________________ 36 What is the general trend of ionization energy going down a column ? ↑ →______________________ ...
... What are valence electrons?↑ →_________________________________________________________________ 34a Compare cation and atomic radii. ↑ →__________________________________________________________________ 36 What is the general trend of ionization energy going down a column ? ↑ →______________________ ...
Chapter7_1 - Department of Chemistry [FSU]
... when 1 kg of octane is burned? How much work is done by the expanding CO2 as 1 kg of octane is burned (again, at 25 oC and 1 atm). (Hint, 1 J = 9.87.10-3 atm.L). What is !E for the reaction? (Hint, the definition of H = E + PV, assume PV is done by carbon dioxide only (ignore water and octane)) ...
... when 1 kg of octane is burned? How much work is done by the expanding CO2 as 1 kg of octane is burned (again, at 25 oC and 1 atm). (Hint, 1 J = 9.87.10-3 atm.L). What is !E for the reaction? (Hint, the definition of H = E + PV, assume PV is done by carbon dioxide only (ignore water and octane)) ...
Spectra of Atoms
... emitted by atoms of a given element is absolutely the same for every atom of that element, no matter how hot or cold it is. Mystery #4. What is the dynamics that causes line spectra? ...
... emitted by atoms of a given element is absolutely the same for every atom of that element, no matter how hot or cold it is. Mystery #4. What is the dynamics that causes line spectra? ...
Bohr`s model of the atom
... 4. Some of these photons run in a direction parallel to the ruby's axis, so they bounce back and forth off the mirrors. As they pass through the crystal, they stimulate emission in other atoms. ...
... 4. Some of these photons run in a direction parallel to the ruby's axis, so they bounce back and forth off the mirrors. As they pass through the crystal, they stimulate emission in other atoms. ...
Many-Electron Atoms Thornton and Rex, Ch. 8
... Possible values of L: L=1, 2, or 3 Possible values of J: for singlet (S=0): J=L for triplet (S=1): J=L-1 or J=L or J=L+1 ...
... Possible values of L: L=1, 2, or 3 Possible values of J: for singlet (S=0): J=L for triplet (S=1): J=L-1 or J=L or J=L+1 ...
Document
... Experimental results: (Geiger and Marsden) 99% of deflected particles have deflection angle 3o However, there are 0.01% of particles have larger angle > 90o Rutherford’s model of the structure of the atom to explain the observed large angle scattering ...
... Experimental results: (Geiger and Marsden) 99% of deflected particles have deflection angle 3o However, there are 0.01% of particles have larger angle > 90o Rutherford’s model of the structure of the atom to explain the observed large angle scattering ...
Chemistry Unit Test Study Guide (2012-2013)
... a. pH range for bases: ____________ True / False. Strong Acids and Strong Bases are both corrosive, which means they eat away at body tissue and dissolve other objects, and should always be handled with care. Interpreting a pH scale diagram: a. Identify the strongest acid shown on the pH scale below ...
... a. pH range for bases: ____________ True / False. Strong Acids and Strong Bases are both corrosive, which means they eat away at body tissue and dissolve other objects, and should always be handled with care. Interpreting a pH scale diagram: a. Identify the strongest acid shown on the pH scale below ...
Quantum-Mechanical Model of the Atom
... • These are listed according to the various forces in nature: – Gravity (gravitons) – Weak force (W & Z bosons, the only fundamental force parDcles with mass) – ElectromagneDsm (photons) – Strong force ...
... • These are listed according to the various forces in nature: – Gravity (gravitons) – Weak force (W & Z bosons, the only fundamental force parDcles with mass) – ElectromagneDsm (photons) – Strong force ...
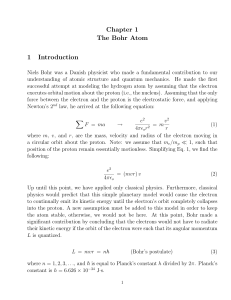
Chapter 1 The Bohr Atom 1 Introduction
... Up until this point, we have applied only classical physics. Furthermore, classical physics would predict that this simple planetary model would cause the electron to continually emit its kinetic energy until the electron’s orbit completely collapses into the proton. A new assumption must be added t ...
... Up until this point, we have applied only classical physics. Furthermore, classical physics would predict that this simple planetary model would cause the electron to continually emit its kinetic energy until the electron’s orbit completely collapses into the proton. A new assumption must be added t ...
Superconcepts
... This material is presented in chapter 6 of Brown et al. 12/e Superconcepts 1. An atom’s bonding & reactive properties are determined by electron configuration. 2. The behavior of electrons in atoms is dictated by quantum mechanics. Concepts a. Newtonian physics don’t accurately describe the behavior ...
