File - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... Density – Density is the mass per unit volume of a substance Element – one of the basic substances that are made of atoms of only one kind and that cannot be separated by ordinary chemical means into simpler substances Electron – A particle of an atom that orbits the atom's nucleus and carries a neg ...
... Density – Density is the mass per unit volume of a substance Element – one of the basic substances that are made of atoms of only one kind and that cannot be separated by ordinary chemical means into simpler substances Electron – A particle of an atom that orbits the atom's nucleus and carries a neg ...
1 Hydrogen Atom: Wave Function Hydrogen Atom
... Ruby is an aluminum oxide crystal in which some Al atoms have been replaced with chromium. Chromium atoms absorb green and blue light and emit or reflect only red light. ...
... Ruby is an aluminum oxide crystal in which some Al atoms have been replaced with chromium. Chromium atoms absorb green and blue light and emit or reflect only red light. ...
nuclear chemistry - Wood County Schools
... Beta Decay: Medium-level radiation from the emission of beta particles (electrons). Positron Emission: Medium-level radiation from the emission of a positron, which is the same as an electron, only with a positive charge, converting a proton into a neutron. Electron Capture: When an atom takes in an ...
... Beta Decay: Medium-level radiation from the emission of beta particles (electrons). Positron Emission: Medium-level radiation from the emission of a positron, which is the same as an electron, only with a positive charge, converting a proton into a neutron. Electron Capture: When an atom takes in an ...
Chemistry PowerPoint
... a. The total mass of the reactants is greater than the total mass of the products b. The total mass of the reactants is less than the total mass of the products c. The total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products d. Mass can be created and destroyed ...
... a. The total mass of the reactants is greater than the total mass of the products b. The total mass of the reactants is less than the total mass of the products c. The total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products d. Mass can be created and destroyed ...
Electron Arrangement
... When non-metal atoms join! Eg. Water (H2O), ammonia (NH3), Methane (CH4). These have specific shapes because of the covalent bonds. Covalent molecular substances tend to have low melting and boiling points because they only have Van der Waals’ forces holding the molecules together. Van der Waals’ fo ...
... When non-metal atoms join! Eg. Water (H2O), ammonia (NH3), Methane (CH4). These have specific shapes because of the covalent bonds. Covalent molecular substances tend to have low melting and boiling points because they only have Van der Waals’ forces holding the molecules together. Van der Waals’ fo ...
Energy levels and atomic structures lectures
... An atom is the smallest constituent unit of ordinary matter that has the properties of a element. Every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Atoms are very small; typical sizes are around 100 pm (a ten-billionth of a meter, in the short scale). An atom consists o ...
... An atom is the smallest constituent unit of ordinary matter that has the properties of a element. Every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Atoms are very small; typical sizes are around 100 pm (a ten-billionth of a meter, in the short scale). An atom consists o ...
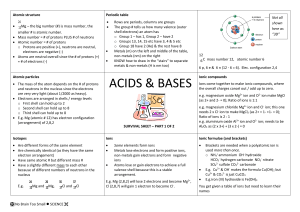
acids and bases - No Brain Too Small
... KNOW how to draw in the “stairs” to separate metals & non-metals (H is nm too) ...
... KNOW how to draw in the “stairs” to separate metals & non-metals (H is nm too) ...
Periodic Table Review Key
... Would atom A gain or lose valence electrons? __lose__ Would atom B gain or lose valence electrons? __neither__ ...
... Would atom A gain or lose valence electrons? __lose__ Would atom B gain or lose valence electrons? __neither__ ...
QUANTUM THEORY OF ATOMS AND MOLECULES
... Problems 2 1. Show that the function = N sin nx/L satisfies the Schrodinger equation for a particle in a 1-D box between x = 0 and x = L and calculate the value of the normalisation factor N. Evaluate the probability of finding the particle between 0.4L and 0.6L when n = 1 and when n = 2. What wo ...
... Problems 2 1. Show that the function = N sin nx/L satisfies the Schrodinger equation for a particle in a 1-D box between x = 0 and x = L and calculate the value of the normalisation factor N. Evaluate the probability of finding the particle between 0.4L and 0.6L when n = 1 and when n = 2. What wo ...
Unit 2 Review for Test
... 45. Name the primary use of the type of macromolecule which is a source of energy. 46. Name the macromolecule which is the primary component in cellular membranes. 47. Name the macromolecule whose function includes structural contributions, communication, and defense against disease. 48. Proteins ar ...
... 45. Name the primary use of the type of macromolecule which is a source of energy. 46. Name the macromolecule which is the primary component in cellular membranes. 47. Name the macromolecule whose function includes structural contributions, communication, and defense against disease. 48. Proteins ar ...
Quantum Numbers and Electron Configurations Worksheet
... Use a phrase to describe why the 2s orbital is more stable (lower energy) versus 2p. When you superimpose the total radial probability of 2s and 2p onto the plot of 1s, you notice that the 2s has a small peak that is inside the 1s shield, which causes them to have more exposure to the full nuclear c ...
... Use a phrase to describe why the 2s orbital is more stable (lower energy) versus 2p. When you superimpose the total radial probability of 2s and 2p onto the plot of 1s, you notice that the 2s has a small peak that is inside the 1s shield, which causes them to have more exposure to the full nuclear c ...
Problem set VI Problem 6.1 Problem 6.2 Problem 6.3 Problem 6.4
... Consider a beam of spin 12 particles in a Stern-Gerlach experiment, having spin aligned in the positive x direction, i.e. |Sx , +i. When this beam goes through a Stern-Gerlach apparatus with an inhomogeneous magnetic field in the z-direction (SGz), it splits into two beams of equal intensity, i.e. | ...
... Consider a beam of spin 12 particles in a Stern-Gerlach experiment, having spin aligned in the positive x direction, i.e. |Sx , +i. When this beam goes through a Stern-Gerlach apparatus with an inhomogeneous magnetic field in the z-direction (SGz), it splits into two beams of equal intensity, i.e. | ...
Chapter 4
... e- may have a wave-particle nature Would explain why e- only had certain orbits ...
... e- may have a wave-particle nature Would explain why e- only had certain orbits ...
1 The Nucleus Total number of nucleons: mass number Number of
... inhibitors of a protein called HMGA-CoA reductase, and they help to control cholesterol biosynthesis and limit cardiovascular ...
... inhibitors of a protein called HMGA-CoA reductase, and they help to control cholesterol biosynthesis and limit cardiovascular ...
Chapter 5 Practice Section 5-1 Discuss the placement (if any) of
... What is the wavelength of radiation with a frequency of 2.3 x 1014 Hz? What is the frequency of radiation with a wavelength of 1.8 x 10-9 m? Rank in order of increasing energy: Purple light, x-rays, Microwaves Rank the above in order of increasing frequency. Rank the above in order of increasing wav ...
... What is the wavelength of radiation with a frequency of 2.3 x 1014 Hz? What is the frequency of radiation with a wavelength of 1.8 x 10-9 m? Rank in order of increasing energy: Purple light, x-rays, Microwaves Rank the above in order of increasing frequency. Rank the above in order of increasing wav ...