Standard EPS Shell Presentation
... 14.2 Bohr model of the atom Danish physicist Neils Bohr proposed the concept of energy levels to explain the spectrum of hydrogen. When an electron moves from a higher energy level to a lower one, the atom gives up the energy difference between the two levels. The energy comes out as different ...
... 14.2 Bohr model of the atom Danish physicist Neils Bohr proposed the concept of energy levels to explain the spectrum of hydrogen. When an electron moves from a higher energy level to a lower one, the atom gives up the energy difference between the two levels. The energy comes out as different ...
CHEMISTRY FINAL EXAM REVIEW SHEET
... Proton: +1 charge, located in nucleus, relative mass = 1 amu Neutron: No charge, located in nucleus, relative mass = 1 amu Electron: -1 charge, located outside of nucleus, relative mass = 1/1840 amu Atomic Number = number of protons in an element. Mass Number = number of protons + neutrons in an ele ...
... Proton: +1 charge, located in nucleus, relative mass = 1 amu Neutron: No charge, located in nucleus, relative mass = 1 amu Electron: -1 charge, located outside of nucleus, relative mass = 1/1840 amu Atomic Number = number of protons in an element. Mass Number = number of protons + neutrons in an ele ...
Developing a new physics for atoms
... the e- will be found at that location: probability density or electron density. This concept of electron density plots led to the development of electron orbitals. ...
... the e- will be found at that location: probability density or electron density. This concept of electron density plots led to the development of electron orbitals. ...
Chapt25_VGO
... electrons scatter from the surface of metals. • They found that electrons incident normal to the crystal face at a speed of 4.35 106 m/s scattered at ø = 50°. • This scattering can be interpreted as a mirror-like reflection from the atomic planes that slice diagonally through the crystal. • The an ...
... electrons scatter from the surface of metals. • They found that electrons incident normal to the crystal face at a speed of 4.35 106 m/s scattered at ø = 50°. • This scattering can be interpreted as a mirror-like reflection from the atomic planes that slice diagonally through the crystal. • The an ...
Terminology 1
... Matter that has a definite or constant composition and distinct properties Matter that has a particular set of characteristics differs from the characteristics of another kind of matter ...
... Matter that has a definite or constant composition and distinct properties Matter that has a particular set of characteristics differs from the characteristics of another kind of matter ...
a) air c) milk f) beer
... compounds for a fixed mass of the other element are in ratios of small whole numbers. ...
... compounds for a fixed mass of the other element are in ratios of small whole numbers. ...
(n=1).
... n = principal quantum number (1, 2, 3, …) l = angular momentum (0, 1, 2, … n-1) ml = component of l (-l < ml < l) ms = spin (-½ , +½) ...
... n = principal quantum number (1, 2, 3, …) l = angular momentum (0, 1, 2, … n-1) ml = component of l (-l < ml < l) ms = spin (-½ , +½) ...
Electrons in Atoms
... In the early 1900’s, scientists conducted experiments involving the interactions of light and matter that could not be explained by the wave model of light. One experiment involved the phenomenon known as the photoelectric effect. ...
... In the early 1900’s, scientists conducted experiments involving the interactions of light and matter that could not be explained by the wave model of light. One experiment involved the phenomenon known as the photoelectric effect. ...
Units 3 and 4 Revision
... Q4. Explain why the metal elements in group 1 are (a) called the alkali metals. (b) stored under oil. Q5. What happens to the melting point of the elements in group 7 (the halogens) as you go the group? Answers:- Q3. Lithium. Q4. (a) The elements in group 1 react with water to form an ...
... Q4. Explain why the metal elements in group 1 are (a) called the alkali metals. (b) stored under oil. Q5. What happens to the melting point of the elements in group 7 (the halogens) as you go the group? Answers:- Q3. Lithium. Q4. (a) The elements in group 1 react with water to form an ...
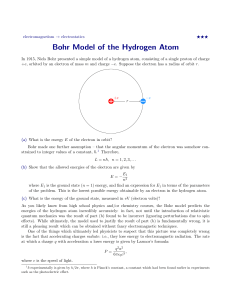
Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom
... (c) What is the energy of the ground state, measured in eV (electron volts)? As you likely know from high school physics and/or chemistry courses, the Bohr model predicts the energies of the hydrogen atom incredibly accurately: in fact, not until the introduction of relativistic quantum mechanics wa ...
... (c) What is the energy of the ground state, measured in eV (electron volts)? As you likely know from high school physics and/or chemistry courses, the Bohr model predicts the energies of the hydrogen atom incredibly accurately: in fact, not until the introduction of relativistic quantum mechanics wa ...
Chp 5 Guided Reading Notes and Vocabulary
... 4. In an electron configuration, what does a superscript stand for? _______________________________________________________________________ 5. In an electron configuration, what does the sum of the superscripts equal? _______________________________________________________________________ Exceptiona ...
... 4. In an electron configuration, what does a superscript stand for? _______________________________________________________________________ 5. In an electron configuration, what does the sum of the superscripts equal? _______________________________________________________________________ Exceptiona ...
from last time:
... 2. Atoms are very small. 3. Atoms have electrons in them, but are electrically neutral. 4. Atoms emit and absorb radiation of discrete wavelengths. The big problem with most models was number 4 – how to account for discrete energy changes. We’re going to start with Bohr’s model because it was the fi ...
... 2. Atoms are very small. 3. Atoms have electrons in them, but are electrically neutral. 4. Atoms emit and absorb radiation of discrete wavelengths. The big problem with most models was number 4 – how to account for discrete energy changes. We’re going to start with Bohr’s model because it was the fi ...
Chapt7
... Energetically excited atoms only emit radiation in discrete energies corresponding to the atom's electronic energy levels. (see Figure 7.11) ...
... Energetically excited atoms only emit radiation in discrete energies corresponding to the atom's electronic energy levels. (see Figure 7.11) ...
Units 1-6
... I can calculate conversions of all types (metric prefix, energy, temperature, density, etc.) including set up, sig figs and units I understand that energy takes different forms, and I can classify energy as potential (chemical, positional, gravitational), kinetic (including temperature) or radiant. ...
... I can calculate conversions of all types (metric prefix, energy, temperature, density, etc.) including set up, sig figs and units I understand that energy takes different forms, and I can classify energy as potential (chemical, positional, gravitational), kinetic (including temperature) or radiant. ...