... This material is presented in chapter 6 of Brown et al. 12/e Superconcepts 1. An atom’s bonding & reactive properties are determined by electron configuration. 2. The behavior of electrons in atoms is dictated by quantum mechanics. Concepts a. Newtonian physics don’t accurately describe the behavior ...
HW-1-Ch1-Atomic-structure-W16
... 4. Calculate the binding energy per nucleon (MeV) of 56Fe isotope of mass 55.952918 amu. ( P= 1.007277 amu,; N= 1.008665 amu; e- = 5.486 x10-4 amu) ...
... 4. Calculate the binding energy per nucleon (MeV) of 56Fe isotope of mass 55.952918 amu. ( P= 1.007277 amu,; N= 1.008665 amu; e- = 5.486 x10-4 amu) ...
The world of Atoms - University of California, Irvine
... “I cannot but confess that I attach only a transitory importance to this interpretation. I still believe in the possibility of a model of reality - that is to say, of a theory which represents things themselves and not merely the probability of their occurrence. On the other hand, it seems to me cer ...
... “I cannot but confess that I attach only a transitory importance to this interpretation. I still believe in the possibility of a model of reality - that is to say, of a theory which represents things themselves and not merely the probability of their occurrence. On the other hand, it seems to me cer ...
S1-2-02: What is the basic subatomic structure of an atom?
... S1-2-09: How do you classify matter using: element, compound, atom, molecule, mixture and pure? 6. Find the words from the choices below which match the definitions (One will not be used): Chemistry, Matter, Mass, Volume, Element, Compound, Mixture, Atoms, Molecule a) ...
... S1-2-09: How do you classify matter using: element, compound, atom, molecule, mixture and pure? 6. Find the words from the choices below which match the definitions (One will not be used): Chemistry, Matter, Mass, Volume, Element, Compound, Mixture, Atoms, Molecule a) ...
The Hydrogen Atom
... If we consider the vibrations of a wire loop, we find that their wavelengths always fit a whole number of times into the loop’s circumference. An electron can circle a nucleus only in orbits that contain an integral number of de Broglie wavelengths. ...
... If we consider the vibrations of a wire loop, we find that their wavelengths always fit a whole number of times into the loop’s circumference. An electron can circle a nucleus only in orbits that contain an integral number of de Broglie wavelengths. ...
Nuclear Chemistry PowerPoint
... parts, releasing a large amount of energy in the process. Most commonly this is done by "firing" a neutron at the nucleus of an atom. The energy of the neutron "bullet" causes the target element to split into two (or more) elements that are lighter than the parent atom. • During the fission of U235, ...
... parts, releasing a large amount of energy in the process. Most commonly this is done by "firing" a neutron at the nucleus of an atom. The energy of the neutron "bullet" causes the target element to split into two (or more) elements that are lighter than the parent atom. • During the fission of U235, ...
Periodic Properties Concepts
... As one reads across the periodic table from left to right in a given period, the pull exerted upon the outer-shell electrons by the positively charged nucleus increases with atomic number. There are more protons in the nucleus and therefore more positive charge. As one reads down the periodic table ...
... As one reads across the periodic table from left to right in a given period, the pull exerted upon the outer-shell electrons by the positively charged nucleus increases with atomic number. There are more protons in the nucleus and therefore more positive charge. As one reads down the periodic table ...
first chapter - damtp - University of Cambridge
... The reason that this does not happen is that very small systems, such as atoms, do not obey classical mechanics. To describe an atom one has to use quantum mechanics. In quantum mechanics, as opposed to classical mechanics, one cannot arbitrarily choose a value for the energy of the orbiting particl ...
... The reason that this does not happen is that very small systems, such as atoms, do not obey classical mechanics. To describe an atom one has to use quantum mechanics. In quantum mechanics, as opposed to classical mechanics, one cannot arbitrarily choose a value for the energy of the orbiting particl ...
Bohr`s equation for the hydrogen atom Bohr derived an equation to
... One result of this principle is that you can never squeeze two particles together to such an extent that they occupy the same state - objects must have a finite volume! It also means that if the exclusion priciple did not apply then all electrons in an atom would end up in the lowest possible energy ...
... One result of this principle is that you can never squeeze two particles together to such an extent that they occupy the same state - objects must have a finite volume! It also means that if the exclusion priciple did not apply then all electrons in an atom would end up in the lowest possible energy ...

![Chapter7_1 - Department of Chemistry [FSU]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016128835_1-aea3c1aec04363d6cbf538e8faf80e45-300x300.png)